CHAPTER 20 Patellofemoral Arthroplasty
Indications and Outcomes
 Initial management of patellofemoral arthritis will consist of conservative measures, including appropriate physical therapy to restore patellofemoral mechanics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications combined with injection treatment, weight reduction, and activity modification. When nonsurgical treatment is ineffective and pain becomes disabling, surgical alternatives may be considered.
Initial management of patellofemoral arthritis will consist of conservative measures, including appropriate physical therapy to restore patellofemoral mechanics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications combined with injection treatment, weight reduction, and activity modification. When nonsurgical treatment is ineffective and pain becomes disabling, surgical alternatives may be considered. Patellofemoral arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty remain the most predictable treatment alternatives for isolated degenerative arthritis of the patellofemoral joint. With the development of new implant designs and improved surgical technique, patellofemoral arthroplasty can provide a more conservative approach with the ability to retain the medial and lateral menisci, as well as the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments.
Patellofemoral arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty remain the most predictable treatment alternatives for isolated degenerative arthritis of the patellofemoral joint. With the development of new implant designs and improved surgical technique, patellofemoral arthroplasty can provide a more conservative approach with the ability to retain the medial and lateral menisci, as well as the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. Appropriate patient selection remains the key factor in achieving high long-term success rates with patellofemoral arthroplasty. The procedure can be considered in patients with primary end-stage osteoarthritis, isolated to the patellofemoral joint. In addition, patients with posttraumatic degenerative arthritis or advanced chondromalacia of either the patellar surface, trochlear surface, or both can also be considered candidates for patellofemoral arthroplasty.
Appropriate patient selection remains the key factor in achieving high long-term success rates with patellofemoral arthroplasty. The procedure can be considered in patients with primary end-stage osteoarthritis, isolated to the patellofemoral joint. In addition, patients with posttraumatic degenerative arthritis or advanced chondromalacia of either the patellar surface, trochlear surface, or both can also be considered candidates for patellofemoral arthroplasty. Patellofemoral arthroplasty is contraindicated in patients with any evidence of tibiofemoral arthritis or advanced chondromalacia in the medial or lateral compartments.
Patellofemoral arthroplasty is contraindicated in patients with any evidence of tibiofemoral arthritis or advanced chondromalacia in the medial or lateral compartments. The surgical technique for patellofemoral arthroplasty is slightly different than that used in total knee arthroplasty.
The surgical technique for patellofemoral arthroplasty is slightly different than that used in total knee arthroplasty.Introduction
Osteoarthritis limited to the patellofemoral joint has been a disabling condition for many patients, and a very challenging clinical entity to treat. The incidence of isolated patellofemoral arthritis has continued to increase and will continue to create greater demands for more definitive treatment options.1 Davies and colleagues reported in a radiologic study that isolated patellofemoral arthritis was found in 9.2% of 206 knees in 174 consecutive patients older than 40 years of age.2 Another study by McAlindon and associates found that as many as 24% of women and 11% of men over the age of 55 with symptomatic knee arthritis had isolated degenerative arthritis of the patellofemoral articulation.3 Initial management of patellofemoral arthritis will consist of conservative measures, including appropriate physical therapy to restore patellofemoral mechanics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications combined with injection treatment, weight reduction, and activity modification. When nonsurgical treatment is ineffective and pain becomes disabling, surgical alternatives may be considered.
Nonarthroplasty options for patellofemoral arthrosis have typically provided incomplete relief, with short-term fair to good results in 20–75% of patients. Arthroscopy with débridement and marrow stimulation procedures have had limited short-term results, with only 40–60% of patients with satisfactory results.4 Osteochondral allograft procedures, autologous chondrocyte implantation, with or without tibial tubercle osteotomy, have also had inconsistent success, with unsatisfactory short-term results reported as high as 25–30%.5,6 Although patellectomy has been considered a surgical alternative, it results in significant alteration of the patellofemoral biomechanics and will significantly decrease both the quadriceps force and the extensor moment arm. Experimentally, this has been shown to reduce extension power by 25–60%, which can require an increase in quadriceps force of 15–30% to achieve adequate extension torque.7,8 Extension lag and decreased knee flexion after patellectomy are common and are frequently associated with residual knee pain and instability resulting in a failure rate as high as 45%.9 In addition, tibiofemoral joint reactive forces have been shown to increase as much as 250% after patellectomy, which therefore will increase the risk of progressive degenerative arthritis of the tibiofemoral joint space.10
Patellofemoral arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty continue to remain the most predictable treatment alternatives for isolated degenerative arthritis of the patellofemoral joint. Although total knee arthroplasty is a successful treatment option for some patients, it may not be desirable in all patients.11 Patellofemoral arthroplasty can provide a more conservative approach, and it may be more appropriate in the properly selected patient. In contrast to total knee arthroplasty, patellofemoral arthroplasty will address only the affected area of pathology, with the ability to preserve the tibiofemoral joint space, medial and lateral menisci, and both the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. More normal knee kinematics and physiologic motion can therefore be preserved with patellofemoral arthroplasty. With the development of new implant designs, and improved surgical technique, more consistent and predictable clinical success can be achieved.
Indications/Contraindications
In the past, success with patellofemoral arthroplasty has been inconsistent and unpredictable. This has largely been related to poor implant design, lack of good surgical instrumentation, and poor patient selection. Appropriate patient selection remains the key factor in achieving high long-term success rates with patellofemoral arthroplasty. The procedure can be considered in patients with primary end-stage osteoarthritis, isolated to the patellofemoral joint. In addition, patients with posttraumatic degenerative arthritis or advanced chondromalacia of either the patellar surface, trochlear surface, or both can also be considered candidates for patellofemoral arthroplasty. Patellar or trochlear dysplasia can also be successfully treated with patellofemoral arthroplasty. Slight tilt or subluxation observed on preoperative tangential radiographs can successfully be treated with patellofemoral arthroplasty. It is extremely important to address any patellar malalignment abnormalities, either preoperatively or intraoperatively. Patellar instability or chronic recurrent patellar dislocation is considered a contraindication to patellofemoral arthroplasty unless the condition has been successfully treated prior to surgery.12 It is important to understand that patellofemoral arthroplasty is a resurfacing procedure and will not correct any preexisting rotational or angular malalignment of the knee. This is a unique difference from total knee arthroplasty in that patellofemoral arthroplasty will not correct or change the mechanical or anatomic axis, as well as femoral or tibial rotation. Preoperative alignment assessment is also critical in determining the likelihood for the future development of degenerative arthritis of the tibiofemoral joint space and/or patellar maltracking, subluxation, and dislocation.
Patellofemoral arthroplasty is contraindicated in patients with any evidence of tibiofemoral arthritis or advanced chondromalacia. This is important to identify preoperatively, as the most common cause for long-term failure, or the need for conversion of patellofemoral arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty, is progressive degenerative arthritis of the tibiofemoral joint space.13 In addition, uncorrected patellar instability combined with severe patellofemoral malalignment will present an increased risk for early failure and usually is best treated with total knee arthroplasty.14 More recent emerging technology has allowed for chondral abnormalities of the medial or lateral femoral condyles to be addressed simultaneously at the time of patellofemoral arthroplasty.15 Clinical experience, however, is limited at this time and such combined procedures should be used only in carefully selected clinical conditions. Patellofemoral arthroplasty is also not appropriate in patients with inflammatory arthritis or chondral calcinosis of the weight-bearing surfaces of the tibiofemoral joint space or menisci. Patients with chronic anterior knee pain that cannot be directly attributed to the patellofemoral joint space are also poor candidates for this procedure. It is also very important that the patient has realistic expectations regarding the extent of pain relief, the duration of recovery, and the allowable postoperative activities following patellofemoral arthroplasty in order to achieve high success rates.
