14 The common carotid artery
14.1 Anatomy review
14.1.1 Origin
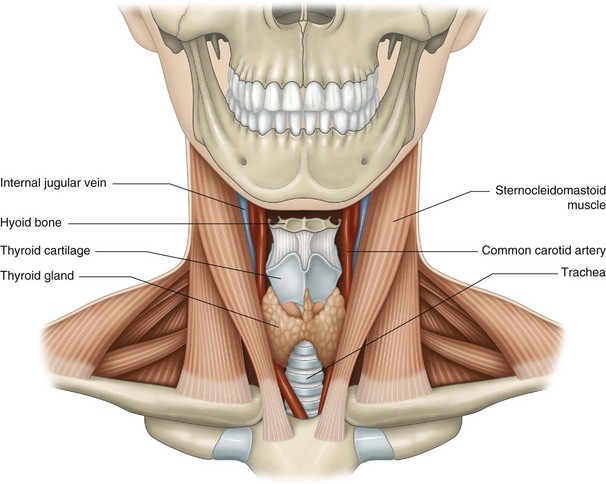
The common carotid arteries (Fig. 14.1) arise:
• on the right, from the brachiocephalic trunk
• on the left, directly from the arch of the aorta, which makes the left carotid longer.
14.1.5 Carotid triangle
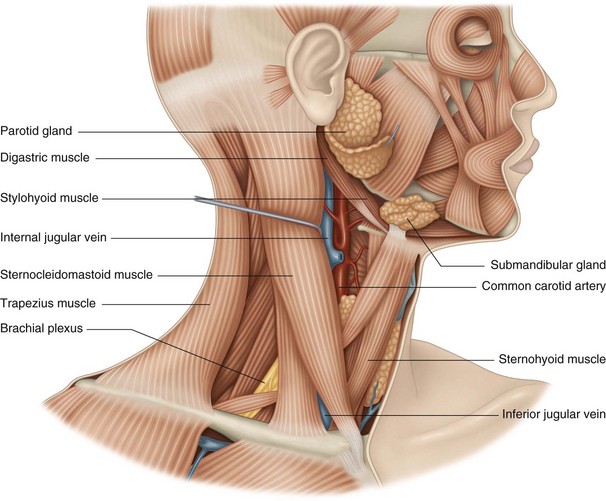
At the level of the carotid triangle, the common carotid artery is covered only by skin and superficial cervical fascia (Fig. 14.2). The triangle is bounded by these muscles:
14.2 Manual approach
14.2.1 Palpation
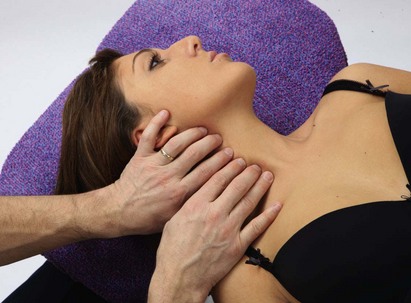
The patient is in decubitus, hands on the abdomen. The patient turns their head slightly towards the artery being palpated. Palpate the artery with two or three fingerpads. The sternocleidomastoid muscle crosses the common carotid artery like an X. Palpation varies depending on whether your fingers are cephalad, medial, or caudad in relation to this muscle crossing (Fig. 14.3).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree