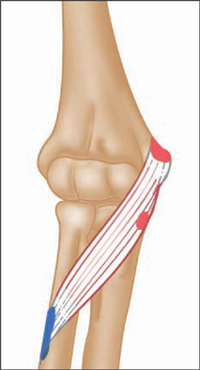
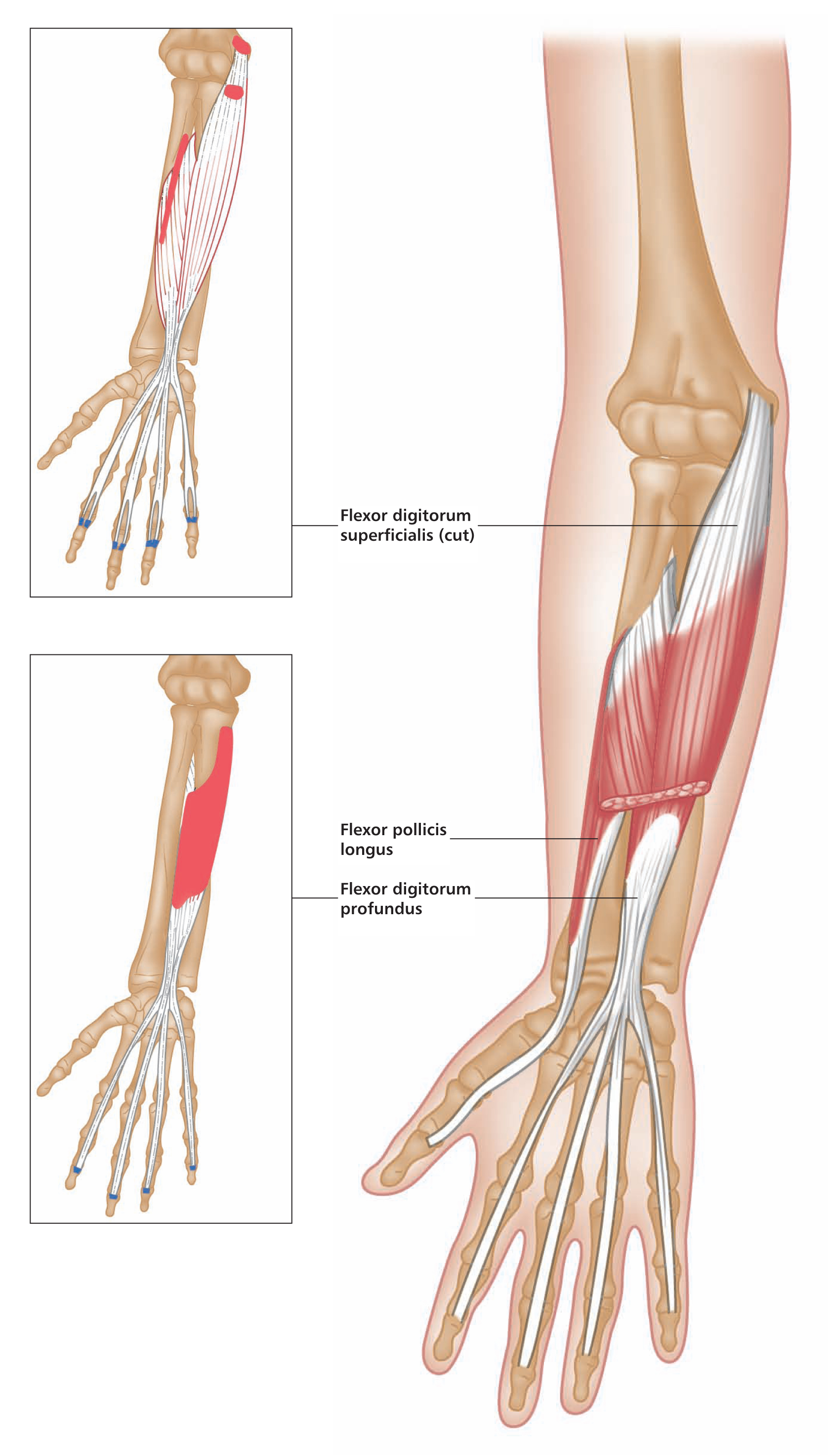
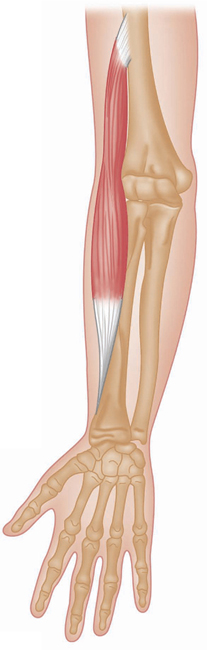
Anterior view, right arm. Latin, pronate, bent forward; teres, rounded, finely shaped. Origin Humeral head: Common flexor origin on the anterior aspect of the medial epicondyle of humerus, and area immediately above (i.e. lower medial end of humerus). Ulnar head: Coronoid process of the ulna (i.e. area on front of upper part of shaft of ulna). Insertion Middle of lateral surface of radius. Action Pronates forearm. Assists flexion of elbow joint. Nerve Median nerve, C6, 7. Basic functional movement Examples: Pouring liquid from a container. Turning a doorknob. Sports that heavily utilise this muscle Examples: Batting in cricket. Hockey dribbling. Volleyball smash. Strengthening exercise Pronation with strength bar Self stretch Weight of stick increases supination via gravity. Includes: flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris. Origin Common flexor origin on the anterior aspect of the medial epicondyle of humerus (i.e. lower medial end of humerus). Insertion Carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. Action Flex the wrist (flexor carpi radialis also abducts the wrist; flexor carpi ulnaris also adducts the wrist). Nerve Flexor carpi radialis: Median nerve, C6, 7, 8. Palmaris longus: Median nerve, C(6), 7, 8, T1. Flexor carpi ulnaris: Ulnar nerve, C7, 8, T1. Basic functional movement Examples: Pulling rope in towards you. Wielding an axe or hammer. Sports that heavily utilise these muscles Examples: Sailing. Water skiing. Golf. Baseball. Cricket. Volleyball. Movements or injuries that may damage these muscles Overextending the wrist resulting from breaking a fall with the hand. Common problems when muscles are chronically tight / shortened / overused Golfer’s elbow (overuse tendonitis of common flexor origin), carpal tunnel syndrome. Strengthening exercises Biceps curl Wrist rolling (palm up) Wrist curl Self stretches Use one hand to gently lever the other wrist into extension. Includes flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus. Origin Superficialis: Common flexor tendon on medial epicondyle of humerus. Coronoid process of ulna. Anterior border of radius. Profundus: Medial and anterior surfaces of the ulna. Insertion Superficialis: Sides of the middle phalanges of the four fingers. Profundus: Base of distal phalanges. Action Superficialis: Flexes the middle phalanges of each finger. Can help flex the wrist. Profundus: Flexes distal phalanges (the only muscle able to do so). Nerve Superficialis: Median nerve, C7, 8, T1. Profundus: Medial half of muscle, ulnar nerve, C7, 8, T1. Lateral half of muscle, median nerve, C7, 8, T1. Sometimes the ulnar nerve supplies the whole muscle. Basic functional movement Examples: ‘Hook grip’, as in carrying a briefcase. ‘Power grip’, as in turning a tap. Typing. Playing the piano and some stringed instruments. Sports that heavily utilise these muscles Examples: Archery. Maintaining grip in racket and batting sports. Judo. Rowing. Rock-face climbing. Movements or injuries that may damage these muscles Overextending the wrist resulting from breaking a fall with the hand. Common problems when muscles are chronically tight / shortened / overused Golfer’s elbow (overuse tendonitis of common flexor origin). Carpal tunnel syndrome. Strengthening exercises Biceps curl Chin-ups Exer. ring finger flexion Self stretch Gently pull each finger in turn into extension. Anterior view, right arm. Latin, brachial, relating to the arm; radius, staff, spoke of wheel. The brachioradialis forms the lateral border of the cubital fossa. The muscle belly is prominent when working against resistance. Part of the superficial group. Origin Upper two-thirds of the anterior aspect of lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus (i.e. lateral part of shaft of humerus, 5–7.5cms (2–3″) above elbow joint). Insertion Lower lateral end of radius, just above the styloid process. Action Flexes elbow joint. Assists in pronating and supinating forearm when these movements are resisted. Nerve Radial nerve, C5, 6. Basic functional movement Example: Turning a cork screw. Sports that heavily utilise this muscle Examples: Baseball. Cricket. Golf. Racket sports. Rowing. Strengthening exercises Biceps curl Chin-ups Upright rowing Self stretch Pronate and supinate forearm. Posterior view, right arm. Latin, supinus, lying on the back. Part of the deep group. Supinator is almost entirely concealed by the superficial muscles. Origin Lower lateral end of humerus (lateral epicondyle) and upper lateral end of ulna, and associated ligaments. Insertion Dorsal and lateral surfaces of upper third of radius. Action Supinates forearm. Nerve Deep radial nerve, C5, 6, (7). Basic functional movement Examples: Turning a door handle, or screwdriver. Sports that heavily utilise this muscle Example: Backhand in racket sports. Strengthening exercise

























![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Muscles of the Forearm and Hand