Patellofemoral arthroplasty has been found to be most suitable for the younger or middle-aged patient (55–60 years), providing a more definitive resolution without the need for performing a total knee arthroplasty.16 Typically, the younger patients have been told to live with their severe disability because they were “too young” for total knee arthroplasty as the only option. It is difficult to recommend the sacrifice of both the medial and lateral compartments, as well as the anterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament, to treat the arthritic patellofemoral compartment if an equally successful and less destructive alternative can be found. Patellofemoral arthroplasty can therefore offer a reasonable treatment option for patients with severe disabling degenerative arthritis isolated to the patellofemoral joint, yet who are too young for total knee arthroplasty, as well as being a less destructive option for the older patient. In the appropriately selected patient, long-term survivorship has been reported as high as 98% with an average follow-up of 17 years.17 It can also be utilized as an interim step when total knee arthroplasty may not be the ideal treatment option due to age or other clinical circumstances.16 Conversion of patellofemoral arthroplasty to total knee arthroplasty has been shown by several authors to be equally successful as primary total knee arthroplasty without the need for bone grafting, special augments, or a varus-valgus constrained revision knee implant.17 Older patients (60–85 years) are also good candidates, as this can provide a more conservative and less invasive approach than total knee arthroplasty.12,18
Clinical Evaluation and Preoperative Planning
A full preoperative evaluation should be undertaken, including a very detailed history and physical examination to verify that the symptoms and clinical findings are isolated to the patellofemoral joint. The history should focus on any elements of prior patellar instability with previous history of recurrent subluxation and/or dislocation. It is extremely important that the symptomatology be localized to the anterior compartment of the knee, and that it originates from the degenerative process of the chondral surfaces of the patellofemoral joint, and is not related to the peripatellar soft tissue structures. Many times these patients will have had prior surgical procedures, with arthroscopy being the most common surgical intervention performed. This sometimes may include lateral release, chondroplasty, and prior realignment procedures. Pain should be primarily isolated to the patellofemoral joint and will frequently be associated with retropatellar crepitus. Patellofemoral pain is often exacerbated by activities such as stair climbing, rising from a chair, sitting with the knee flexed, squatting, and walking on uneven ground. Leslie and Bentley have found that the clinical triad of quadriceps wasting greater than 2 cm, chronic effusion, and retropatellar crepitance are the best physical predictors of articular cartilage breakdown of the patellofemoral joint.19
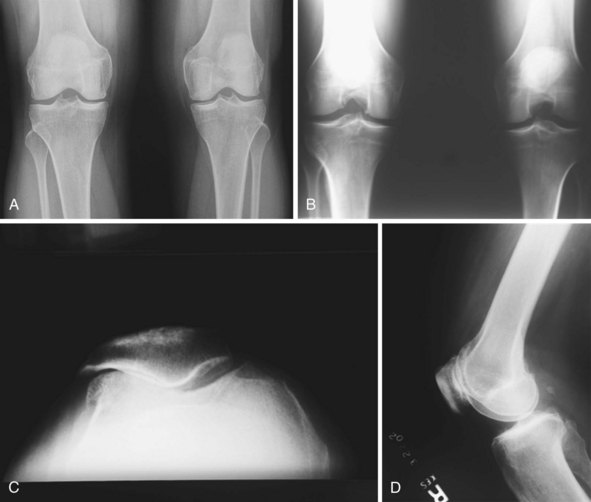
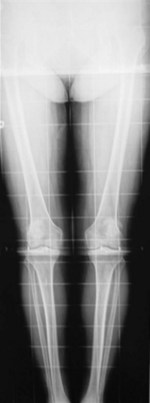
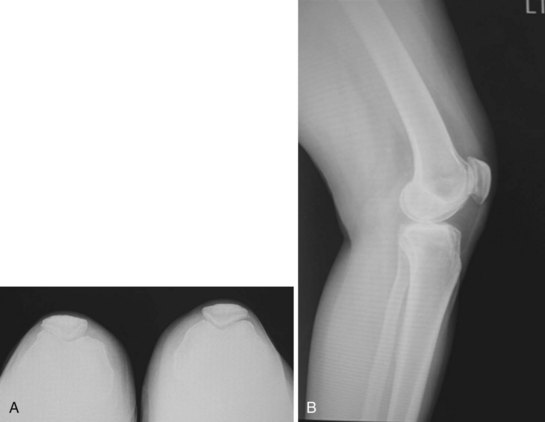
Standing weight-bearing radiographs are essential for evaluation of the femorotibial joint space; these should include a standing bilateral anteroposterior view, a 45° flexion posteroanterior view, and lateral and skyline views20 (Fig. 20–1). A long-leg standing weight-bearing (1.37 cm) axial alignment radiograph is also necessary to further evaluate the anatomic and mechanical axis of the knee (Fig. 20–2). Mild changes of the tibiofemoral joint space may be accepted; however, if there are any concerns for early degeneration of the chondral surface of the medial or lateral compartments, or associated meniscal pathology, then further evaluation is required either arthroscopically or at the time of surgery. Lateral radiographs are helpful in demonstrating degenerative changes of the patellofemoral joint but more useful for the assessment of patella alta or patella baja. Tangential radiographic views or skyline views are helpful in confirming the presence of severe degenerative change of the patellofemoral joint, but sometimes may not accurately identify the severity of the degeneration. It is not uncommon to observe some apparent joint space preservation with minimal or no osteophytes in the presence of severe articular cartilage loss (Fig. 20–3).
Arthroscopic evaluation has been helpful in this setting when there are questions as to the severity and degree of cartilage degeneration, as well as any other concerns for intra-articular pathology (Fig. 20–4). The clinical success of arthroscopy for isolated osteoarthritis of the patellofemoral joint has been unpredictable, but it can have value in evaluating the severity of the chondral change if this is not clearly defined on the preoperative radiographic evaluation, or there is uncertainty for the indication to perform a patellofemoral arthroplasty. Other areas of concern, such as early degeneration of the tibiofemoral joint space and meniscal pathology, may also be evaluated at the time of arthroscopic evaluation. This evaluation is extremely critical, as this will certainly play into the future prognosis and long-term success of patellofemoral arthroplasty. Photographs from prior arthroscopic treatment can also be of extreme value in a thorough evaluation of the knee to validate whether the degenerative process is isolated to the patellofemoral joint.

Figure 20–4 (A) Arthroscopic view of the patellofemoral joint of the patient in Figure 20–3 revealing severe grade IV degenerative changes on both the patellar and trochlear surfaces. (B) Arthroscopic view of the medial compartment of the same patient revealing intact articular surfaces and a normal medial meniscus. (C) Arthroscopic view of the lateral compartment showing a normal lateral meniscus and normal articular cartilage.
Surgical Technique
Setup and Equipment
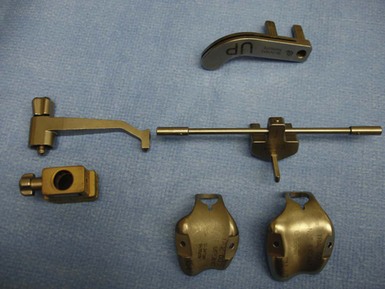
The procedure is approached in a manner similar to that of total knee arthroplasty, utilizing general or regional anesthesia. A short-acting spinal anesthetic with light sedation is preferable, as this will allow for a more successful approach with pain management. This has also been very beneficial in initiating early weight bearing and recovery of quadriceps muscle function within hours after the procedure. After induction of anesthesia, the patient is positioned in the supine position, with a small bolster placed at the foot of the bed to allow for knee flexion between 70° and 90° (Fig. 20–5). Hyperflexion is not necessary and can sometimes hinder the exposure of the distal femur. The surgical instrumentation is relatively simple and follows the same principles as total knee arthroplasty (Fig. 20–6). Intramedullary instrumentation is used for the anterior femoral resection, followed by preparation of the trochlea with a simple motorized rasp.
Technical Description
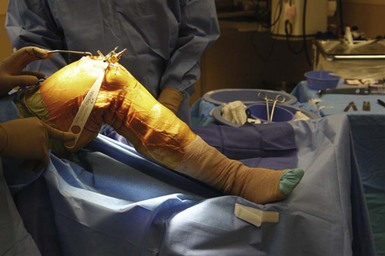
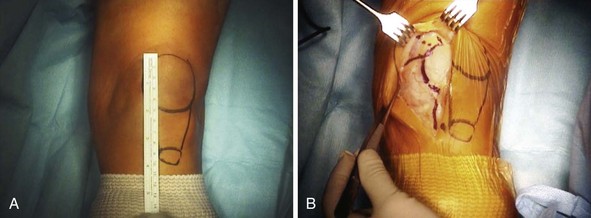
The surgical exposure for patellofemoral arthroplasty is slightly different than that used in total knee arthroplasty. Care must be taken to evaluate, observe, and protect the normal anatomy throughout the procedure. The skin incision is made just medial to the midline in order to minimize problems with point-loading during kneeling20 (Fig. 20–7). The incision should extend from approximately 1–2 cm above the superior pole of the patella to just 1 cm below the joint line. It is not necessary to extend the incision distally as much as would be performed in a total knee arthroplasty as most of the exposure will focus on the anterior and distal femur. The joint capsule and synovium can be opened using a standard short medial patellar arthrotomy or a midvastus approach (Fig. 20–8). A small mini-arthrotomy is ideal, as this will facilitate exposure for referencing the anterior cortex during the procedure. Care is taken to minimize resection of the fat pad and be cautious of the anterior horn of the lateral and medial menisci, as well as the intermeniscal ligament.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree