Total Knee Arthroplasty via the Mini-Subvastus Approach
Introduction
Mini-subvastus approach uses anterior incision and evolved from Hofmann subvastus technique
Incision shorter than traditional medial parapatellar approach, but incision length does not define mini-subvastus
Approach tries to improve functional recovery from total knee arthroplasty (TKA) by avoiding quadriceps arthrotomy and patellar eversion
Follows standard surgical sequence
Surgical guides are scaled-down versions of traditional TKA instruments
Same steps, with slight adjustments
Benefit—More rapid recovery without increased risk of complication
Patient Selection
Indications
Approach can work for nearly all primary TKA patients
Permits extension of subvastus release even in obese and muscular patients
Contraindications
Knees requiring removal of significant hardware from prior fixation
TKA requiring augments or stems due to severe deformity
Procedure
Room Setup/Patient Positioning
Supine position
For significant external hip rotation, can tilt table away from surgical side
Use mechanical leg holder
Suggest more than one assistant to handle multiple retractors
Special Instruments/Equipment/Implants
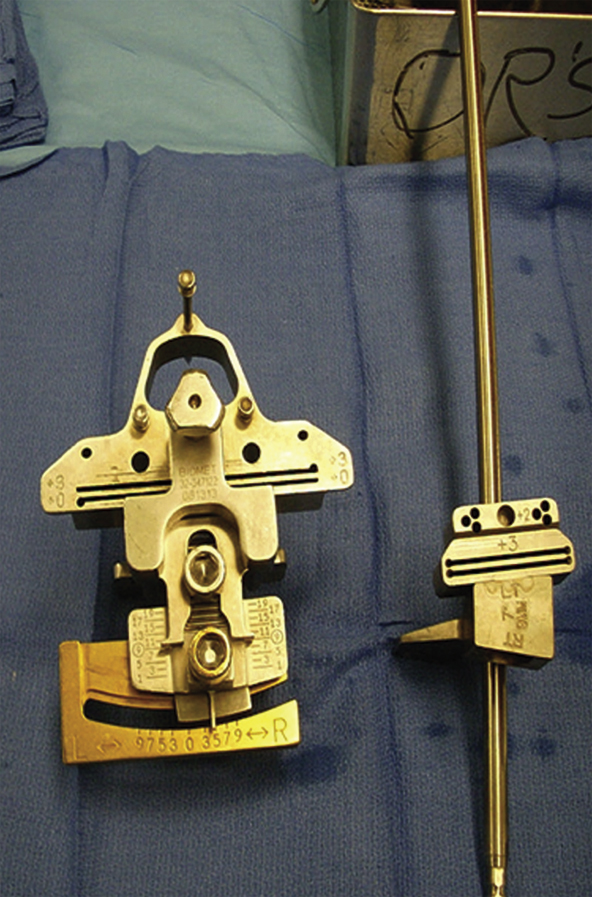
Figure 1Photograph depicts distal femoral cutting guides for total knee arthroplasty. The large instrument is for traditional total knee arthroplasty, and the smaller one is used in minimally invasive surgery.
Instruments are lower-profile versions of standard TKA instruments (Figure 1)
Use drill pins, not push pins, which can deflect
Full-thickness, thin retractors to protect skin and ligaments, minimize skin trauma
| Video 64.1 Total Knee Arthroplasty via the Mini-Subvastus Approach. William C. Schroer, MD (12 min) |
Surgical Technique
Incision and Arthrotomy
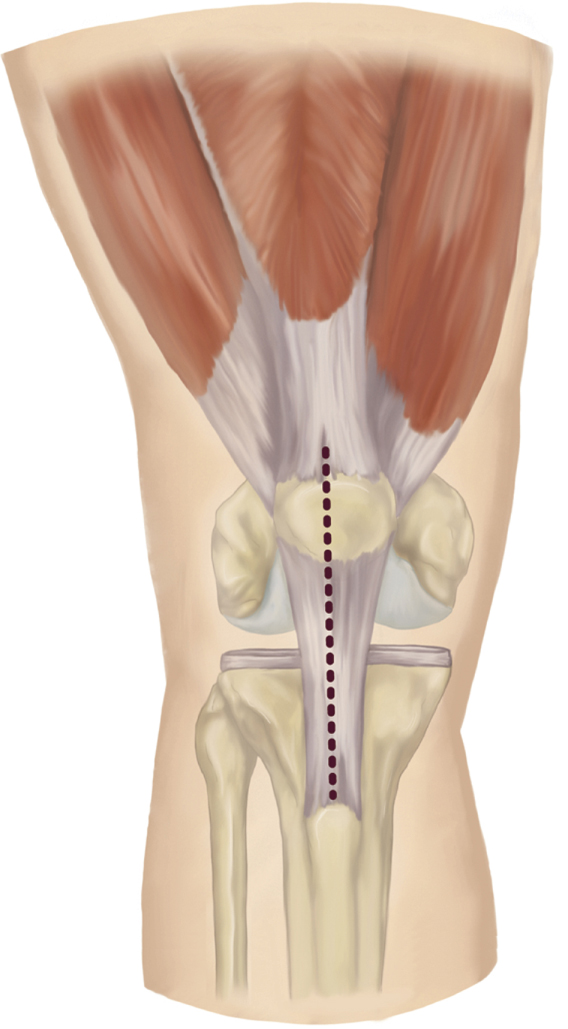
Figure 2Illustration shows the skin incision (dashed line) for the mini-subvastus approach for total knee arthroplasty.
Make 10- to 16-cm midline incision from superior pole of patella to tibial tubercle (Figure 2)
Perform subcutaneous mobilization medially and superiorly for patella mobility
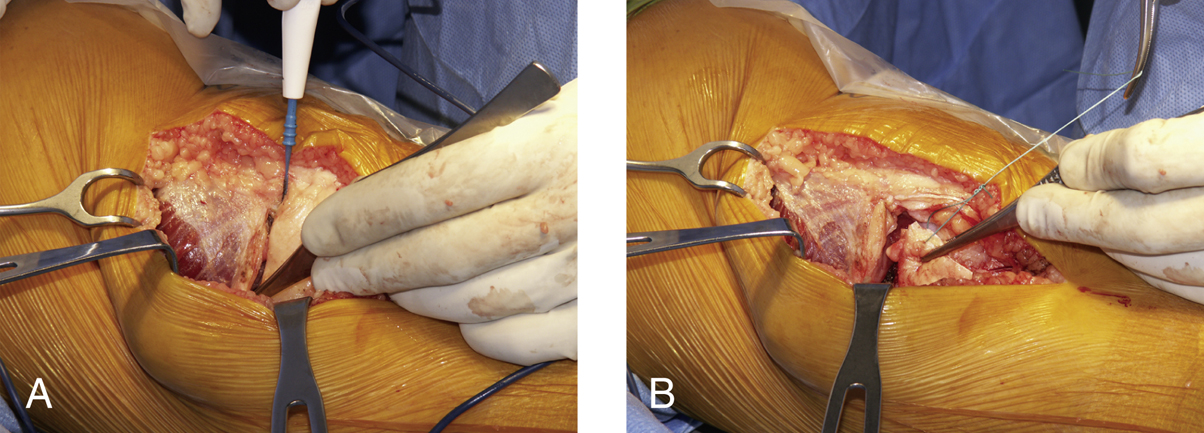
Make horizontal arthrotomy along inferior aspect of vastus medialis obliquus (VMO), leaving cuff of retinaculum on VMO for closure (Figure 3, A)
Complete arthrotomy in standard manner along medial patellar tendon
Tag reflected retinaculum containing medial patellofemoral ligament for protection and retraction (Figure 3, B)
Patellar Mobilization
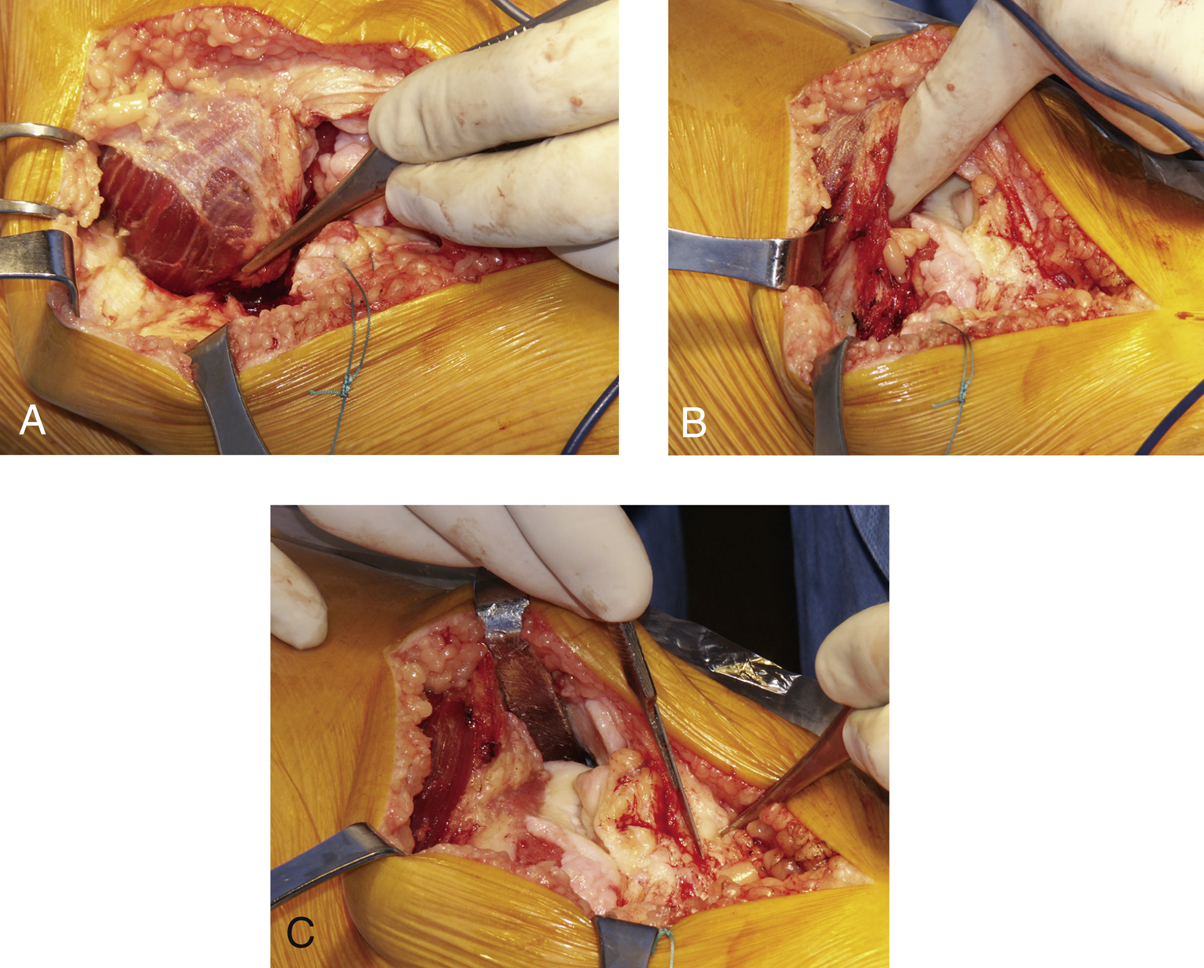
Figure 4Intraoperative photographs show subvastus release and patellar mobilization in total knee arthroplasty via the mini-subvastus approach. A, The vastus medialis obliquus (VMO) is released through the retinacular cuff. The forceps are grabbing the recently released retinacular cuff. Note that the patella has started to move laterally. B, The surgeon’s index finger is under the capsular reflection. Note that the VMO is releasing laterally. C, A Z retractor has subluxated the patella laterally. Note that the entire anterior distal femur is well visualized. Excision of the fat pad as shown completes the mobilization of the patella.

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree