CHAPTER 5 Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is caused by inflammation of the synovium,1 which is the lining of the joints, and it may be triggered by disordered immunity. It can lead to long-term joint damage, resulting in chronic pain, loss of function and even disability.
1 Western medical aetiology and pathology
(1) Genetic aetiology
When the genetic marker HLA-DR4, a human leukocyte antigen that is a genetic anomaly, is found in white blood cells there is a risk for developing RA. The marker’s function is to distinguish one’s own cells from foreign invaders.2 If HLA-DR4 cannot differentiate between the two, it may attack self cells.
2 Diagnosis by Western medicine
The most commonly used tests are:
3 Chinese medicine aetiology and pathology
Chinese medicine says: ‘The four external evils known as Wind, Cold, Heat and Dampness attack the human body and cause Bi syndromes’. Chinese medicine teaches that exterior pathogens can attack the body when Qi and Blood are deficient and so cannot protect the body very well. This attack, coupled with the Qi and Blood deficiency, can result in Bi syndrome. Thus, the aetiology of Bi syndrome is complicated. It involves some combination of the external pathogens Wind, Dampness, Cold and Heat that invade the body as a result of an internal deficiency of Qi and Blood. These external pathogens stay in the channels and obstruct the flow of Blood and Qi, causing Bi syndrome.
4 General treatment principle
Differentiation and treatment
1 Wind-heat-dampness syndrome
Clinical manifestations
Redness, swelling around the joints, and a heat sensation and pain in the damaged joints. The joint is too painful to be touched, but the pain can be relieved by cold. There may be fever and thirst. The tongue is red, with a dry, yellow coating. The pulse is slippery and rapid.
Treatment principle
Dispel pathogenic Wind, Heat and Dampness, remove obstruction in the channels and stop pain.
Herbal treatment
BAI HU JIA GUI ZHI TANG variation
White Tiger plus Cinnamon Twig Decoction
Shi Gao Gypsum fibrosum 30 g (decoct first for 30 min)
Zhi Mu Anemarrhenae Rhizoma 12 g
Gan Cao Glycyrrhizae Radix 6 g
Gui Zhi Cinnamomi Ramulus 10 g
Ren Dong Teng Lonicerae Caulis 30 g
Chi Shao Paeoniae Radix rubra 12 g
Qin Jiao Gentianae macrophyllae Radix 12 g
The herbs above are decocted in water for oral administration.
2 Wind-cold-dampness syndrome
Treatment principle
Dispel pathogenic Wind-Cold-Dampness, remove obstruction in the channels and stop pain.
Herbal treatment
Remove Painful Obstruction Decoction
Qiang Huo Notopterygii Rhizoma seu Radix 6 g
Du Huo Angelicae pubescentis Radix 10 g
Gui Zhi Cinnamomi Ramulus 10 g
Qin Jiao Gentianae macrophyllae Radix 12 g
Dang Gui Angelicae sinensis Radix 10 g
Chuan Xiong Chuanxiong Rhizoma 10 g
Hai Feng Teng Piperis kadsurae Caulis 30 g
Ji Xue Teng Spatholobi Caulis 30 g
The herbs above are decocted in water for oral administration.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



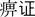 , some of which have symptoms and signs that may be similar to those of RA. Bi means obstruction and it is caused by pathogens creating blockage in the channels. This blockage prevents Qi and Blood from travelling through the channels smoothly and performing their functions of warming and nourishing the joints and extremities, thus causing serious symptoms.
, some of which have symptoms and signs that may be similar to those of RA. Bi means obstruction and it is caused by pathogens creating blockage in the channels. This blockage prevents Qi and Blood from travelling through the channels smoothly and performing their functions of warming and nourishing the joints and extremities, thus causing serious symptoms.