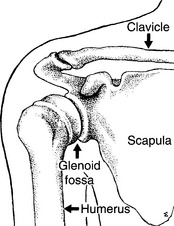
Shoulder Instability, Anterior
Common signs and symptoms
• Numbness or paralysis in the upper arm and deltoid muscle from pinching, stretching, or pressure on the blood vessels or nerves
Preventive measures
• Maintain appropriate conditioning that includes cardiovascular fitness and shoulder strength, flexibility, and endurance training.
Possible complications
• Damage to nearby nerves or major blood vessels, causing temporary or permanent weakness, paralysis, numbness, coldness, and paleness of the arm or hand
• Fracture or joint cartilage injury as a result of the dislocation or as a result of the reduction (repositioning) of the dislocation
• Repeated shoulder dislocations, particularly if the previous dislocation is not healed completely or is not appropriately rehabilitated; most recurrent dislocations are caused by repeated injury, but with an increasing number of dislocations, less force is necessary to cause dislocation.
Medication
• Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen (do not take for 7 days before surgery), or other over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, are often recommended. Take these as directed by your physician, and contact your doctor immediately if any bleeding, stomach upset, or signs of an allergic reaction occur.
When to call your doctor
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree