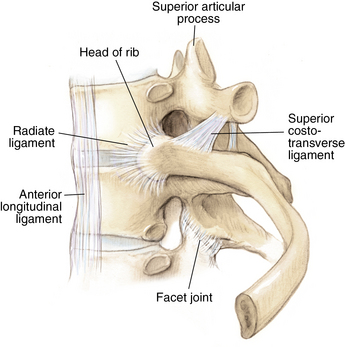
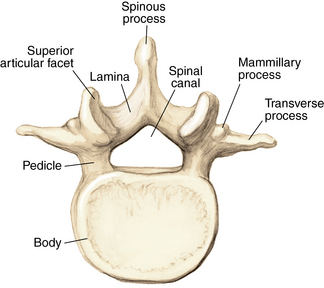
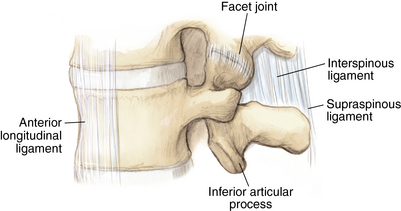
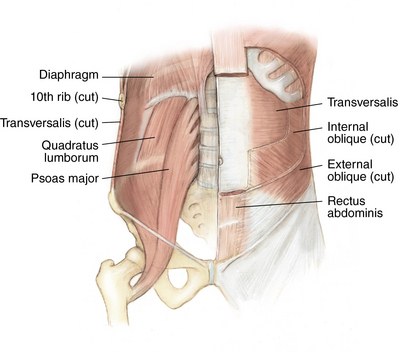
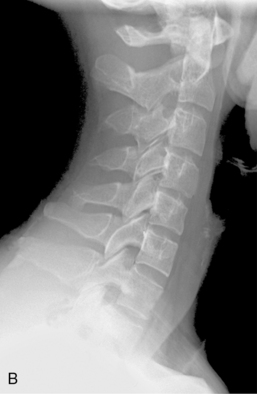
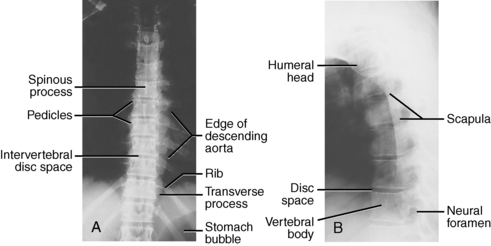
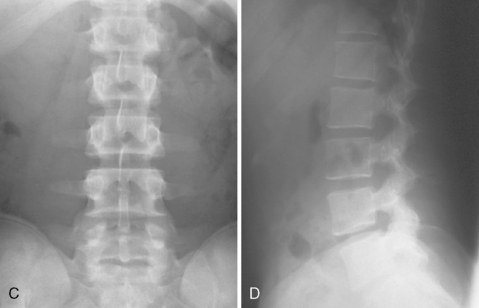
1 Spine Figure 1-8. Anterior cervical spine muscles. (From Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches: Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 219.) Figure 1-9. Posterior view of the spine musculature, superficial and intermediate layers. (From Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches: Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 222.) Figure 1-10. Posterior view of the spine musculature, deep view. (From Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches: Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 223.) Figure 1-12. The spinal cord and nerve root orientation. (From Miller MD, Hart JA, MacKnight JM, editors: Essential orthopaedics: Philadelphia, 2010, Saunders, p 457.) Figure 1-13. The cross-sectional anatomy of the spinal cord. (From Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches: Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 225.) Figure 1-16. Normal cervical spine x-ray studies. A, Anteroposterior view. B, Lateral view. (A, From Schwartz AJ: Imaging of degenerative cervical disease, Spine State Art Rev 14:545-569, 2000; B, from Pretorious ES, Solomon JA, editors: Radiology secrets, ed 2, Philadelphia, 2006, Mosby.) Figure 1-17. Normal spine x-ray studies. A, Anteroposterior (AP) view of the thoracic spine. B, Lateral view of the thoracic spine. C, AP view of the lumbar spine. D, Lateral view of the lumbar spine. (A and B, From Mettler F: Essentials of radiology, ed 2, Philadelphia, 2005, Saunders; C and D, from Mercier L: Practical orthopedics, ed 6, Philadelphia, 2008, Mosby.) Inspect for edema, rash, or deformity. • Forward leaning or cane, walker, shopping cart use: spinal stenosis • Trendelenburg gait: hip disease Palpate specific structures to evaluate complaint: • Musculature of trunk or spine Percuss costovertebral angles (CVAs). Normal range of motion (ROM): Table 1-1 Table 1-1. Neurovascular examination: Figure 1-18 Figure 1-19. Hoffman reflex. (From Fong W, et al. Evaluation of cervical spine disorders. In Devlin VJ, editor: Spine secrets plus, ed 2, St. Louis, 2012, Mosby, p 38.) Table 1-2. ICD-9 codes: 805.2 Closed fracture of dorsal thoracic vertebra without mention of spinal cord injury CPT codes: 22520 Percutaneous vertebroplasty, 1 vertebral body; thoracic 22521 Percutaneous vertebroplasty, 1 vertebral body; lumbar 22522 Each additional thoracic or lumbar vertebral body 22523 Percutaneous vertebral augmentation, including cavity creation using mechanical device, 1 vertebral body; thoracic 22524 Percutaneous vertebral augmentation, including cavity creation using mechanical device, 1 vertebral body; lumbar 22525 Each additional thoracic or lumbar vertebral body 72291 Radiological supervision and interpretation • Approach depends on lesion location, with the classic approach being transpedicular (can also be anterolateral, posterolateral, or parapedicular). • A trocar and cannula are introduced into the bone, one or two transpedicular needles are placed using fluoroscopy, and cement is introduced per the manufacturer’s instructions. • Caution is used to prevent and/or address any potential leaks of the cement outside the bony cavity.
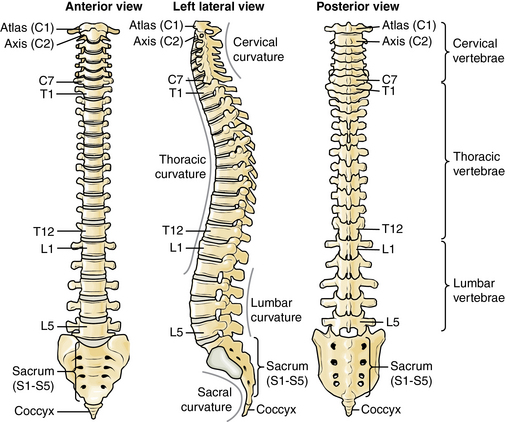
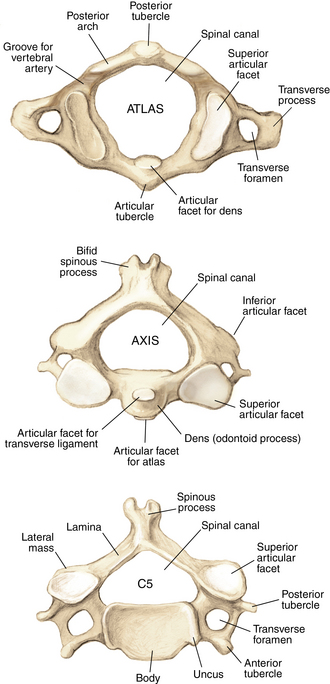
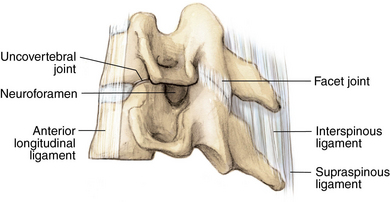
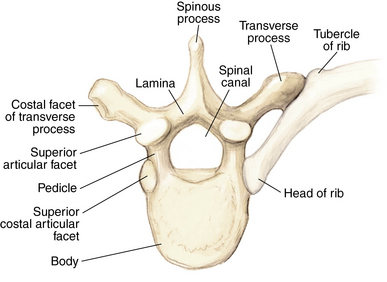
Anatomy
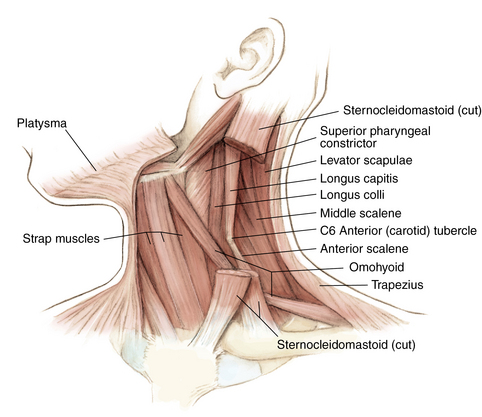
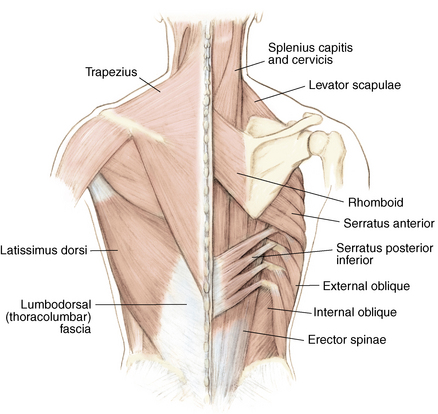
Muscles and soft tissue: Figures 1-8 through 1-11
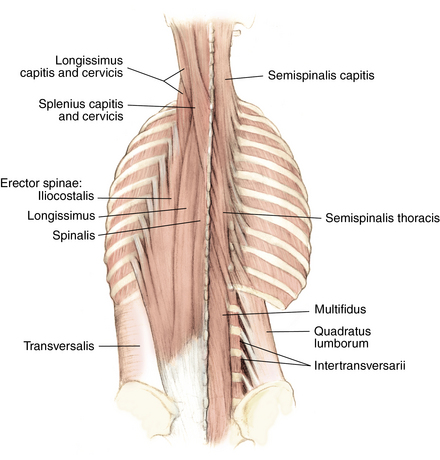
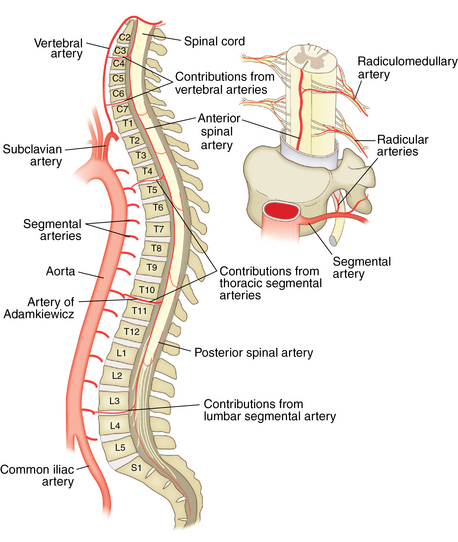
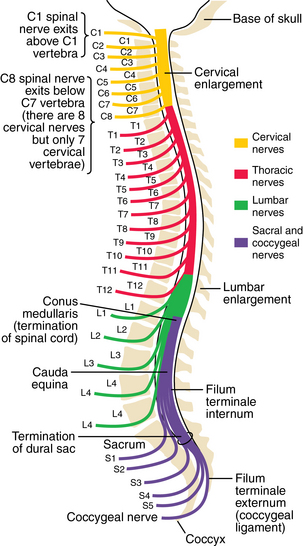
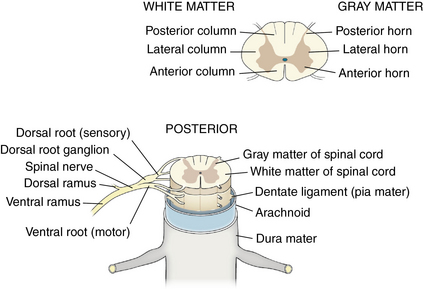
Nerves and arteries: Figures 1-12 through 1-14
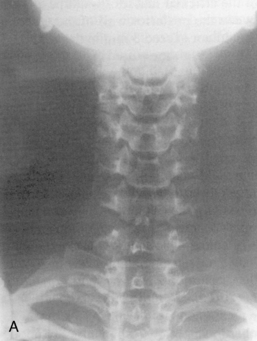
Normal x-ray appearance: Figures 1-16 and 1-17
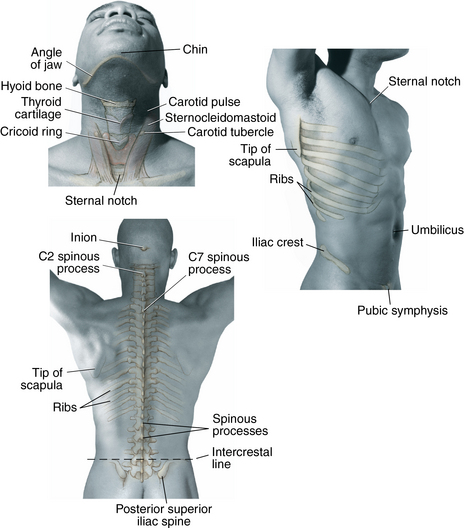
Physical examination
Motion
Range (Degrees)
Cervical extension
60
Cervical flexion
75
Cervical lateral flexion
45
Cervical rotation
80
Thoracic flexion
50
Thoracic rotation
30
Lumbar extension
60
Lumbar flexion
25
Special tests
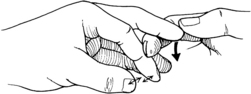
 Hoffman reflex: Hoffmann reflex most often reflects the presence of an upper motor neuron lesion from spinal cord compression. A positive test result is elicited by flicking either the volar or dorsal surfaces of the middle finger and observing the reflex contraction of the thumb and index finger to form an “OK” sign (Fig. 1-19).
Hoffman reflex: Hoffmann reflex most often reflects the presence of an upper motor neuron lesion from spinal cord compression. A positive test result is elicited by flicking either the volar or dorsal surfaces of the middle finger and observing the reflex contraction of the thumb and index finger to form an “OK” sign (Fig. 1-19).
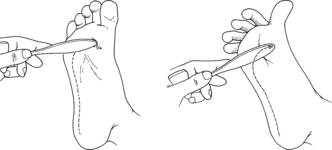
 Babinski reflex: Involuntary dorsiflexion of the hallux and spreading of the lesser toes occur in response to forceful scratching of the plantar or lateral aspect of the foot (Fig. 1-20).
Babinski reflex: Involuntary dorsiflexion of the hallux and spreading of the lesser toes occur in response to forceful scratching of the plantar or lateral aspect of the foot (Fig. 1-20).
 Clonus: Involuntary repetitive dorsiflexion of ankle occurs in response to one-time forceful dorsiflexion of the ankle by the examiner (Fig. 1-21).
Clonus: Involuntary repetitive dorsiflexion of ankle occurs in response to one-time forceful dorsiflexion of the ankle by the examiner (Fig. 1-21).
 Bulbocavernosus reflex: This refers to anal sphincter contraction in response to squeezing the glans penis or tugging on the Foley catheter tube carefully and involves the S1-S3 nerve roots. This is a spinal cord–mediated reflex. Following spinal cord trauma, the presence or absence of this reflex carries prognostic significance; in cases of cervical or thoracic spinal cord injury (SCI), absence of this reflex documents continuation of spinal shock or spinal injury at the level of the reflex arc. Return of the reflex signals the end of spinal shock. In lumbar injuries below the level of the spinal cord, absence of the reflex may reflect cauda equina injury.
Bulbocavernosus reflex: This refers to anal sphincter contraction in response to squeezing the glans penis or tugging on the Foley catheter tube carefully and involves the S1-S3 nerve roots. This is a spinal cord–mediated reflex. Following spinal cord trauma, the presence or absence of this reflex carries prognostic significance; in cases of cervical or thoracic spinal cord injury (SCI), absence of this reflex documents continuation of spinal shock or spinal injury at the level of the reflex arc. Return of the reflex signals the end of spinal shock. In lumbar injuries below the level of the spinal cord, absence of the reflex may reflect cauda equina injury.
 Straight leg raise: The test is performed by passively raising the leg while the patient is supine. A positive test result is indicated by reproduction if radicular symptoms on the involved side (Fig. 1-22).
Straight leg raise: The test is performed by passively raising the leg while the patient is supine. A positive test result is indicated by reproduction if radicular symptoms on the involved side (Fig. 1-22).
