Total Knee Arthroplasty via Small-Incision Midvastus Approach
Introduction
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is highly successful in managing symptomatic end-stage knee arthritis
Traditionally performed through standard medial parapatellar arthrotomy with eversion of patella
TKA is now possible using smaller incision, less disruption of extensor mechanism
Benefits—Earlier return of quadriceps function and motion, improved flexion, less postoperative narcotic use, and improved cosmesis
Safe and accurate use of small-incision midvastus approach depends on understanding of anatomy, gentle soft-tissue handling, use of mobile window through accurate retractor placement, and minimally invasive surgery instrument use
Patient Selection
Indications
Same as those for standard TKA—Disability from knee arthritis, refractory to nonsurgical measures
Should first try course of activity modification, anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, and weight reduction
Contraindications
TABLE 1
Relative Contraindications to the Small-Incision Midvastus Approach
| Substantial quadriceps muscle mass in men |
| Significant obesity (body mass index >40 kg/m2) |
| Severe coronal plane deformity |
| Flexion contracture >25° |
| Passive flexion <80° |
| Severe patella baja |
| Significant scarring of the quadriceps mechanism |
| Revision surgery |
No absolute contraindications
Relative contraindications listed in Table 1.
Preoperative Imaging
Standing AP, lateral, 45° flexed PA, Merchant view radiographs
Interpret radiographs for deformity, bone loss, presence of patella baja, and bone quality
For deformity, useful to anticipate appropriate distal femoral cut angle and height of tibial resection
Procedure
Patient Positioning
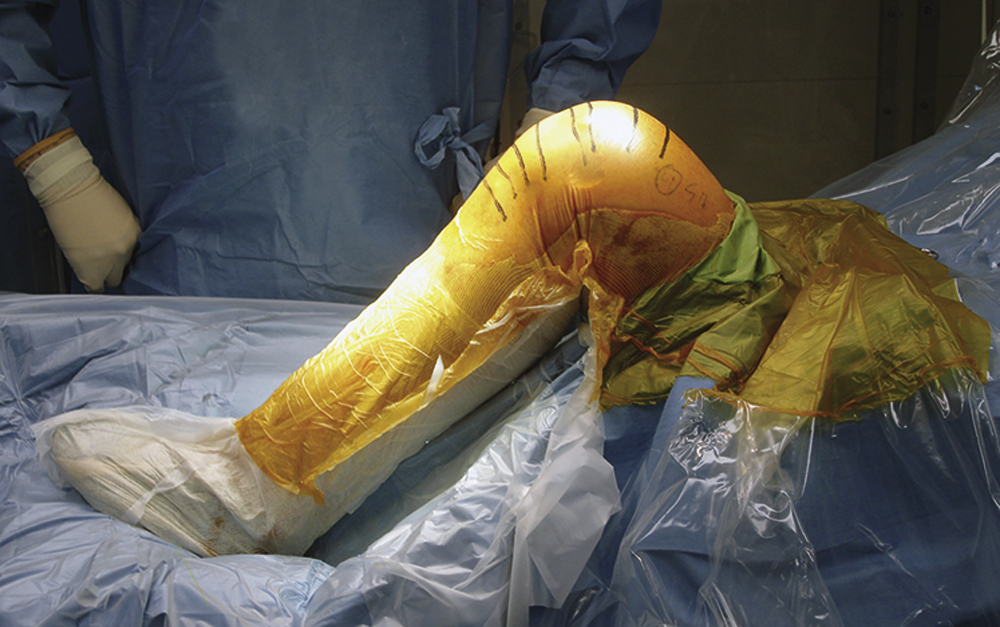
Figure 1Photograph shows a patient positioned on the operating table with a bump placed across from the opposite ankle to hold the leg at 70° to 90°.
Same as for standard TKA
Bolstered sandbag under drapes at level of opposite angle so knee can flex at 70° to 90° (Figure 1)
Use lateral support so leg sits without being held by assistant
Special Instruments
Specialized instrumentation is critical
Smaller cutting blocks and guides with rounded edges for smaller incisions
Side-specific instruments and cutting guides
Rigid saw blade with narrow body that fans out at distal tip
Some systems have implants specifically for use with minimally invasive technique, such as short keel or modular stem tibial components and asymmetric tibial trays
Surgical Technique
| Video 63.1 Mini-Midvastus Approach. Steven B. Haas, MD, MPH; Stephen Kim, MD (16 min) |
Anesthesia
Authors prefer combined spinal/epidural anesthetic with indwelling epidural patient-controlled anesthesia for 48 hours
Bupivacaine femoral nerve block
Intravenous cefazolin; vancomycin for penicillin allergy
Exposure
Exsanguinate leg with Esmarch bandage; inflate tourniquet to 250 to 300 mm Hg
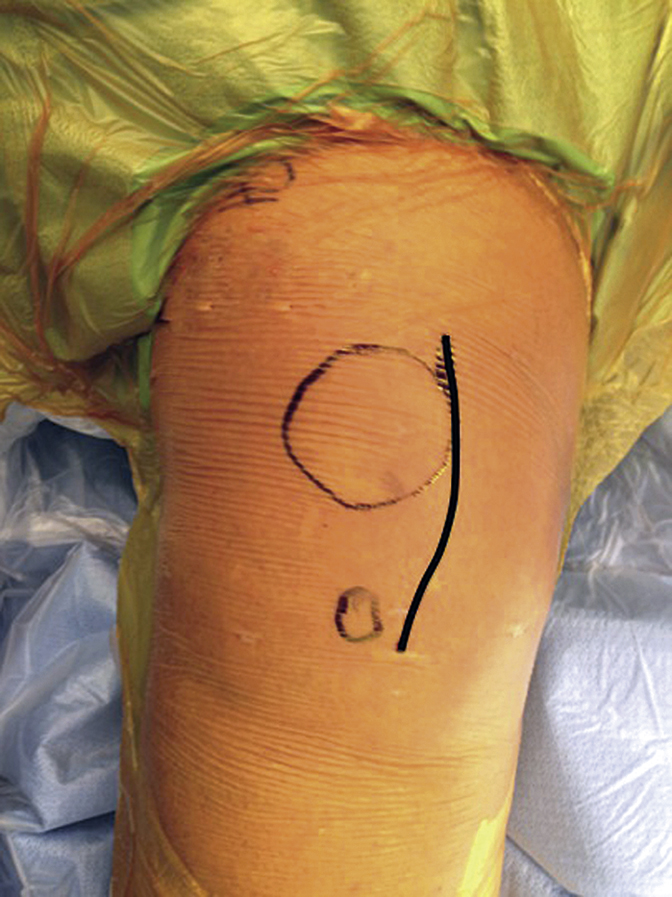
Make longitudinal incision at junction of middle and medial thirds of patella, 1 cm above proximal half of medial tibial tubercle, 8.5 to 12 cm long (Figure 2)
Perform medial arthrotomy from superior pole of patella to level of tibial tubercle; leave 5-mm cuff of tissue adjacent to tubercle
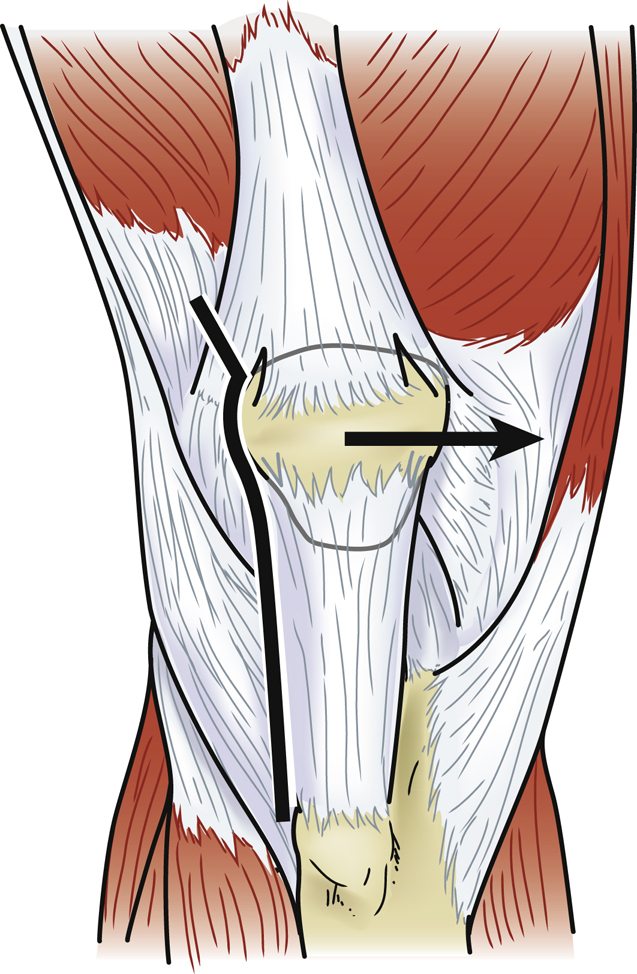
Split vastus medialis obliquus (VMO) in line with its fibers at level of superior pole of patella (Figure 3)
Initiate first centimeter of VMO muscle split sharply and finish with blunt finger dissection; prevents injury to distal innervation of vastus musculature; split is 2 to 4 cm long
Preserve suprapatellar pouch except in severe inflammatory disease
Extend knee and carry subperiosteal dissection around medial pretibial border, releasing meniscotibial attachments
Retract and subluxate patella laterally, do not evert; partially excise infrapatellar fat pad
Release tibial attachment of anterior cruciate ligament and anterior horn of lateral meniscus
Place thin bent Hohmann retractor laterally to retract patella
Create small synovial window over anterolateral femoral cortex to aid initial anterior femoral resection
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


