Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty for Rotator Cuff Arthropathy
Introduction
Cuff tear arthropathy is characterized by superior migration of humeral head, erosions of inferior acromion and superior glenoid, and collapse of soft, atrophic head
Patients cannot elevate arm above 90° and have limited external rotation
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty features a medialized center of rotation and lengthened deltoid lever arm.
Patient Selection
Indications
Most common indication is cuff tear arthropathy
Patients older than 65 or 70 years with irreparable cuff tear and pseudoparesis of elevation
Must have functioning deltoid muscle and adequate glenoid bone stock
Contraindications
Absolute—Deltoid loss, inadequate glenoid bone stock, infection
Relative—Age younger than 65 years, rheumatoid arthritis
Preoperative Imaging
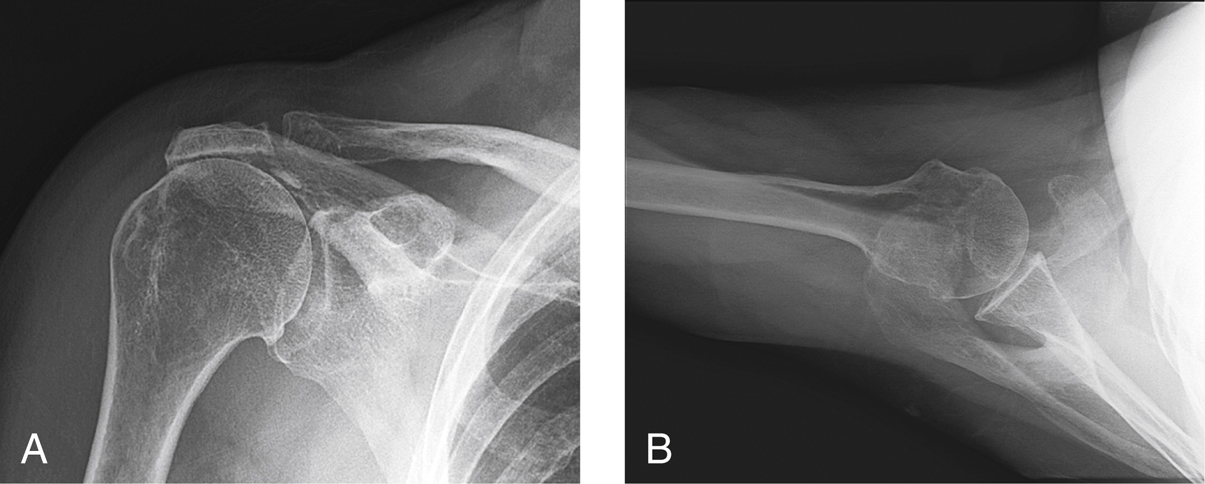
Figure 1Preoperative AP (A) and axillary lateral (B) radiographs show the typical changes seen in cuff tear arthropathy. Note the rounding of the greater tuberosity, decreased acromiohumeral distance, and thinning of the acromial arch.
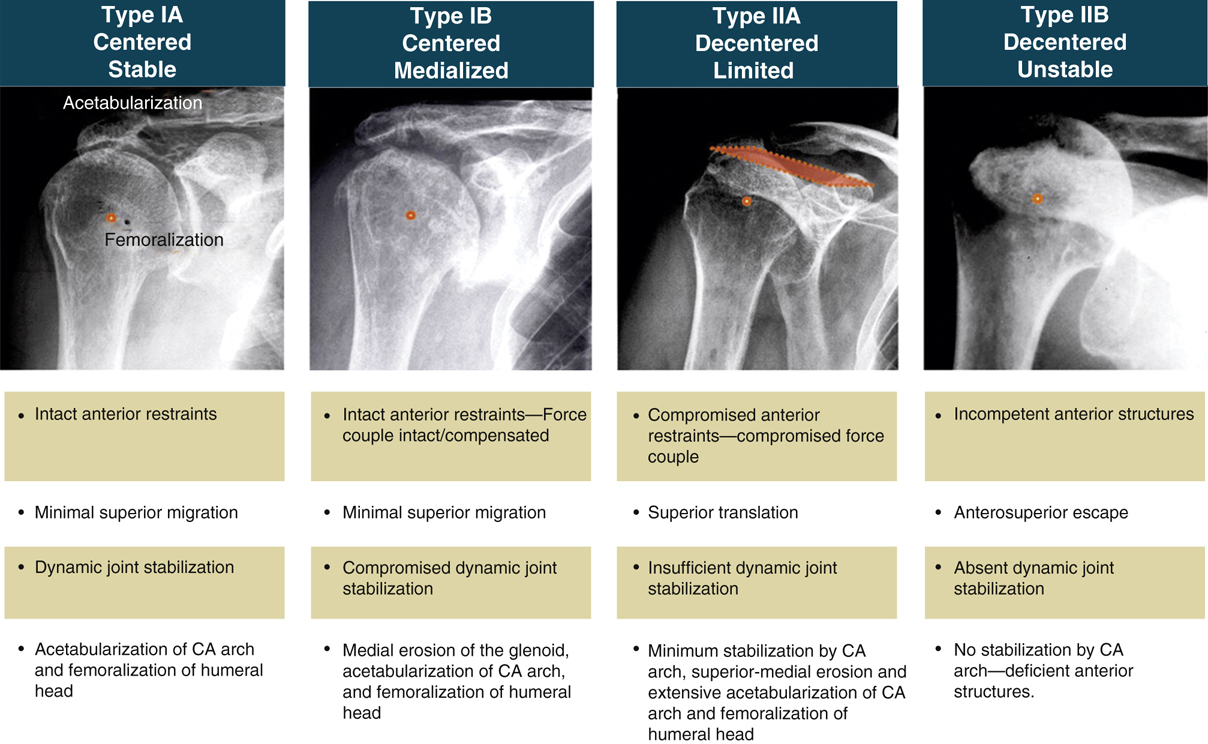
Figure 2Illustration showing the Seebauer classification of cuff tear arthropathy. CA = coracoacromial.
(Adapted with permission from Visotsky JL, Basamania C, Seebauer L, Rockwood CA, Jensen KL : Cuff tear arthropathy: Pathogenesis, classification, and algorithm for treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am2004;86:35-40.)
Plain AP and axillary radiographs (Figure 1)
Characteristic findings—Area of collapse of proximal humeral surface, paucity of osteophytes, reduced acromiohumeral distance, rounding of greater tuberosity, and erosion of undersurface of acromion
Seebauer classification is most useful; describes functional and biomechanical finding (Figure 2)
Use CT to assess glenoid bone stock
Use MRI to assess degree of cuff atrophy and fatty infiltration
Procedure
Room Setup/Patient Positioning
Semi-Fowler position; head in headrest with patient on edge of table so arm can be fully extended
True AP of the shoulder is obtained with C-arm
Record position of machine at time of imaging for use during the case
Surgical Technique
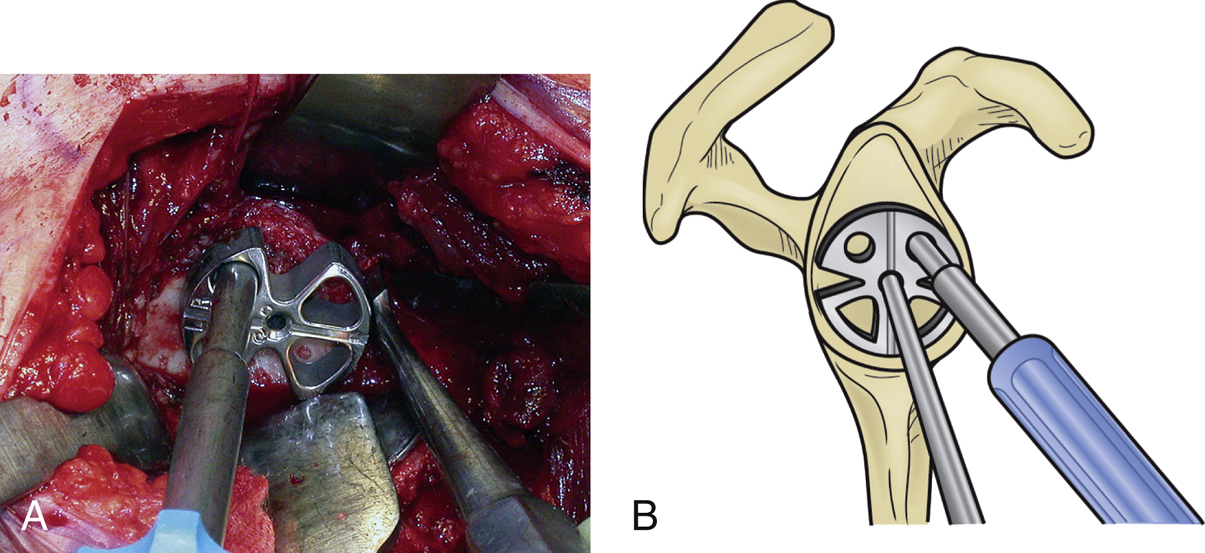
Figure 3Images show correct positioning of the glenoid baseplate positioner for reverse total shoulder arthropathy. A, Intraoperative photograph shows the glenoid baseplate positioner in place. Note the key elevator at the inferior aspect of the glenoid and the positioner placed just above it. B, Corresponding diagram of the glenoid baseplate positioner illustrates proper positioning at the inferior glenoid with the central guide pin in place.

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


