
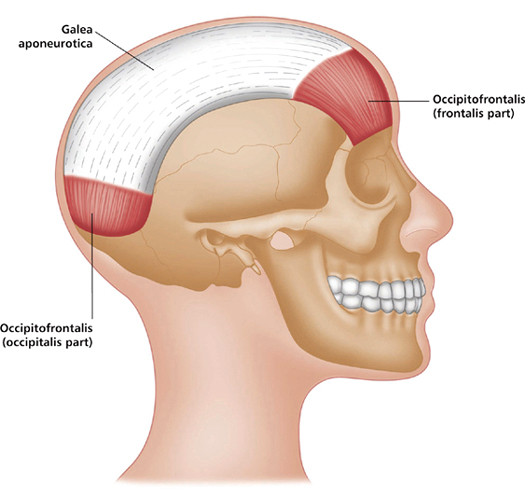
Greek, epi-, above, upon; cranium, skull.
This muscle is effectively two muscles (occipitalis and frontalis), united by an aponeurosis called the galea aponeurotica, so named because it forms what resembles a helmet upon the skull.
Origin
Occipitalis: Occipital bone. Mastoid process of temporal bone.
Frontalis: Galea aponeurotica.
Insertion
Occipitalis: Galea aponeurotica (a sheet-like tendon leading to frontal belly).
Frontalis: Fascia and skin above eyes and nose.
Action
Occipitalis: Pulls scalp backward.
Frontalis: Pulls scalp forwards.
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve.
Basic functional movement
Example: Raises eyebrows (wrinkles skin of forehead horizontally).

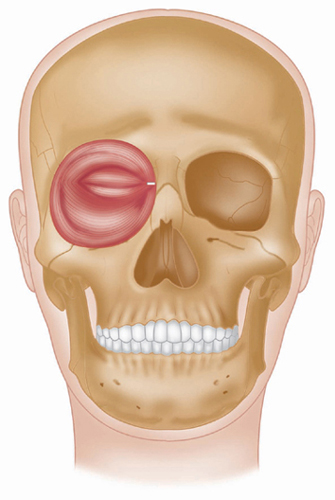
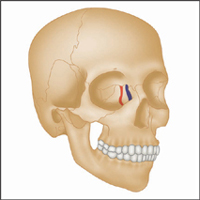
Lacrimal part
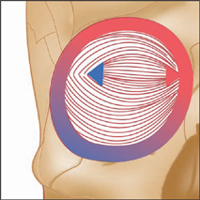
Orbital and palpebral part
Latin, orbis, orb, circle; oculi, of the eye.
This complex and extremely important muscle consists of three parts, which together form an important protective mechanism surrounding the eye.
Origin
Frontal bone. Medial wall of orbit (on maxilla).
Insertion
Circular path around orbit, returning to origin.
Action
Strongly closes eyelids (firmly ‘screws up’ the eye).
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve (temporal and zygomatic branches).
(in eyelids)
Latin, pertaining to an eyelid.
Origin
Medial palpebral ligament.
Insertion
Lateral palpebral ligament into zygomatic bone.
Action
Gently closes eyelids (and comes into action involuntarily, as in blinking).
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve (temporal and zygomatic branches).
(behind medial palpebral ligament and lacrimal sac)
Latin, pertaining to the tears.
Origin
Lacrimal bone.
Insertion
Lateral palpebral raphe.
Action
Dilates lacrimal sac and brings lacrimal canals onto surface of eye.
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve (temporal and zygomatic branches).

