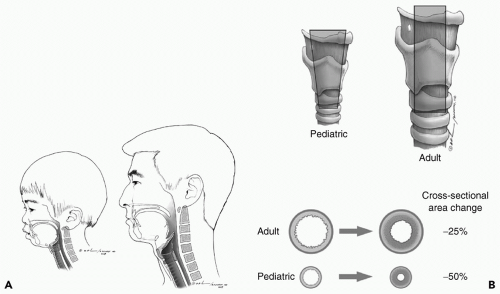
Decreased mineralization of bone means thatbone offers less protection to structures in the central nervous system (CNS), thorax, and abdomen.
Decreased muscle strength per unit volume means not only diminished protection of the cervical spine and abdomen, but decreased Starling effect in the heart.
Increased surface area relative to body mass means dramatically increased vulnerability to radiative and evaporative loss of heat and fluid.
TABLE 1 GUIDELINES FOR EQUIPMENT AND SUPPLIES FOR USE IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT (ED)a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Shorter trachea (even relative to body size)
Anteriorly displaced epiglottis
Prominent occiput
High larynx
Proportionately large tongue and smaller mouth
Narrowed at the cricoid cartilage
correctly sized laryngoscope (especially the narrower Miller blade), and having the assistant pull gentle traction at the side of the mouth. Finally, the typical narrowing of the cricoid cartilage has traditionally translated into use of uncuffed tubes for children in order to avoid subglottic stenosis from balloon pressure injury, and while some have recently questioned this practice in the intensive care unit (ICU) setting, it remains true that a correctly sized (a classic heuristic is to choose a tube with the same external diameter as the pinky finger) uncuffed tube is easier to place. Finally, all of these anatomic differences mean that esophageal intubation is common but easily detected with use of end-tidal CO2 devices now widely available.
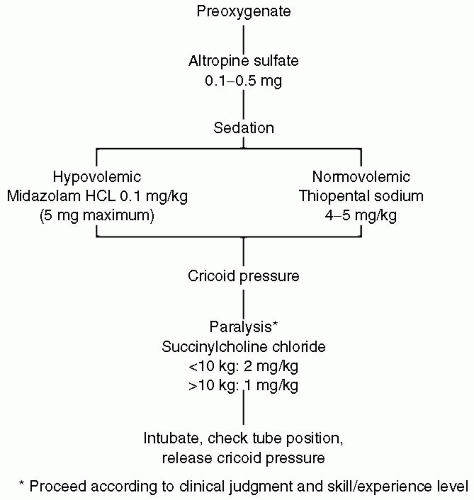 Figure 2 Algorithm for rapid sequence induction of the pediatric trauma patient. (From American College of Surgeons, 1997.) |
Inability to spontaneously protect the airway (e.g., Glasgow Coma Scale [GCS] <8, overdose, drugs, facial trauma)
Inability to ventilate (e.g., flail chest)
Inability to oxygenate (e.g., pulmonary contusion, smoke inhalation, and cardiac instability)
child. Distinguishing the source of the tachycardia can be challenging. Often, the pediatric patient will maintain a normal blood pressure until 40% or more of the estimated blood volume has been lost. Hypotension in the pediatric patient is always concerning.
Normalization of HR (to age-appropriate levels)
Increasing pulse pressure
Improved skin color and extremity warmth
Clearing sensorium (as measured by GCS)
Increasing MAP
Production of urine (2 mL/kg/hour in infants, 1 mL/kg/ hour in adolescents)
adults, children are more likely to have seizures associated with injury and therefore to have transient altered mental status from postictal states. The routine use of prophylactic antiseizure medication, however, has not been shown to be efficacious.16 In addition, children seem to suffer more mental status degradation from shock and therefore better recovery from resuscitation.
TABLE 2 GLASGOW COMA SCALE REVISED FOR USE IN PEDIATRIC POPULATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unobstructed visualization and palpation of the entire body
Determination of exposure to toxins (CO, acid, petroleum distillates, etc.)
Protection from exposure in the trauma bay in particular, protection from hypothermia
The presence or absence of fluid in the abdominal cavity
The presence or absence of fluid in the thorax
The presence of fluid in the pericardium (where it is the test of choice for tamponade)
Decompress the bladder and stomach.
Use a supraumbilical incision to avoid the high-riding pediatric bladder, and use the open or seldinger technique to direct a catheter toward the pelvis.
Gross blood is a positive result. If no blood is seen, instill 10 mL per kg (up to 1 L) of warmed Ringers lactate solution and allow it to drain. As in adults, with microscopic analysis, a positive test is given by: >100,000 RBC per mm3, >500 WBC per mm3, bile, urine, or food material.
CPR >20 minutes (in or out of hospital)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree