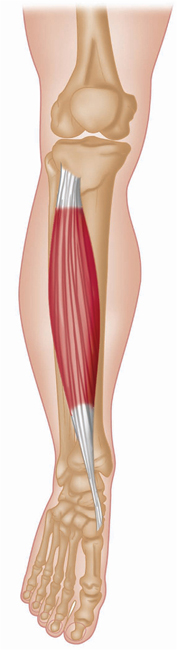
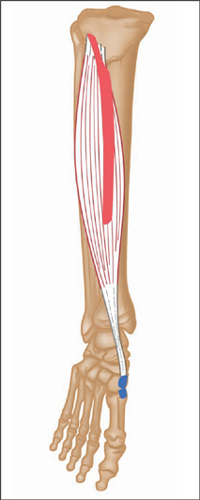
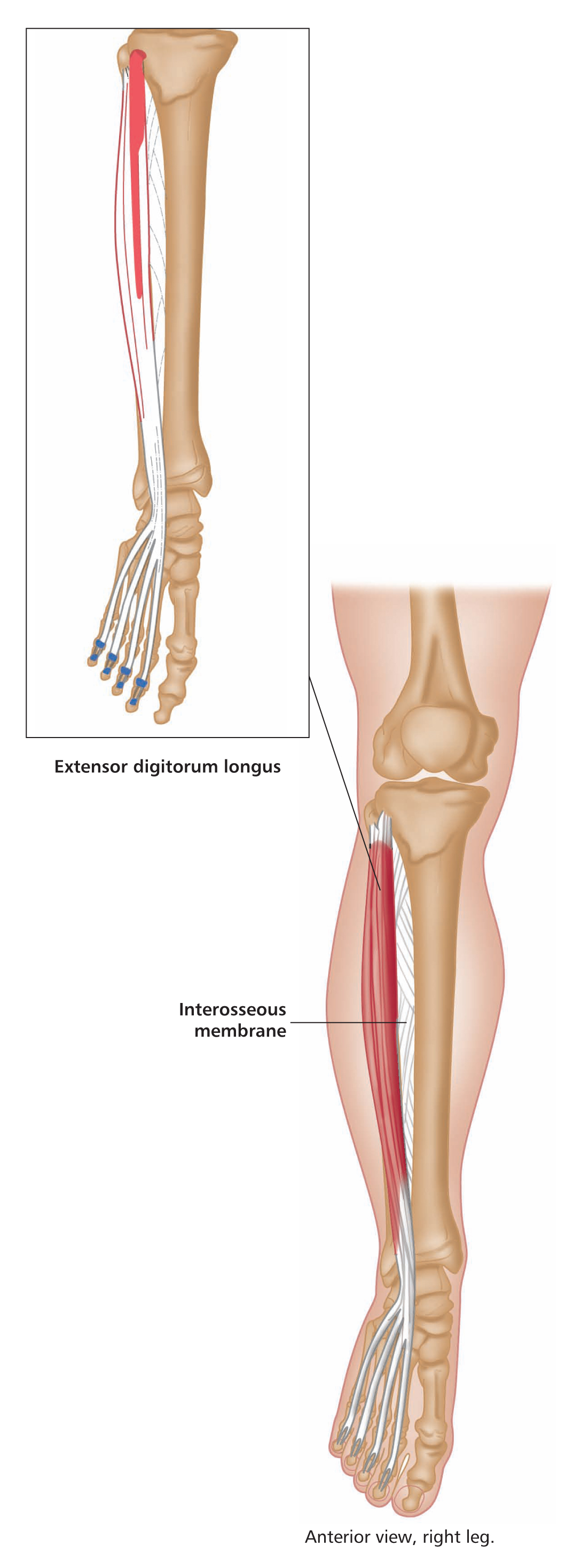
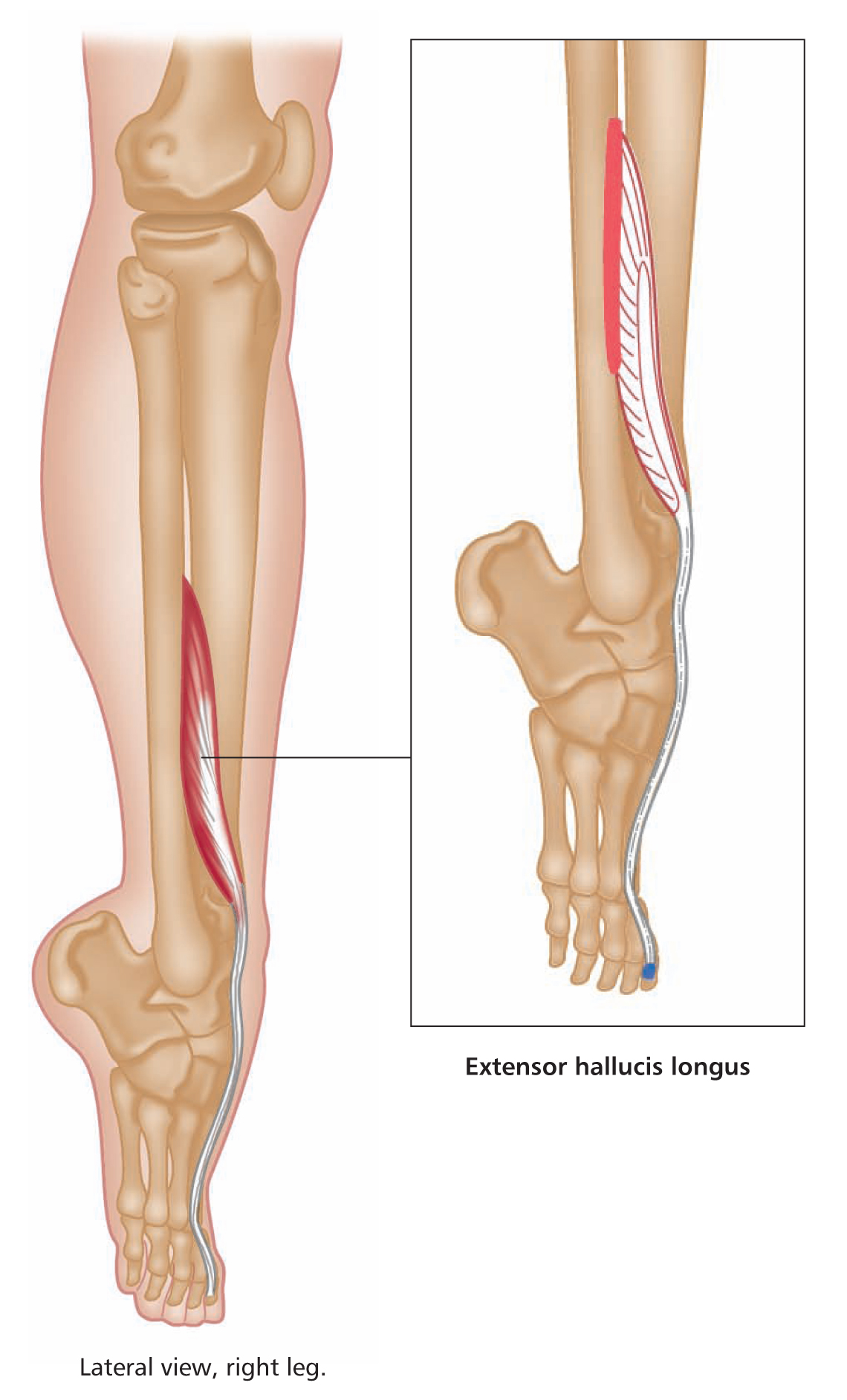
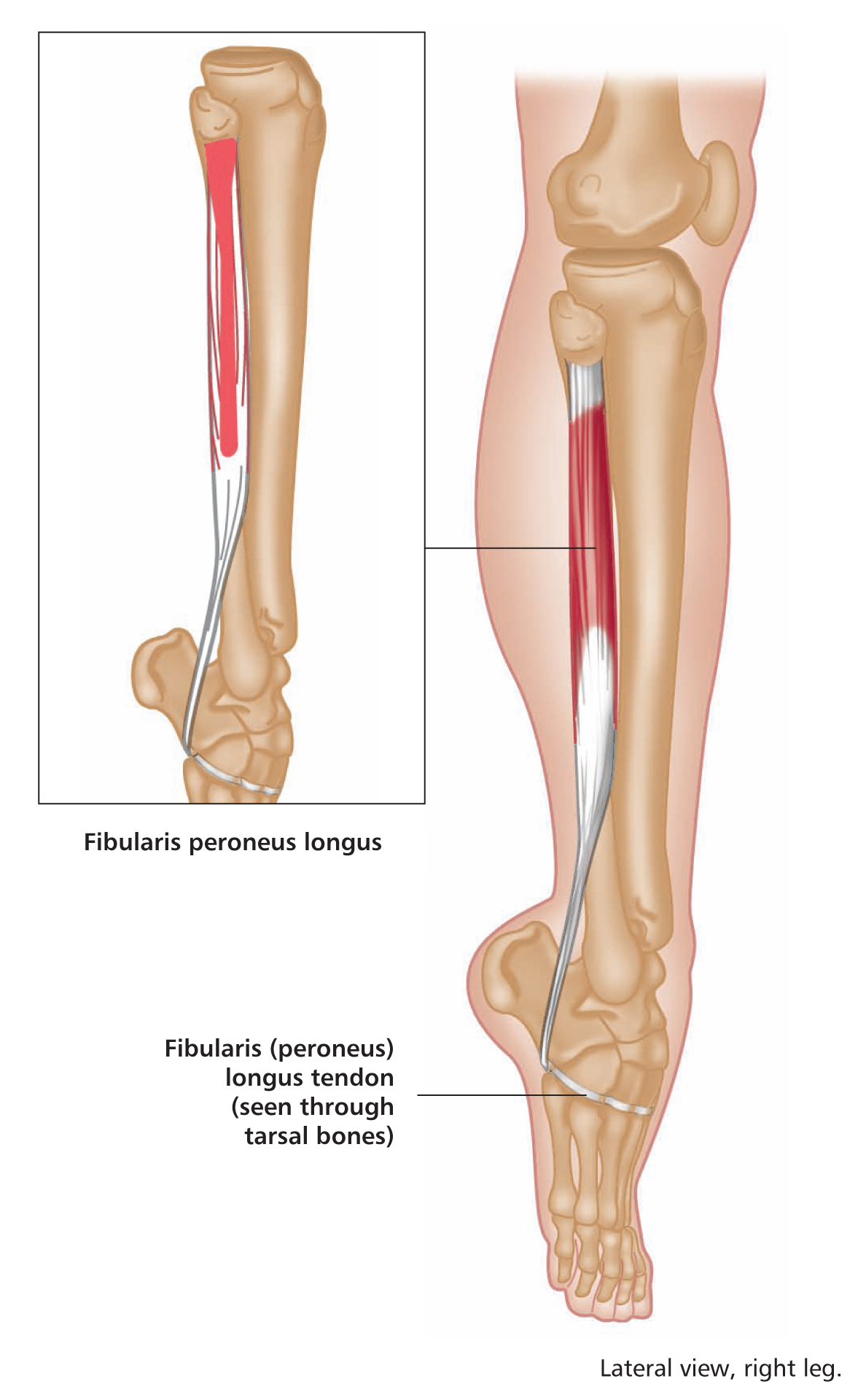
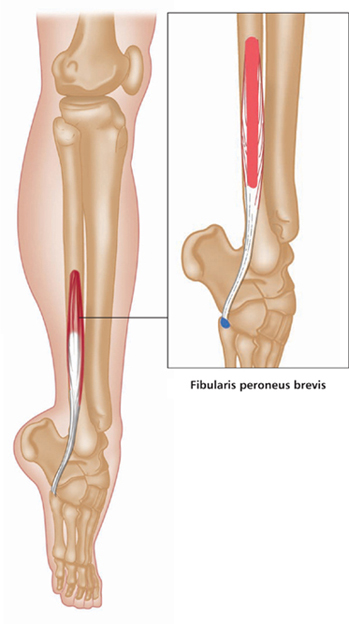
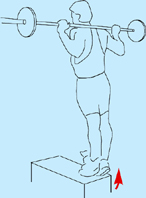
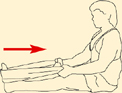
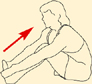
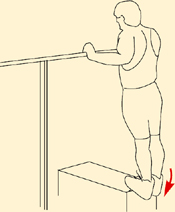
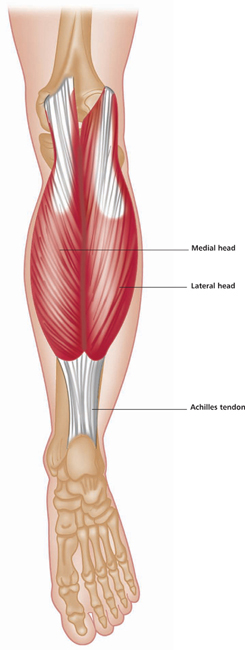
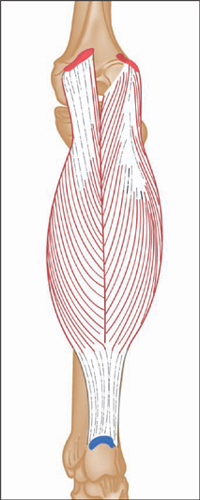
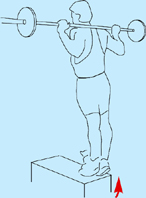
Anterior view, right leg. Latin, tibia, pipe or flute, shinbone; anterior, before. Origin Upper half of lateral and anterior surface of tibia (including lateral condyle of tibia). Insertion Medial edge of front of foot (medial cuneiform bone and base of first metatarsal). Action Dorsiflexes (lifts up) the foot. Inverts the foot. Nerve Deep peroneal nerve, L4, 5, S1. Basic functional movement Example: Walking and running (helps prevent the foot from slapping onto the ground after the heel strikes. Lifts the foot clear of the ground as the leg swings forward). Sports that heavily utilise this muscle Examples: Hill walking. Mountaineering. Running. Breast stroke swimming. Cycling (the pedal up phase). Movements or injuries that may damage this muscle Excessive jumping onto hard surfaces. Strengthening exercises Toe raise Quads knee extension Self stretches Latin, extensor, to extend; digit, toe; hallux, great toe; longus, long. Like the corresponding tendons in the hand, the extensor digitorum longus forms extensor hoods on the dorsum of the proximal phalanges of the foot. These hoods are joined by the tendons of the lumbricales and extensor digitorum brevis, but not by the interossei. The extensor hallucis longus lies between and deep to tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus. Origin Anterior surface of fibula and interosseous membrane (fibrous tissue between the tibia and fibula). Extensor digitorum longus also arises from the lateral condyle (upper outer part) of tibia. Insertion Extensor digitorum longus: Phalanges of lateral four lateral toes. Extensor hallucis longus: Distal phalanx of great toe. Action Extensor digitorum longus: Extends toes. Dorsiflexes ankle joint and everts foot. Extensor hallucis longus: Extends great toe. Dorsiflexes ankle joint and inverts foot. Nerve Fibular (peroneal) nerve, L4, 5, S1. Basic functional movement Walking up the stairs (ensuring the toes clear the steps). Sports that heavily utilise these muscles Examples: Hill walking. Mountaineering. Breast stroke swimming. Cycling (the pedal up phase). Movements or injuries that may damage these muscles Tendon easily bruised by compression (e.g. if toe is stepped on). Strengthening exercise Toe raise Self stretches Plantar view, right leg. Latin, fibula, pin / buckle; longus, long; brevis, short. The course of the tendon of insertion of fibularis longus helps maintain the transverse and lateral longitudinal arches of the foot. A slip of muscle from fibularis brevis often joins the long extensor tendon of the little toe, whereupon it is known as peroneus digiti minimi. Fibularis tertius is a partially separated lower lateral part of extensor digitorum longus. Origin Longus: Upper two-thirds of lateral surface of fibula. Brevis: Lower two-thirds of lateral surface of fibula. Insertion Longus: Base of first metatarsal. Brevis: Base of fifth metatarsal. Action Everts the foot. Assists plantar flexion of ankle joint (i.e. points the foot). Nerve Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve, L4, 5, S1. Basic functional movement Example: Walking on uneven surfaces. Sports that heavily utilise these muscles Examples: Running. Soccer. Jumping. Movements or injuries that may damage these muscles Forced inversion of the ankle (i.e. overstretching the lateral aspect of the ankle) may create chronic problems with ankle joint stability. Strengthening exercises Calf raise (standing heel raise) Calf raise (seated heel raise) Self stretches Stretch increases dorsiflexion rather than inversion. Posterior view, right leg. Greek, gaster, stomach; kneme, leg. Gastrocnemius is part of the composite muscle known as triceps surae, which forms the prominent contour of the calf. The triceps surae comprises: gastrocnemius, soleus and plantaris. The popliteal fossa at the back of the knee is formed inferiorly by the bellies of gastrocnemius and plantaris, laterally by the tendon of biceps femoris, and medially by the tendons of semimembranosus and semitendinosus. Origin Medial head: Lower posterior surface of femur above medial condyle. Lateral head: Lateral condyle and lower posterior surface of femur. Insertion Posterior surface of calcaneus (heel bone) via the calcaneal tendon (Achilles tendon); which is a fusion of the tendons of gastrocnemius and soleus. Action Plantar flexes (points) foot at ankle joint. Assists in flexion of knee joint. It is a main propelling force in walking and running. Nerve Tibial nerve, S1, 2. Basic functional movement Standing on ‘tip-toes’. Sports that heavily utilise this muscle Examples: Most sports requiring running and jumping, esp. sprinting, high jump, long jump, volleyball, basketball. Ballet. Push off in the swim start. Trampoline. Movements or injuries that may damage this muscle Explosive jumping, or landing badly when jumping down, may rupture the tendocalcaneous (Achilles tendon) at its junction with the muscle belly. Common problems when muscle is chronically tight / shortened Constant wearing of high-heeled shoes tends to cause this muscle to shorten, which can effect postural integrity. Strengthening exercises





![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Muscles of the Leg and Foot






