Chapter 110 Panax ginseng (Korean Ginseng)
Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer (family: Araliaceae)
Common names: Korean ginseng, Chinese ginseng, Asiatic ginseng, Oriental ginseng
 General Description
General Description
• Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng)
• Panax japonicus C.A. Meyer (Japanese ginseng)
• Panax pseudoginseng (Himalayan ginseng)
P. ginseng C.A. Meyer is the most widely used and most extensively studied species.1,2
Its pharmacology is the major focus of this chapter.
Ginseng is often processed in two forms, white and red. White ginseng is the dried root whose peripheral skin is frequently peeled off. Red ginseng is the steamed root, which has a caramel-like color.2
There are many types and grades of ginseng and ginseng extracts, which vary according to the source, age, and parts of the root used, where it was grown, the time of harvesting, and the methods of preparation.1–3 Old, wild, well-formed roots are the most valued, whereas rootlets of cultivated plants are considered the lowest grade. High-quality preparations are usually in the form of extracts of the main root of plants between 4 and 6 years old that have been standardized for ginsenoside content (see later) and ratio to ensure optimum pharmacologic effect.
 Chemical Composition
Chemical Composition
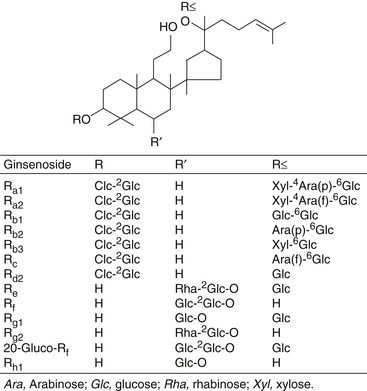
As can be seen from Figure 110-1, the ginsenosides differ primarily in their sugar groups.
Ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Re, and Rg1 are present in significant concentrations in Korean ginseng. In contrast, American ginseng (P. quinquefolius) contains primarily ginsenosides Rb1 and Re and does not contain ginsenosides Rf, Rb2, or, in some instances, Rg1.4 These features allow for easy detection of species with high-pressure liquid chromatography.
Other components of ginseng are as follows1,2:
• Free and glucoside-bound sterols (e.g., β-sitosterol and its β-glucoside)
• Polyacetylene derivatives β-elemene and panaxynol
• Low-molecular-weight polysaccharides
• Vitamins (e.g., thiamine, riboflavin, B12, nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid, biotin)
• Minerals (including germanium)5
• Simple sugars (glucose, fructose, sucrose, maltose, trisaccharides, etc.)
• Unique proteins (e.g., panaxagin, a protein that possesses antifungal, antiviral, translation-inhibiting, and ribonuclease activities)6
Although it was reported that ginseng contains large amounts of germanium (i.e., 300 ppm), a follow-up study using highly sensitive (detection limit of 1 ppb), flameless atomic absorption spectrometry combined with solvent extraction demonstrated that the highest concentration of germanium measured in samples of ginseng purchased in the Osaka market was only 6 ppb.5 More research is needed to accurately determine the germanium content of botanical medicines, because the reported concentrations vary widely. Such low levels suggest that a connection between the pharmacology of ginseng and its germanium content is unlikely.
 History and Folk Use
History and Folk Use
Perhaps the most famous medicinal plant of China, ginseng has been generally used alone or in combination with other herbs to restore the “Yang” quality. It has also been used as a tonic for its revitalizing properties, especially after a long illness. Conditions for which ginseng is used in folk medicine are shown in Box 110-1. It has been used as an alterative, anodyne, aperitif, aphrodisiac, cardiotonic, carminative, emetic, estrogenic, expectorant, gonadotrophic, nervine, sedative, sialogogue, stimulant, stomachic, and tranquilizer.1,2 As can be seen from this list, ginseng has been used for most conditions, reflecting a broad range of nutritional and medicinal properties.
 Pharmacology and Clinical Indications
Pharmacology and Clinical Indications
Over the years, ginseng has been reported to have numerous pharmacologic effects in humans and laboratory animals, including the following1,2,7:
• General stimulatory effects during stress
• Decrease in sensitivity to stress
• Increase in mental and physical capacity for work
• Improved endocrine system function
• Amelioration of radiation sickness, experimental neurosis, and cancer
• Enhanced protein synthesis and cell reproduction
• Improved glucose control in diabetes
• Modulation of various immune system parameters
• Lowering of serum cholesterol
Some of these actions are discussed in greater detail in the following sections.
Adaptogenic and Antistress Activity
Ginseng was originally investigated for its adaptogenic qualities. An adaptogen was defined in 1957 by the Russian pharmacologist I.I. Brekhman2 as a substance with the following properties:
• It must be innocuous and cause minimal disorders in the physiologic functions of an organism.
• It must have a nonspecific action (i.e., it should increase resistance to adverse influences through a wide range of physical, chemical, and biochemical factors).
• It usually has a normalizing action irrespective of the direction of the pathologic state.
According to tradition and scientific evidence, ginseng possesses this kind of equilibrating, tonic, antistress action, and so the term adaptogen is quite appropriate to describe its general effects.2,7,8
Ginseng delays the alarm phase response in Selye’s classic model of stress. Animal studies found that adrenal cholesterol levels were many times higher in animals given ginseng than in their matched controls, indicating greater tolerance of stress and delayed alarm phase response.9–11
Italian researchers studied the effect of a standardized ginseng extract, the ginsenoside composition of which was accurately determined, on the adrenal functions of rats exposed to cold.10 The ginseng extract significantly counteracted body temperature decline without affecting blood glucose or cortisone levels. In a group of adrenalectomized rats, the ginseng extract had no significant effects. Administration of hydrocortisone to the adrenalectomized rats did, however, cause body temperature to be maintained when the rats were exposed to cold.
Histologic findings in this study were as follows:
• Evidence of hyperfunctioning in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus in rats fed the ginseng extract
• Remarkable increase in corticotropic basophilic cells (adrenocorticotropic hormone [ACTH] producing) in the pars distalis of the pituitary gland
• Hyperplasia of the adrenal zona fasciculata, indicating that hyperfunctioning of the adrenal was promoted by the administration of the ginseng extract
Other researchers demonstrated that ginseng saponins significantly increased plasma ACTH and corticosteroids (in a parallel kinetic pattern).12,13 Because this effect could be blocked by dexamethasone (which acts on the hypothalamus and pituitary to prevent ACTH release), it was concluded that ginsenosides act predominantly on the hypothalamus or pituitary to promote secretion of ACTH. This conclusion was confirmed further by indirect studies. ACTH first stimulates an increase in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in the adrenal and then promotes corticosteroid synthesis. Ginseng administration was shown to increase adrenal cAMP in normal rats, but not in hypophysectomized rats.
• The antistress action of ginseng is greatly reduced by adrenalectomy.
• Ginseng continues to exert its antistress action after hypophysectomy only if ACTH is administered.
• Histologic and chemical evidence demonstrates a strong link between ginseng and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
Ginseng may prove especially effective in restoration of normal adrenal function and prevention of adrenal atrophy associated with corticosteroid administration. In rats, ginseng was found to inhibit cortisone-induced adrenal and thymic atrophy.14
Antifatigue (Mental and Physical) Activity
Some of the first studies of ginseng’s adaptogenic activities were performed during the late 1950s and early 1960s by Brekhman and Dardymov7,8 in the Soviet Union and by Petkov15–17 in Bulgaria.
In one of Brekhman’s experiments, Soviet soldiers given an extract of ginseng ran faster in a 3-km race than those given a placebo. In another, radio operators tested after administration of ginseng extract transmitted text significantly faster and with fewer mistakes than those given placebo. These and similar results reported by European researchers, who demonstrated improvement in human physical and mental performance after administration of ginseng extracts, prompted researchers to confirm the results in experimental models using mice.2,7,8,15
In perhaps the best known of these experiments, mice were subjected to swimming in cold water or running up an apparently endless rope to determine whether ginseng could lengthen the time to exhaustion. The results indicated that ginseng possessed significant antifatigue activity, because a clearly dose-dependent increase in time to exhaustion was noted in mice receiving ginseng.2,8,18–20 In one study, the time to exhaustion was lengthened by up to 183% in the mice given ginseng 30 minutes before exercising compared with controls.8
Experimental animal studies indicated that much of the antifatigue action of ginseng was due to the stimulant effect of ginseng on the central nervous system (CNS). Stress coupled with ginseng ingestion induced alterations in energy metabolism during prolonged exercise.9,16–20
Ginseng has been shown to improve locomotor activity,21 modify electroencephalographic (EEG) tracings,16 improve metabolic activity in the CNS,22 and affect the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (discussed later), all of which could be largely responsible for ginseng’s antifatigue activity in mental and physical performance. The CNS activity of ginseng is essentially different from that of usual stimulants. Although stimulants are active under most situations, ginseng reveals its stimulatory action only with the challenge of stress.22
On the physical level, ginseng’s antifatigue properties appear to be closely related to its ability to spare glycogen utilization in exercising muscle.9 Exercise physiologists clearly established that during prolonged exercise, the development of fatigue is closely related to the depletion of glycogen stores and the buildup of lactic acid, both in skeletal muscle and in the liver. If an adequate supply of oxygen is available to the working muscle, nonesterified fatty acids are the preferential energy substrate, thus sparing utilization of muscle glycogen, blood glucose, and, consequently, liver glycogen. The greater the ability to conserve body carbohydrate stores through mobilization and oxidizing of fatty acids, the greater the amount of time to exhaustion. Ginseng enhances fatty acid oxidation during prolonged exercise, thereby sparing muscle glycogen stores.9
Mental and physical antifatigue activity effects were demonstrated in both animal studies and double-blind clinical trials in humans. In one double-blind clinical study, nurses who switched from day to night duty rated themselves for competence, mood, and general well-being, and were evaluated with an objective test of psychophysical performance, blood cell counts, and blood chemistry analysis. The group administered ginseng demonstrated higher scores in competence, mood parameters, and objective psychophysical performance than those who received a placebo.23
From a clinical standpoint, ginseng’s antifatigue properties may be useful whenever fatigue or lack of vigilance is apparent. In particular, cancer patients who underwent chemotherapy, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and athletes were all shown to benefit from ginseng use. In regards to COPD, in one double-blind study, 92 adults with COPD were randomly assigned to receive either ginseng or placebo.24 Pulmonary function tests, maximum voluntary ventilation, maximum inspiratory pressure, and maximal oxygen consumption were studied before treatment and every 2 weeks for the 3-month study. In the ginseng group, but not in the control group, all parameters were significantly higher than baseline and higher than the parameters in the placebo group. Maximum increases, in comparison with baseline, were forced vital capacity 32.5%, forced expiratory volume1.0 27.0%, maximum voluntary ventilation 40.4%, maximum inspiratory pressure 47.0%, and maximal oxygen consumption 37.5%. No side effects were observed.
In a large study in 290 cancer patients, subjects were randomized in a double-blind manner to receive American ginseng in doses of 750, 1000, or 2000 mg/day or placebo given in twice daily dosing over 8 weeks. Over twice as many patients on ginseng perceived a benefit and were satisfied with treatment over those on placebo.25 In another double-blind trial, 53 cancer patients were randomly assigned to receive ginseng (3000 mg/day) or placebo for 12 weeks. Quality of life was assessed using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Assessment-BREF (WHOQOL-BREF) and the General Health Questionnaire-12.26 After 12 weeks of therapy, the “psychological domain ” score of the WHOQOL-BREF was significantly improved in patients randomized to ginseng, compared with those randomized to placebo. There was a tendency for ginseng to improve the “physical health” and “environment” domain scores of the WHOQOL-BREF, compared with placebo. The General Health Questionnaire-12 total score was significantly improved in patients treated with ginseng than in those with placebo. These results from clinical trials indicate ginseng is of benefit in improving some aspects of mental and physical functioning in cancer patients.
Cognitive Performance
Standardized extracts of P. ginseng alone or in combination with Ginkgo biloba (a formula called Gincosan) were shown to improve cognitive performance in animal and clinical studies.27–36 In one of the earlier studies (a double-blind, crossover design) in university students in Italy, ginseng extract alone was compared with placebo in various tests of psychomotor performance. A favorable effect of ginseng relative to baseline performance was observed in attention (cancellation test), mental arithmetic, logical deduction, integrated sensorimotor function (choice reaction time), and auditory reaction time. However, statistically significant superiority of the ginseng group over the placebo group was noted only for mental arithmetic. It was interesting to note that during the course of the trial, the students taking ginseng reported a greater sensation of well-being.29 Later studies in college-aged students showed similar results with a clear dose dependency.30–32 However, unlike studies in older subjects, no positive effect on mood or quality of life has yet been demonstrated with ginseng administered to healthy young adults.
The benefits of ginseng on cognitive performance, mood, and quality of life assessment are considerably greater in middle-aged adults than in younger adults. In several studies of the administration of ginseng alone or in combination with G. biloba extract, significant improvements were noted, not only in tests of cognition and memory, but also in social functioning and mental health.33–35 In one study, however, the results attenuated after 4 weeks of use, indicating that cotherapy with G. biloba may be more efficacious or that cycling of the ginseng dosage may be necessary to produce a prolonged effect.35
Both G. biloba and P. ginseng have been shown to modulate aspects of cognitive performance, including effects on EEG recordings. One double-blind, placebo-controlled, balanced crossover experiment assessed, in 15 healthy volunteers, the effects of single doses of G. biloba extract (360 mg), a proprietary P. ginseng extract (200 mg G115), and an identical placebo on auditory-evoked potentials, contingent negative variation, and resting power within the δ, θ, α, and β wavebands.36 The results showed that ginseng use led to a significant shortening of the latency of the P300 component of the evoked potential. Both ginseng and ginkgo also led to significant reductions in frontal “eyes closed” θ and β activity, with additional reduction for ginseng in the α waveband. These findings demonstrated for the first time that P. ginseng can directly modulate EEG activity, and that these effects are more pronounced than those that follow ingestion of G. biloba. Additional studies with G115 also showed an ability to enhance cognitive function in normal subjects.37–39
In regards to improving cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), there appears to be some benefit based upon the results from an open label study.40 In the study, consecutive AD patients were randomly assigned to the ginseng (n = 58) or the control group (n = 39), and the ginseng group was treated with P. ginseng powder (4.5 g/day) for 12 weeks. Cognitive performances were monitored using the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Alzheimer’s disease assessment scale (ADAS) during 12 weeks of the ginseng treatment and for 12 weeks after the ginseng discontinuation. MMSE and ADAS scales showed no baseline difference between the groups. After ginseng treatment, the cognitive subscale of ADAS and the MMSE scores began to show improvements and continued up to 12 weeks. After discontinuing ginseng, the improved ADAS and MMSE scores declined to the levels of the control group. These results suggest that P. ginseng is clinically effective in the cognitive performance of AD patients.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree