Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Fifth Metatarsal Fractures
Patient Selection
Indications
Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) indicated for proximal fifth metatarsal fractures in zone II (Jones fractures) or zone III (stress fractures)
Particularly indicated in setting of delayed union of fracture treated nonsurgically and for acute fracture in athlete
Contraindications
Skin compromise, active infection on surgical foot, vascular insufficiency, immunocompromised patients, neuropathy, patients with varus heel, and tendency for lateral foot overload
For varus heel, consider ORIF with concomitant correction of hindfoot malalignment, surgically or with orthoses
Preoperative Imaging
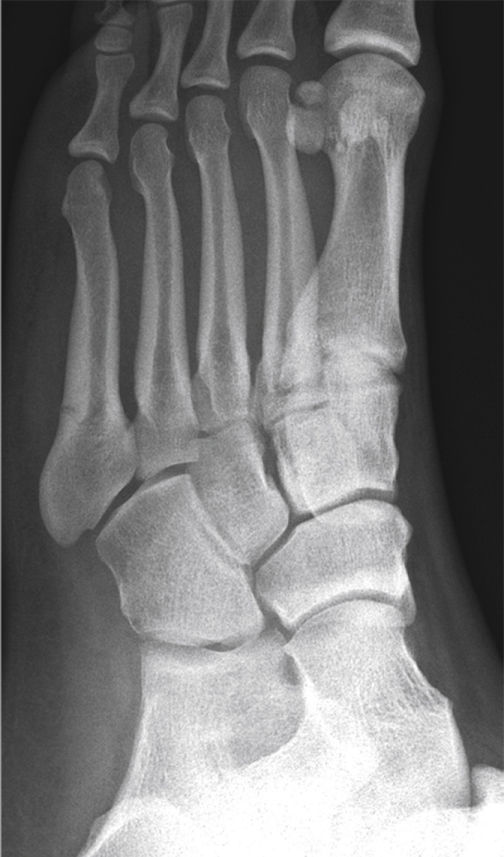
Figure 1Non–weight-bearing oblique radiograph shows the foot of a 22-year-old college athlete with a zone II base-of-the-fifth-metatarsal fracture (Jones fracture). Note that the subtle fracture extends into the articulation between the fourth and fifth metatarsal bases, thus designating this fracture as a zone II injury.
AP, oblique, lateral plain radiographs (Figure 1)
CT, MRI rarely indicated
Procedure
Room Setup/Patient Positioning
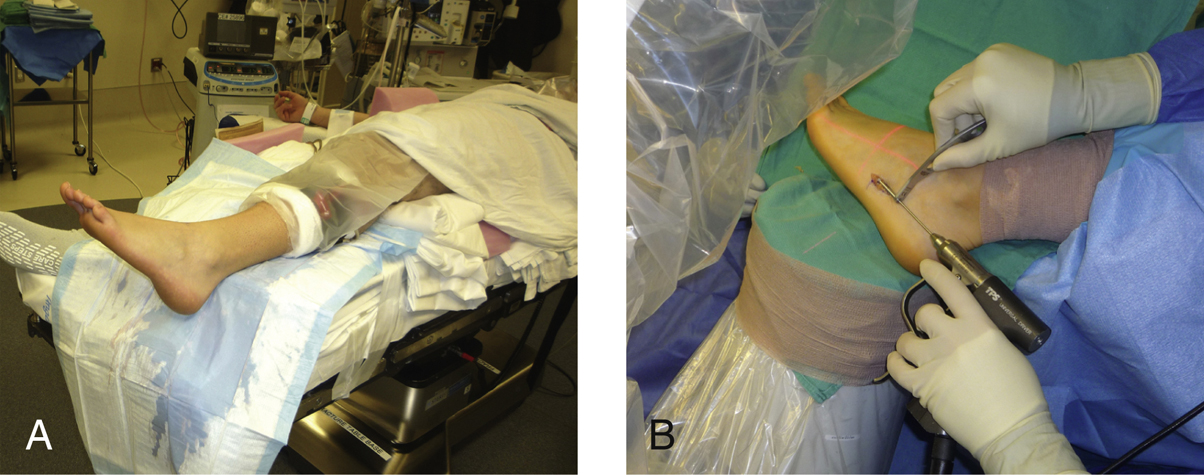
Figure 2Intraoperative photographs show patient positioning for open reduction and internal fixation of a proximal fifth metatarsal fracture. A, The patient is positioned on the edge of the operating table with support under the ipsilateral hip and lower leg, allowing satisfactory access to the base of the fifth metatarsal. B, The fluoroscopy unit may easily be positioned adjacent to the table so that it can serve as a lateral extension to the operating table, to support the surgical foot during the fluoroscopic portions of the procedure.
Supine position with bump under ipsilateral hip; foot at edge of table (Figure 2)
May use calf or ankle tourniquet; place distal to fibular head to avoid pressure on common peroneal nerve
Special Instruments/Equipment/Implants
Fluoroscopy unit
Cannulated drill system
Graduated taps
Solid screws
Dedicated instrument and implant sets
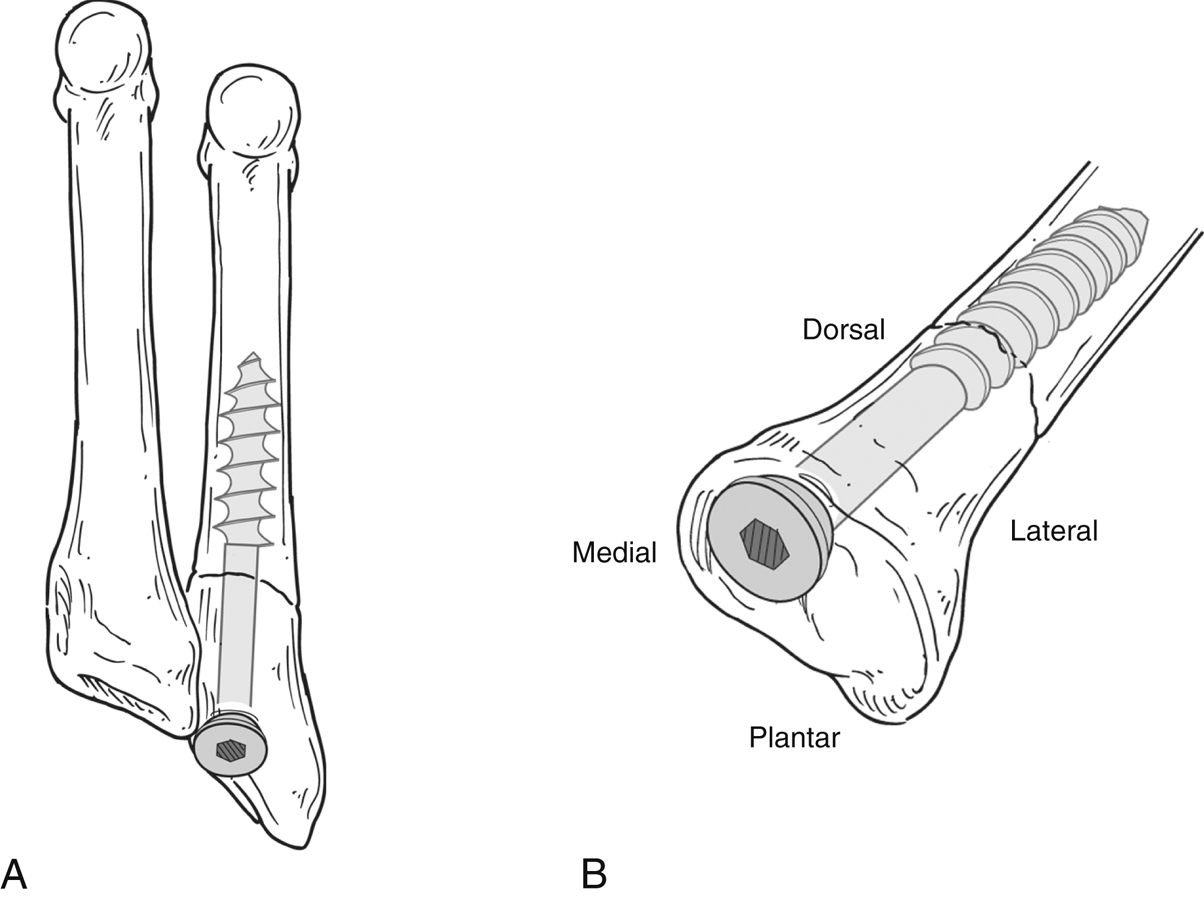
Intramedullary Screw Fixation
Intramedullary screw fixation is most widely used
Precontoured hooked plates may be used in cases of comminution, poor bone quality, revision
| Video 83.1 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Fifth Metatarsal Fracture Using Intramedullary Screw. Mark E. Easley, MD (9 min) |
Approach
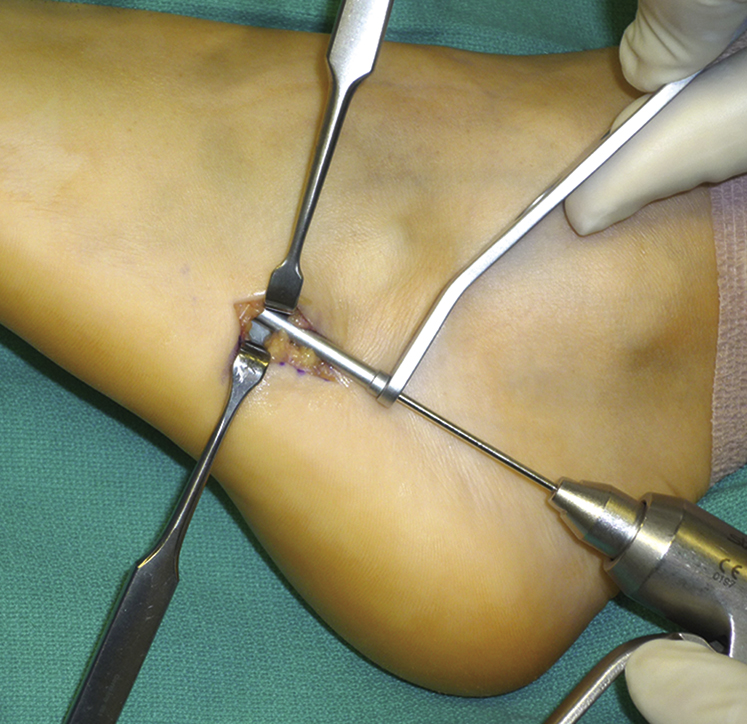
Figure 3Intraoperative photograph shows the surgical approach for open reduction and internal fixation of a proximal fifth metatarsal fracture. An incision is made approximately 1 to 2 cm proximal to the fifth metatarsal base, in line with the fifth metatarsal shaft. The assistant retracts the peroneus brevis tendon and sural nerve dorsally and the peroneus longus tendon plantarward, and the surgeon uses a protective sleeve for guide pin, drill, and tap.