53 Total Wrist Arthrodesis
Indications
- Post-traumatic, rheumatoid, or osteoarthritis with radiocarpal and midcarpal degeneration
- Bone loss or deformity due to infection or tumor
- Fixed wrist deformity from neurological deficit
Technique
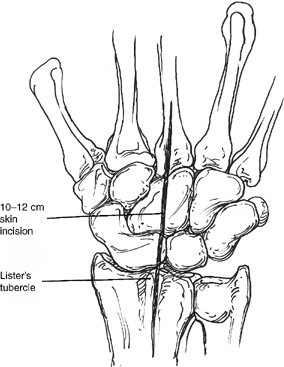
- A dorsal, longitudinal 10 to 12 cm skin incision is centered over Lister’s tubercle (Fig. 53-1).
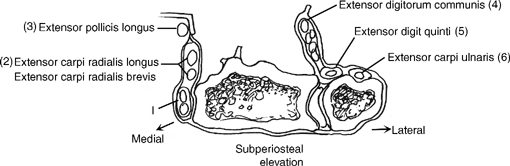
- The extensor retinaculum is incised through the third dorsal compartment.
- Extensor pollicis longus (EPL) is transposed radially.
- Make a longitudinal incision through the periosteum and capsule from the midshaft of the third metacarpal, across the wrist joint, and in the floor of the third extensor compartment.
- Capsular flaps are raised off the carpus in both the radial and ulnar directions.
- Resect a segment of the posterior interosseous nerve as it enters the dorsal wrist capsule.
- The dorsal surface of the distal radius is exposed by subperiosteal elevation of the second and fourth extensor compartments (Fig. 53-2)
Figure 53-1
Figure 53-2
Figure 53-3
Pitfall
With the exception of the third compartment, do not open the extensor compartments. This reduces the risk of tendon adhesions.
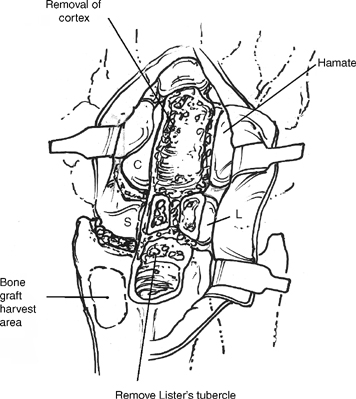
- Remove Lister’s tubercle to provide a flat surface over the dorsal aspect of the distal radius.
- The dorsal surfaces of the scaphoid (S), lunate (L), capitate (C), and third carpometacarpal joint are removed.
- Excise the remaining cartilage and subchondral bone from the articular surfaces of the intercarpal, third carpometacarpal, and radiocarpal joints (Fig. 53-3).
- In some cases, the volar-most portions of the intercarpal and carpometacarpal joint surfaces can be retained to maintain anatomical intercarpal spacing and wrist height.
Pitfall
Include the third carpometacarpal joint in the fusion to reduce the risk of fatigue fracture of the plate.
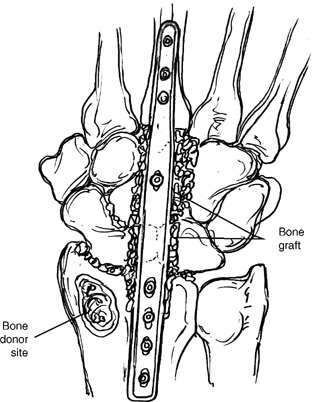
- Bone graft is obtained from the distal radius or from the iliac crest if there are large bone defects.
- A wrist arthrodesis plate is chosen to span from the third metacarpal shaft to the distal radius. Attempt to engage six cortices with screws through the plate into both the metacarpal and distal radius.