Percutaneous Pinning of Proximal Humerus Fractures
Patient Selection
Indications
For select two-, three-, and four-part fractures
Displaced surgical neck fractures without calcar or medial comminution
Three-part fractures where height and version can be restored
Valgus-impacted four-part fracture
Timing of surgery affects success; reduction performed more than 1 week from injury may be difficult due to hematoma and scarring
Contraindications
Osteopenic bone is a relative contraindication
Extensive comminution of the tuberosities, medial calcar, or head segment
Varus-displaced fractures with loss of medial bone integrity
Three- and four-part fracture-dislocations or head-split fractures
Preoperative Imaging
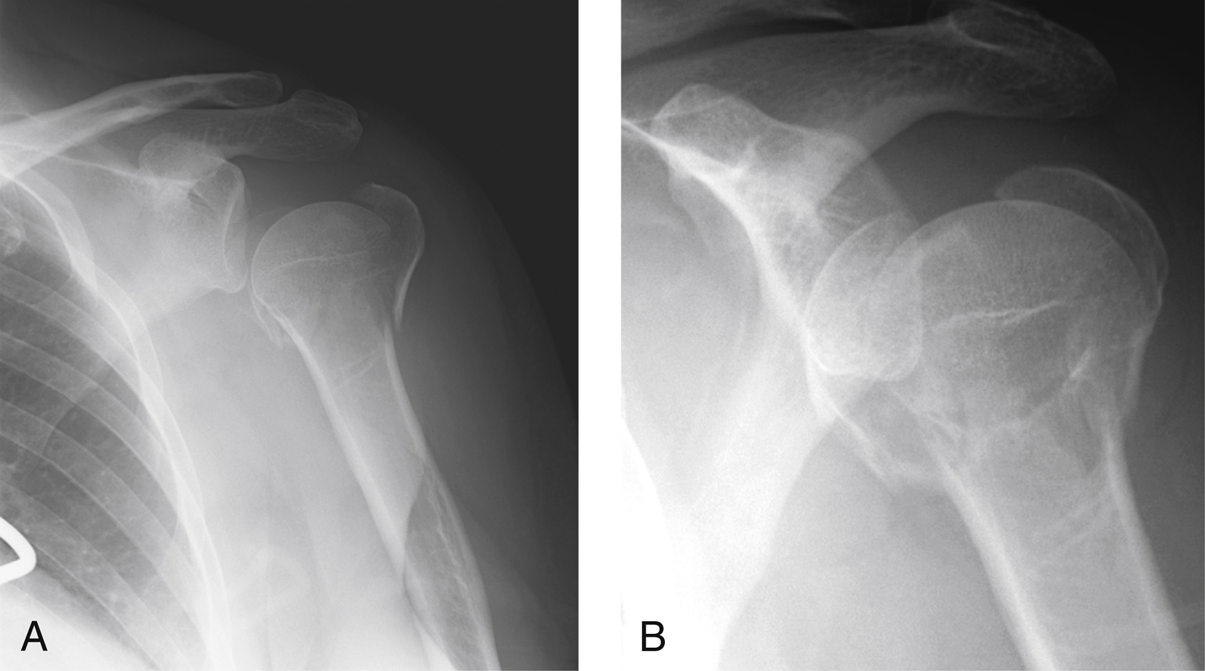
Figure 1Grashey (A) and AP (B) views of the shoulder demonstrate a valgus-impacted four-part proximal humerus fracture.
True AP, scapular lateral, and axillary lateral radiographs (Figure 1)
CT helps assess fragment positioning, angulation, and comminution
MRI usually not indicated
| Video 27.1 Percutaneous Pinning: When and How to Do It. Jonathan P. Braman, MD; Evan L. Flatow, MD (7 min) |
Procedure
Room Setup/Patient Positioning
Beach-chair position
Articulating arm positioner is routinely used
Must be able to obtain high-quality multiplanar fluoroscopic imaging
Special Instruments/Equipment/Implants
Small elevators, bone tamps, small skin hooks, surgical clamps
3.5-/4.0-mm partially threaded cannulated screws to fix tuberosity fragments
Rigid, terminally threaded 2.4- or 2.8-mm pins used for shaft-to-head fixation
Surgical Technique
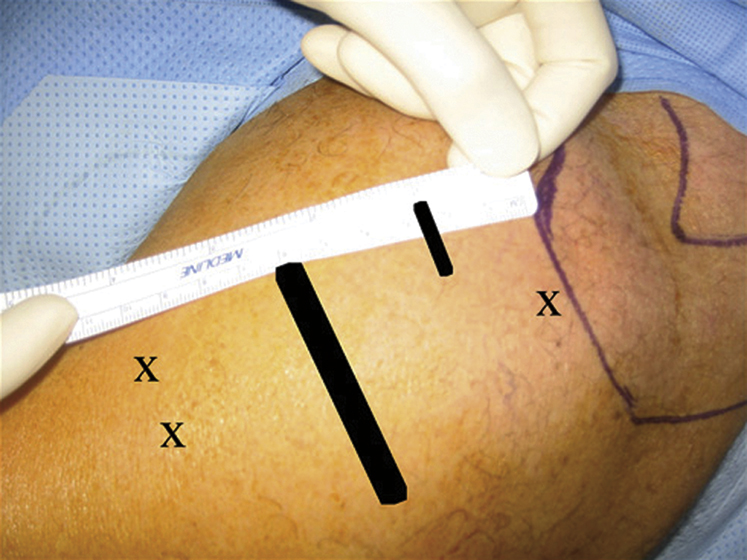
Figure 2Photograph shows markings (X) for placement of portals for fracture reduction and pin placement, including the distal portals for placement of 2.8-mm pins into the shaft and head. The tuberosity Kirschner wire portal, next to the lateral acromion, is denoted by the purple line. The short black line denotes placement of the reduction portal, usually 2 to 3 cm distal to the anterolateral acromial corner. The long black line denotes the typical course of the axillary nerve, approximately 5 cm distal to the lateral edge of the acromion.

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


