Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty via Extended Trochanteric Osteotomy
Introduction
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) predictably provides pain relief and improved function in patients with hip arthritis
Despite the success of THA, several situations necessitate revision of the femoral implant
Extended trochanteric osteotomy (ETO) is a surgical technique that allows exposure of the proximal femur using a controlled cortical fracture
ETO facilitates the removal of well-fixed femoral implants and provides improved surgical exposure to the acetabulum and femur to allow concentric placement of a new implant through
Improved access
Concentric reaming of the distal femur
Appropriate abductor tensioning
Improved acetabular visualization
Predictable healing of the osteotomy
Familiarity with ETO technique is critical for surgeons who perform revision THA or primary THA in patients with proximal femoral deformity
Patient Selection
Indications
Removal of well-fixed cemented, proximally coated, or extensively coated femoral implant
Indications for removing a well-fixed implant include sepsis, recurrent dislocation due to femoral implant malposition or offset, excess corrosion or fatigue failure, and the need for improved acetabular exposure
Extensive bone damage can occur while attempting to remove a well-fixed implant when the bone-prosthesis interface cannot be disrupted distally with proximal exposure alone
A cortical window can help but will weaken the remaining host bone and require a longer stem to bypass the stress riser
Removal of well-fixed distal cement
Challenging, especially when proximal femoral remodeling has occurred or a previous implant was cemented into varus position
Proximal exposure alone is shown to result in a higher prevalence of cortical perforations
ETO length can be planned to allow easy visual access to the distal cement plug such that drills, taps, and curets can disrupt the bone-cement interface and facilitate removal of retained cement
Proximal femoral varus remodeling
Observed in up to 30% of patients with a loose femoral stem
Component extraction may be easy, but reconstruction is challenging due to the deformity
ETO allows concentric reaming of femoral canal
Attempting distal fixation in a femur with proximal deformity results in a high prevalence of cortical perforation, undersizing of the femoral implant, and/or varus malposition
Improved acetabular exposure
Relative indication
Required because of heterotopic bone formation or the need to visualize anterior and posterior columns
ETO may minimize inadvertent fracture during femoral revision for severe trochanteric osteolysis
Rarely, ETO is used in primary THA patients with prior osteotomy, malunion, or deformity due to congenital dysplasia
Contraindications
No absolute contraindications
Rare indications when impaction bone grafting inside an ectatic femoral shaft is preferable to noncemented femoral fixation because of poor bone quality
Preoperative Imaging
Standard AP pelvis view
AP and lateral femur views
Procedure
Preoperative Planning

Figure 1AP radiograph of a hip with a cemented total hip arthroplasty shows mechanical failure with associated proximal femoral varus remodeling, causing a “conflict.” An extended trochanteric osteotomy is required for correction of the proximal deformity, as well as distal cement extraction. Note the conflict.
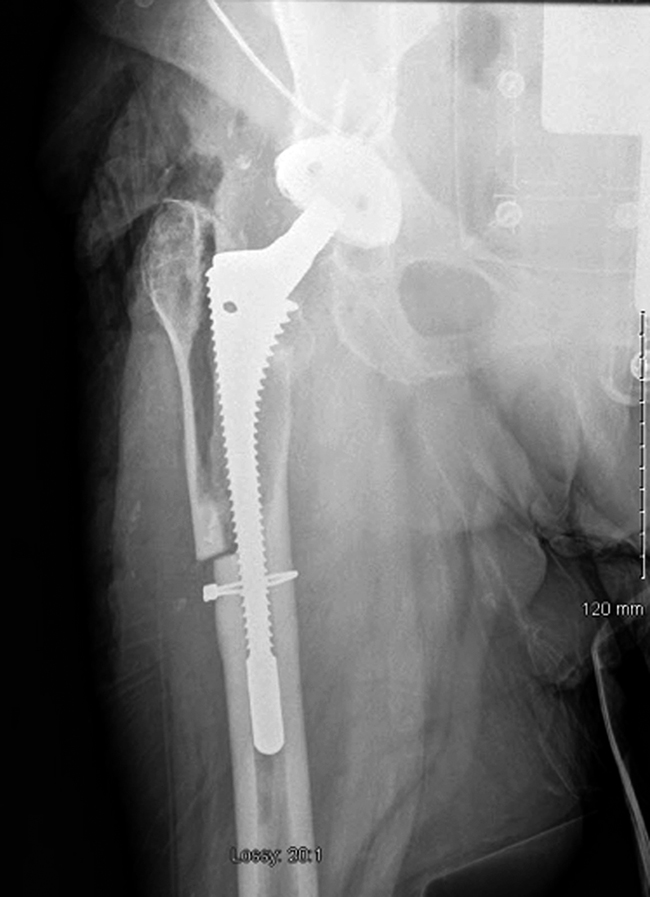
Figure 2AP radiograph of a hip with a periprosthetic fracture. When determining the length of the osteotomy, it is important to consider the future femoral reconstruction.
Length of ETO depends on surgical indication
Varus remodeling—Length of ETO should extend at least to apex of deformity to account for “conflict” (inability to place femoral implant in neutral position due to varus [Figure 1])
Removal of retained distal cement—Length of ETO needs to be within a few centimeters of the distal cement plug
ETO can be shorter if used for improved surgical exposure or loose distal cement mantle
Sufficient length of cortical bone below the lesser trochanter is required to securely reattach fragment
Minimum of two cables are required to securely fix the trochanteric fragment
ETO should be at least 14 cm below tip of the greater trochanter
Length of ETO also depends on the implant chosen for reconstruction
If extensively porous-coated stem is used, a minimum of 4 to 5 cm of scratch-fit required to obtain axial and rotational stability (Figure 2)
If a tapered stem is used, ETO must not extend past the distal metaphyseal/diaphyseal flare
Length is measured from tip of the greater or lesser trochanter
Special Instruments/Equipment/Implants
Small oscillating sagittal saw with a narrow blade for longitudinal limb of ETO
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