 Waddell signs: These are tests for nonorganic low back pain:
Waddell signs: These are tests for nonorganic low back pain:
Differential diagnosis: Table 1-2
Low back pain
Lumbar muscle pain
Degenerative disc disease
Lumbar facet disease
Nephrolithiasis
Lumbar compression fracture
Osteomyelitis
Malingering
Ovarian cyst
Lumbar radiculopathy
Herniated disc
Foraminal stenosis
Spinal stenosis
Neuropathy
Cervical or thoracic pain
Muscle strain
AAA
Fracture
Facet disease
Degenerative disc disease
Ankylosing spondylitis
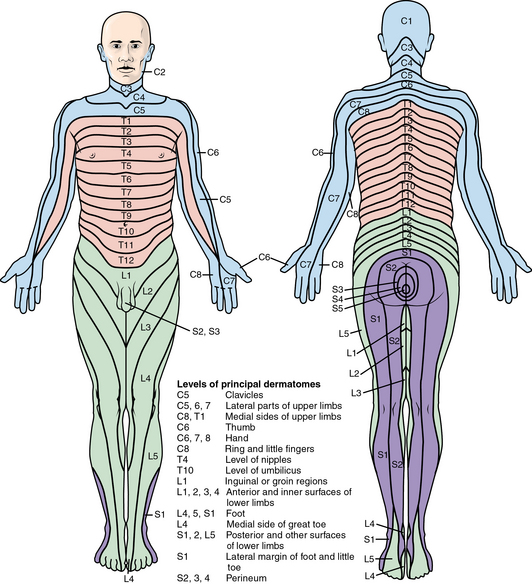
Regional or dermatomal pain
Shingles
Deformity
Scoliosis
Kyphosis
Lumbar strain
Treatment options
 A short 1- to 2-day rest period for severe pain is prescribed.
A short 1- to 2-day rest period for severe pain is prescribed.
 Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen is recommended.
Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen is recommended.
 Skeletal muscle relaxants are used sparingly.
Skeletal muscle relaxants are used sparingly.
 Physical therapy and “back school” can be beneficial for persistent pain.
Physical therapy and “back school” can be beneficial for persistent pain.
 Advanced imaging is used only in the most refractory cases.
Advanced imaging is used only in the most refractory cases.
 Long-term prevention with core strengthening and ROM exercises is indicated.
Long-term prevention with core strengthening and ROM exercises is indicated.
Differential diagnosis
 Intra-abdominal or pelvic disease such as nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis, abdominal aortic aneurysm, intra-abdominal, intrapelvic, or spinal mass, or metastasis
Intra-abdominal or pelvic disease such as nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis, abdominal aortic aneurysm, intra-abdominal, intrapelvic, or spinal mass, or metastasis
 Occult vertebral body fracture: Bone scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) will identify injury in cases of persistent pain.
Occult vertebral body fracture: Bone scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) will identify injury in cases of persistent pain.
 Malingering: Secondary gain must be considered. Assess with Waddell signs.
Malingering: Secondary gain must be considered. Assess with Waddell signs.
Vertebral compression fracture
Imaging
 AP or lateral views (with possible flexion or extension views) may show depressed or wedged end plates.
AP or lateral views (with possible flexion or extension views) may show depressed or wedged end plates.
 Look for other injury such as spinous process fracture in higher-velocity injury.
Look for other injury such as spinous process fracture in higher-velocity injury.
 MRI is indicated if radiculopathy is present or for planning a cement procedure. Use contrast if concern exists for pathologic fracture.
MRI is indicated if radiculopathy is present or for planning a cement procedure. Use contrast if concern exists for pathologic fracture.
Treatment options
 A short 1- to 2-day rest period is indicated for severe pain.
A short 1- to 2-day rest period is indicated for severe pain.
 Narcotic pain medications are prescribed.
Narcotic pain medications are prescribed.
 Use skeletal muscle relaxants sparingly.
Use skeletal muscle relaxants sparingly.
 LSO brace or lumbar corset is recommended.
LSO brace or lumbar corset is recommended.
 Physical therapy and “back school” can be beneficial for persistent pain.
Physical therapy and “back school” can be beneficial for persistent pain.
 MRI is used for evaluation for pathologic fracture or cement procedure.
MRI is used for evaluation for pathologic fracture or cement procedure.
Operative management
Codes
Surgical procedures
 Cement augmentation (vertebroplasty)
Cement augmentation (vertebroplasty)
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Spine