CHAPTER 27 Practical Issues in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty—The Secrets for Success
Introduction
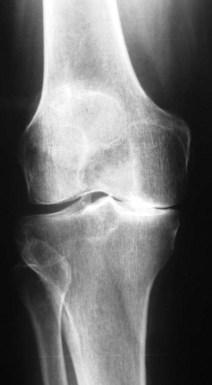
The single most important determinant in a good outcome following a UKA is patient selection (Fig. 27–1). Most authors refer to the traditional selection criteria originally written by Kozinn and Scott.1 These criteria say that UKAs should not be used in patients with more than a 10° fixed flexion contracture or varus or valgus deformity, and they should be used predominantly in thin, elderly, low-demand patients. Flexion deformity is usually considered the most important of these exclusions. More recently, there has been a cautious expansion of the indications to include younger2,3 and heavier4–6 patients. While the data are still relatively short term, there are increasing reports of the successful use of this concept in young (less than 60 years of age) patients at midterm follow-up. If this procedure can provide reasonable outcomes at 10 years, the thinking goes, then this relatively less involved procedure will have served as a “time buyer” until a further conversion to a TKR is performed. There is a growing appeal of thinking of a UKA as a patient’s first arthroplasty for the younger patient and a last arthroplasty for an elderly patient. Another reason for the increased use of UKA in younger patients is that the concept is an appealing one to these patients and, with the increased use of the Internet and direct-to-patient marketing, patients in this age category are increasingly aware of these surgical options and frequently seek out these procedures. Weight has been a concern with UKA procedures but, like use in younger patients, there are reports showing that excess weight, in and of itself, is not a contraindication. These reports are still in the midterm, but the traditional criterion of an 85- to 90-kg limit is being challenged.
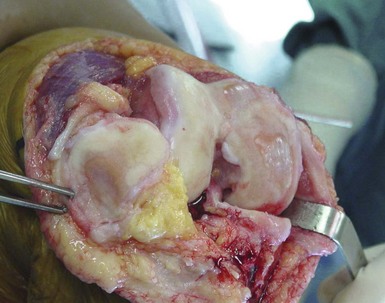
There are several other important aspects to patient selection. These include the status of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), the amount of disease present in the other compartments, the presence of crystalline disease and other inflammatory arthropathies, and location of a patient’s pain. Most surgeons feel that a functioning ACL is important, particularly with mobile-bearing devices. The amount of disease in other compartments is controversial. Most surgeons will accept up to Grade 3 Outerbridge damage but not Grade 4, but some surgeons ignore cartilage damage in the patellofemoral joint entirely. The damage often seen on the medial aspect of the lateral femoral compartment due to irritation of the tibial spine is usually ignored (Fig. 27–2). The presence of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals on radiographs or at surgery or the finding of an inflammatory synovium at the time of arthrotomy would be considered by most to be a contraindication to proceeding with a UKA. Some surgeons feel that, for a patient to be a UKA candidate, he or she should be able to point with one finger to the area of pain (medial femoral-tibial joint for medial UKA). Patients with more anterior knee pain or those who complain of pain while going up or down stairs are, in their minds, less ideal candidates for this type of surgery. This idea, however, is also being challenged and now many surgeons are not as concerned with the location of the pain as they are with the preoperative radiographs and examination. Another important factor in patient selection is the patient’s understanding of the concept and the procedure. Patients looking for the most predictable surgical management of their knee disease are probably best served by having a TKR despite the isolated nature of their disease. On the other hand, many patients find the idea of a less invasive procedure, where only the diseased part of the knee is replaced, an appealing one even if it does not have as good long-term follow up as a TKR. It is important that the patient understand the differences and the pros and cons of both approaches.
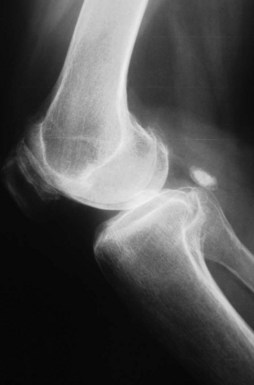
Once appropriate patient selection has occurred, UKA preoperative planning is important. A UKA should be thought of as replacing what has worn away. It should not be used to correct a significant malalignment or deformity. A general sense of the patient’s knee is important. Has the patient always had a varus knee? If so, it is important not to overcorrect the joint line. Using the anteroposterior (AP) radiograph, the surgeon should plan the level of tibial resection to be essentially perpendicular to the long axis of the tibia, although slight undercorrection is acceptable (Fig. 27–3). Because only one part of the joint is being replaced, it is imperative that the lateral radiograph be evaluated so the UKA will reproduce the preexisting posterior tibial slope. Failure to do so will lead to loosening and implant failure. The range of posterior tibial slope has been measured to be anywhere from 0° to 22° (Fig. 27–4).
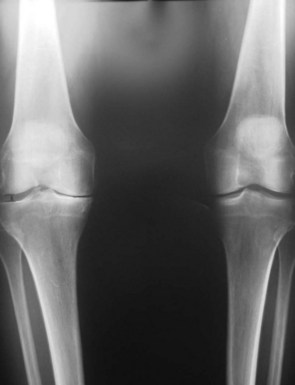
Figure 27–3 AP view of the knee. The surgeon should aim for perpendicular or slight undercorrection of the knee.
Technique
At each step of the procedure there are several keys to success.
Appropriate Exposure
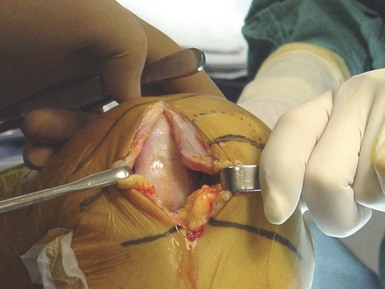
Most UKAs are now performed via a “minimally invasive” approach (Fig. 27–5). In the strictest sense, this does not describe the length of the incision; rather, it means that the extensor mechanism is not displaced from the trochlear groove. With the patella in place, the femoral-tibial alignment and orientation are easier to gauge and evaluate. Incisions should extend approximately from the top of the patella to the joint line. An adequate synovectomy at the arthrotomy enhances visualization and allows for further inspection of the remaining joint, ligaments, and synovium. As opposed to a TKR, where most of the surgery is done either at full extension or at 90° of flexion, a UKA is performed at a variety of flexion positions, and therefore the incision should be large enough to allow an adequate view of the joint. Soft tissues are at risk in these small incisions, so retractor placement is important, particularly along the medial joint line to protect damage to the medial collateral ligament. Extending the length of the incision should always be done if visualization is compromised.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree