8 Spinous Process Fixation Systems
8.1 Introduction
Spinous process fixation is another method utilized to provide spinal stability following interbody fusion. These devices are designed to provide additional stability through interspinous fusion.1 Many interspinous fixation devices (IFDs) also provide interspinous process spacing, which can provide further decompression.1 Additionally, the placement of this device only requires a single midline incision, which may make it a more expedient procedure compared to standard pedicle screw fixation. Surgical indications are presented in ▶ Table 8.1.
8.1.1 Interspinous Fixation Device Components
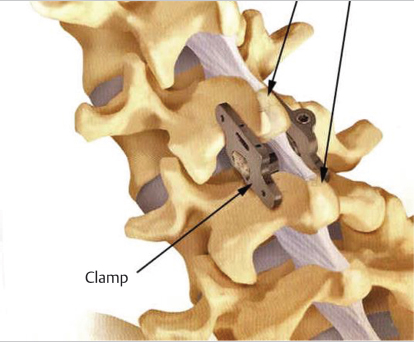
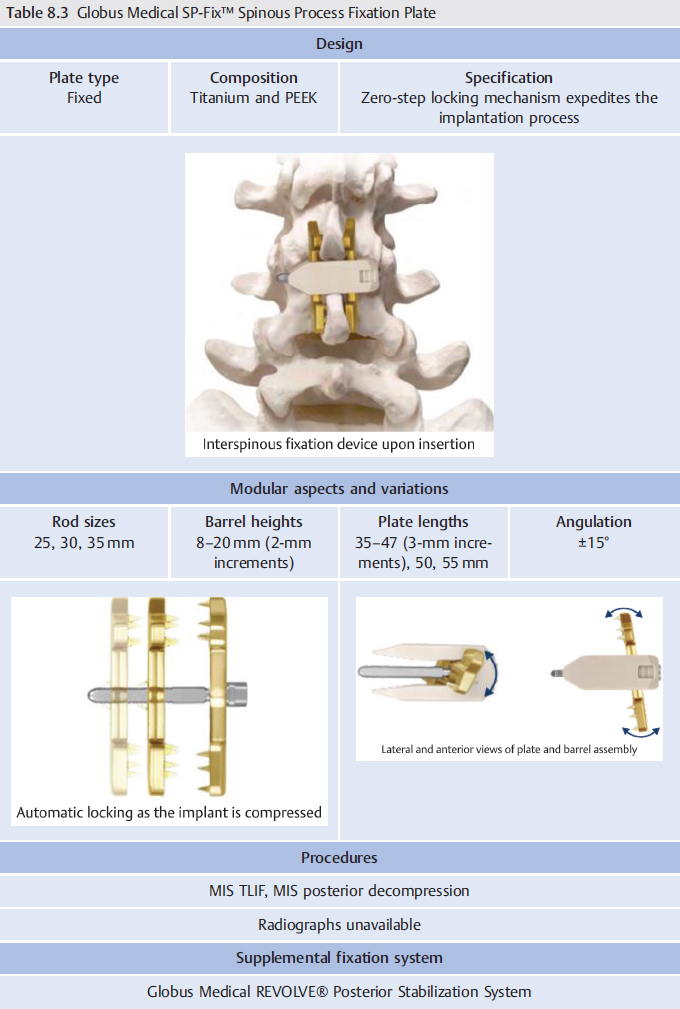
IFDs contain plates that clamp to the lateral aspects of adjacent spinous processes (▶ Fig. 8.1).2 The clamps are often fixed to the spinous processes through the use of rivets or spiked plates. By securing segment motion posteriorly, an IFD can provide rigidity to the two adjacent vertebrae to which it is secured.2 IFDs can be composed of a variety of materials, including polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and titanium.
Table 8.1 Surgical indications for interspinous fixation devices
Indications |
• Posterior approach spinal fusion • Thoracic procedures • Lumbosacral procedures • Degenerative disk disease • Spondylolisthesis • Spinal fracture/dislocation • Spinal tumor |
Fig. 8.1 Interspinous fixation device with clamps fixated on the spinous processes of two adjacent lumbar vertebrae. (Adapted from Aspen® MIS Fusion System Surgical Technique Guide, Zimmer Biomet, 2014.)
8.1.2 Outcomes
Spinous process fixation has exhibited promising outcomes with regard to its efficacy. Previous studies have demonstrated similar fusion rates when utilizing either supplemental spinous process fixation or pedicle screw fixation.1,3,4 Additionally, IFDs have exhibited comparable rigidity to pedicle screws, especially in flexion–extension movements of the lumbar spine.5,6 This is supplemented with evidence of reduced motion at adjacent segments, suggesting a reduced risk for adjacent segment disease when IFDs are utilized.1 However, the literature is limited regarding high-quality comparative studies. Few studies have examined the complication profile of IFDs.1 Furthermore, evidence regarding long-term outcomes and benefits of IFDs has not been addressed.1 As such, the literature is inadequate to identify the true advantages of IFDs over other methods of fixation.
8.2 Spinous Process Fixation Systems
Table 8.2 Alphatec Spine BridgePoint® Spinous Process Fixation System
Design | ||
Device type Fixed | Composition Titanium alloy | Specifications Angulating and telescoping plates enhance device fit and promote fusion |
| ||
Modular aspects and variations | ||
Widths Small: 35–40 mm Medium: 40–45 mm Large: 45–50 mm | Angulation ±14° | Compression/distraction Telescoping plates provide up to 5 mm adjustment |
| ||
Procedures | ||
MIS TLIF, MIS posterior decompression | ||
Radiographs unavailable | ||
Supplemental fixation system | ||
Alphatec Spine Illico® Posterior Stabilization System | ||