Surgical Treatment of Basal Joint Arthritis of the Thumb
Introduction
Arthritis of the thumb carpometacarpal joint is common, and with advancing age is present in a high percentage of patients
Although symptomatic thumb CMC joint arthritis is common, there are many patients who are asymptomatic or who find adequate treatment with nonsurgical care
Multiple surgical options are available with no clear evidence for a superior procedure; the author uses variation of Thompson’s abductor pollicis longus (APL) suspensionplasty
Patient Selection
Painful Eaton stage II, III, or IV basal joint arthritis
Symptoms that persist despite nonsurgical management such as splints, NSAIDs, cortisone injections, activity modifications, or therapy programs
Diagnostic Imaging
Radiographs useful for preoperative planning, assessment
Radiographic staging does not correlate well with symptoms
Procedure
Room Setup/Patient Positioning
Most commonly, general anesthesia or regional anesthesia is used
Supine position; hand on table/arm board
Apply well-padded tourniquet around upper arm
Surgical Technique
Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspensionplasty
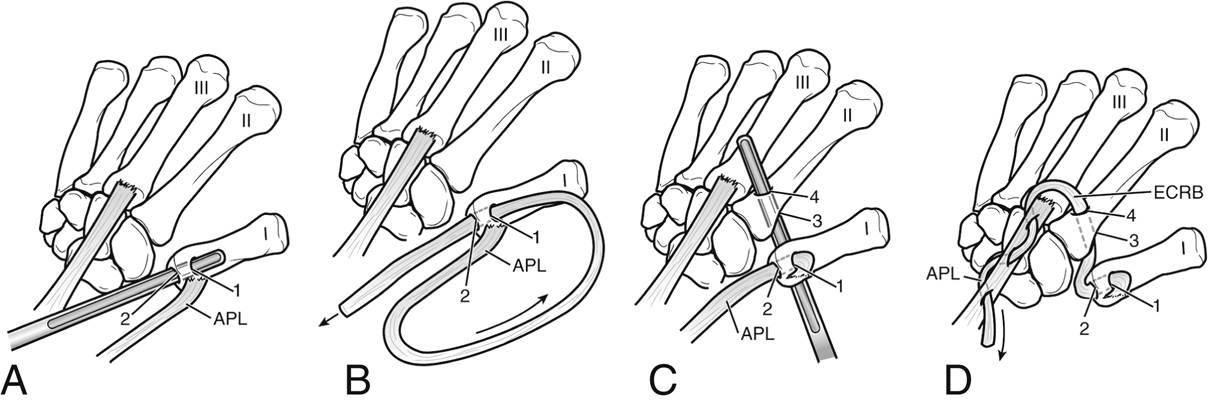
Figure 1Illustrations demonstrate the surgical technique for abductor pollicis longus (APL) suspensionplasty. A, Creation of a bone tunnel in the thumb metacarpal. The bone tunnel is carefully created to connect hole 2, which is located in the articular center of the metacarpal base, and hole 1, which is located at the dorsal surface of the proximal metacarpal metaphysis 1 cm distal to the articular surface. B, After division of the APL at the proximal musculotendinous junction, the free end of the APL tendon is passed through the bone tunnel from hole 1 to hole 2. C, A bone tunnel is created from palmar (3) to dorsal (4) in the index metacarpal at the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction. D, The APL tendon is passed through both bone tunnels at the thumb and index metacarpal (from 1 through 2 and from 3 through 4), emerging dorsally from the index metacarpal tunnel with a weave through the extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) tendon to anchor the ligament reconstruction and tension the tendon transfer. I = thumb metacarpal; II = index finger metacarpal; III = long finger metacarpal.
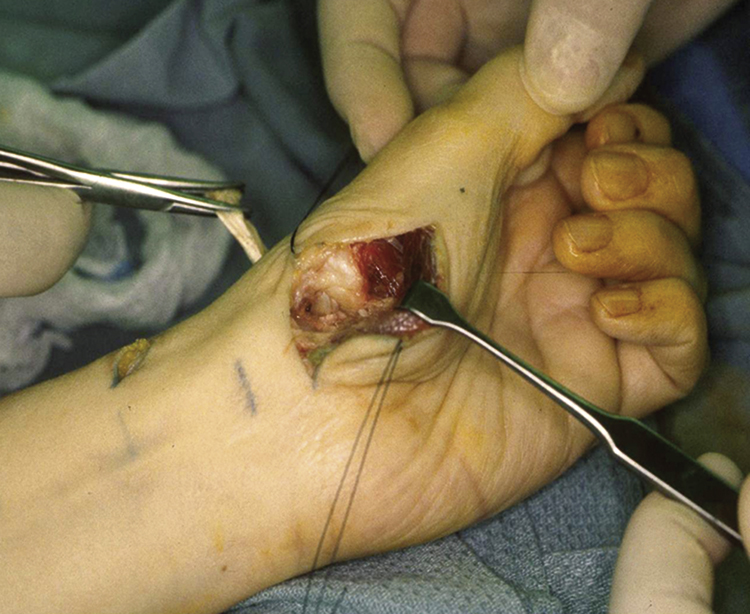
Figure 2Intraoperative photograph shows assessment of the ligamentous reconstruction in APL suspensionplasty. The APL has been passed through the second bone tunnel, which is a palmar-to-dorsal transverse bone tunnel at the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction of the proximal index metacarpal. The tendon is being tensioned by the clamp on the upper left. By applying this tension, the thumb is suspended into a position that maintains the space that the trapezium had once occupied and the overall thumb ray length is maintained.
Make Wagner incision transversely over flexor carpi radialis (FCR) tendon curving to glabrous skin junction at radial border of thumb metacarpal distally
Raise skin, subcutaneous flaps and retract; preserve branches of radial sensory nerve
Dissect dorsally to expose extensor mechanism over metacarpal and APL insertion at base
Perform subperiosteal dissection between extensor pollicis longus (EPL) and extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) 1 cm distal to APL insertion
Reflect thenar muscles off radial aspect of metacarpal, including accessory APL
Distract thumb to expose scaphotrapezial (ST) and trapeziometacarpal (TMC) joints; expose trapezium subperiosteally and remove in pieces; remove osteophytes from capsule
Expose base of thumb metacarpal; Carroll elevator is helpful
Pierce center of articular surface with awl, Kirschner wire (K-wire), or drill; make second hole dorsally 1 cm distal to articular surface
Use curet to expand holes and join them with intramedullary tunnel; avoid fracturing bone
Harvest APL at musculotendinous junction with tendon stripper; use rotating action while holding stripper; trim free end of tendon as needed
Pass APL retrograde through dorsal metacarpal hole and out articular hole using tendon passer or loop of wire (Figure 1)
Inspect ST joint for significant wear; if present, remove abnormal cartilage, subchondral bone with curet

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


