
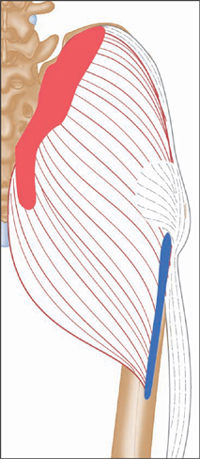
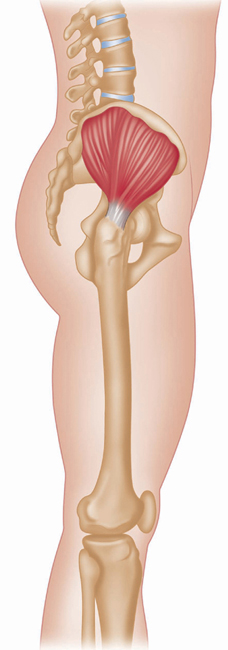
Posterior view, right leg.
Greek, gloutos, buttocks; maximus, biggest.
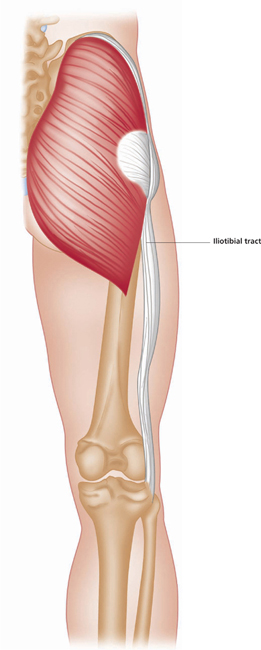
The gluteus maximus is the most coarsely fibred and heaviest muscle in the body, forming the bulk of the buttock.
Origin
Outer surface of ilium and posterior surface of sacrum and coccyx (over sacroiliac joint).
Insertion
Upper posterior area of femur. Iliotibial tract (long tendon) of fascia lata muscle.
Action
Extends and laterally rotates hip joint (forceful extension as in running or rising from sitting). Extends trunk. Assists in adduction of hip joint.
Nerve
Inferior gluteal nerve, L5, S1, 2.
Basic functional movement
Examples: Walking upstairs. Rising from sitting.
Sports that heavily utilise this muscle
Examples: Running. Surfing. Wind surfing. Jumping. Weightlifting (‘clean’ phase, i.e. lifting weights up from floor).
Strengthening exercises
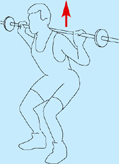
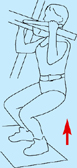
Squats
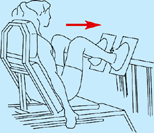
Seated leg press
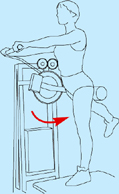
Multi-hip machine (cable hip extension / cable kick-back)
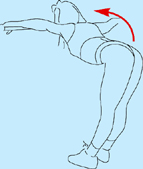
Good morning exercise
Self stretches
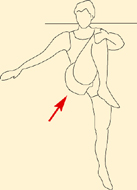
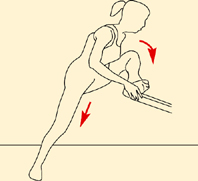
In lying, pull knee to opposite shoulder. Avoid after pregnancy due to stress on pelvis.

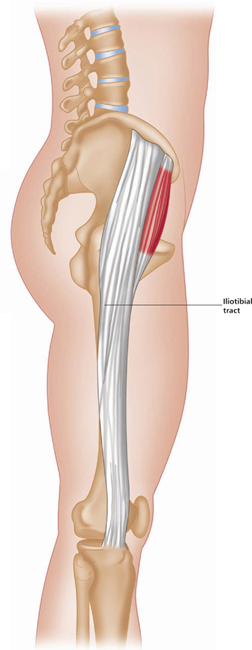
Lateral view, right leg.
Latin, tensor, a stretcher; fasciae, band(s); latae, broad.
This muscle lies anterior to gluteus maximus, on the lateral side of the hip.
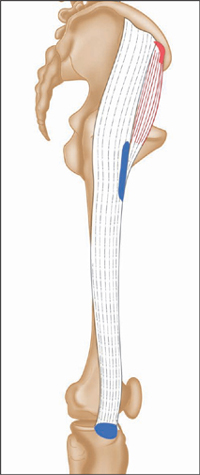
Origin
Outer edge of iliac crest, towards the front.
Insertion
Joins iliotibial tract (long fascia lata tendon) just below the hip, which runs to the upper lateral side of the tibia.
Action
Flexes, abducts and medially rotates the hip joint. Tenses the fascia lata, thus stabilizing the knee.
Nerve
Superior gluteal nerve, L4, 5, S1.
Basic functional movement
Example: Walking.
Sports that heavily utilise this muscle
Examples: Horse riding. Hurdling. Water skiing.
Common problems when muscle is chronically tight / shortened
Pelvic imbalances, leading to pain in hips, lower back and lateral area of knees.
Strengthening exercises
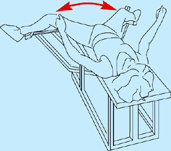
Abductor machine
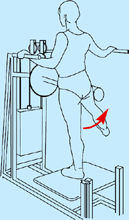
Multi-hip machine (cable hip abduction)
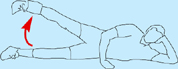
Hip abduction
Self stretches
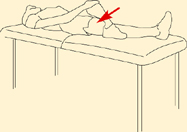
Hand on knee and pull across body.
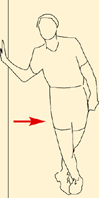
Push your hips away from the wall.


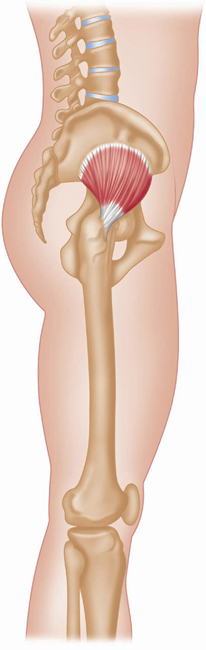
Lateral view, right leg.
Greek, gloutos, buttocks; medius, middle.
This muscle is mostly deep to and therefore obscured by gluteus maximus, but appears on the surface between gluteus maximus and tensor fasciae latae. During walking, this muscle, with gluteus minimus, prevents the pelvis from dropping towards the non weight-bearing leg.
Origin
Upper outer surface of ilium.
Insertion
Lateral surface of greater trochanter (top) of femur.
Action
Abducts the hip joint. Anterior fibres medially rotate the hip joint. Posterior fibres slightly laterally rotate the hip joint.
Nerve
Superior gluteal nerve, L4, 5, S1.
Basic functional movement
Example: Stepping sideways over an object such as a low fence.
Sports that heavily utilise this muscle
Examples: All sports requiring side-stepping, esp. cross-country skiing, ice skating.
Common problems when muscle is chronically tight / shortened
Pelvic imbalances, leading to pain in hips, lower back and knees.
Strengthening exercises
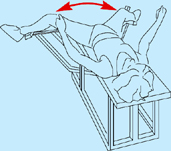
Abductor machine
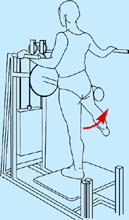
Multi-hip machine (cable hip abduction)
Self stretches
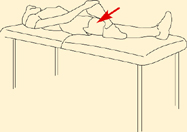
Hand on knee and pull across body.
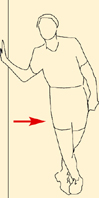
Push your hips away from the wall.

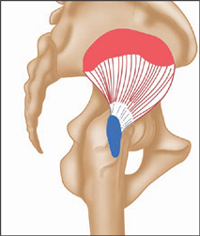
Lateral view, right leg.
Greek, gloutos, buttocks; minimus, smallest.
This muscle is situated deep to gluteus medius, whose fibres obscure it.
Origin
Middle outer surface of ilium, below origin of gluteus medius.
Insertion
Anterior border of greater trochanter (top) of femur.
Action
Abducts and medially rotates hip joint.
Nerve
Superior gluteal nerve, L4, 5, S1.
Basic functional movement
Example: Stepping sideways over an object such as a low fence.
Sports that heavily utilise this muscle
Examples: All sports requiring side-stepping, esp. cross-country skiing, ice skating.
Common problems when muscle is chronically tight / shortened
Pelvic imbalances, leading to pain in hips, lower back and knees.
Strengthening exercises
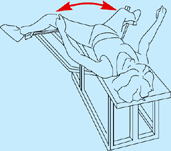
Abductor machine
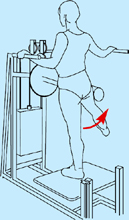
Multi-hip machine (cable hip abduction)
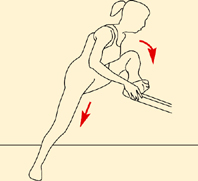
Self stretches
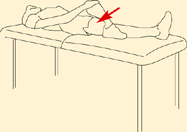
Hand on knee and pull across body.
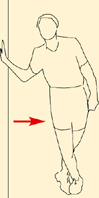
Push your hips away from the wall.