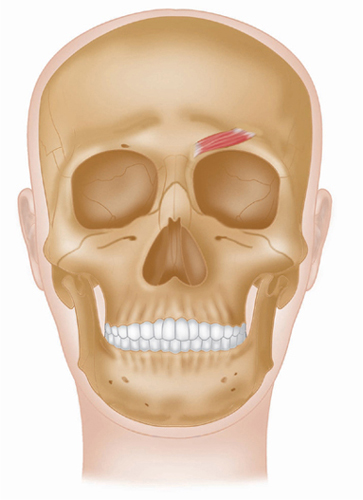
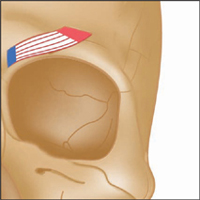
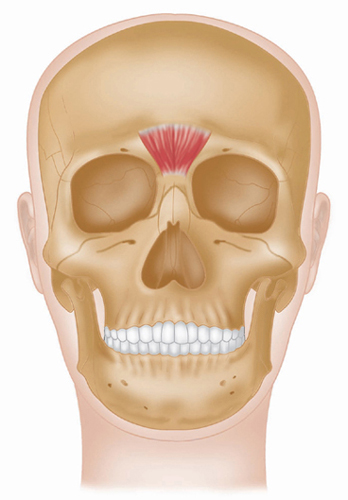
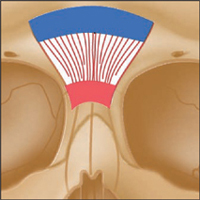
Latin, corrugator, muscle which wrinkles; supercilii, of the eyebrow.
Origin
Medial end of supercilliary arch of frontal bone.
Insertion
Deep surface of skin under medial half of the eyebrows.
Action
Draws eyebrows medially and downward, so producing vertical wrinkles, as in frowning.
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve (temporal branch).
Basic functional movement
Facilitates facial expression.

Latin, long, slender.
Origin
Fascia over nasal bone. Lateral nasal cartilage.
Insertion
Skin between eyebrows.
Action
Wrinkles nose. Pulls medial portion of eyebrows downwards.
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve.
Basic functional movement
Example: Enables strong ‘sniffing’ and sneezing.

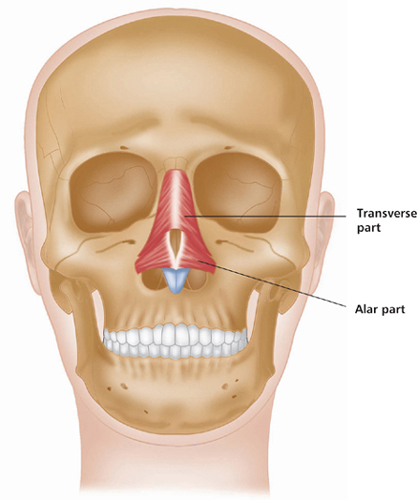
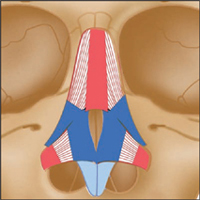
Latin, nasus, nose.
Origin
Middle of maxilla (above incisor and canine teeth). Greater alar cartilage. Skin on nose.
Insertion
Joins muscle of opposite side across bridge of nose. Skin at tip of nose.
Action
Maintains opening of external nares during forceful inhalation (i.e. flares the nostrils).
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve (buccal branches).
Basic functional movement
Example: Strongly breathing in through the nose.

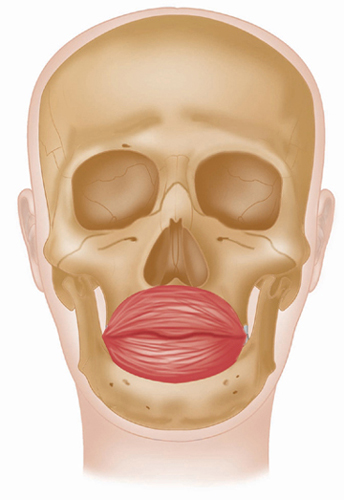
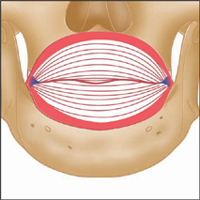
Latin, orbis, orb, circle; oris, pertaining to the mouth.
This is a composite sphincter muscle that encircles the mouth. It receives fasciculi from many other muscles.
Origin
Muscle fibres surrounding the opening of mouth, attached to the skin, muscle and fascia of the lips and surrounding area.
Insertion
Skin and fascia at corner of mouth.
Action
Closes lips, compresses lips against teeth, protrudes (purses) lips, and shapes lips during speech.
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve (buccal and mandibular branches).
Basic functional movement
Facial expressions involving the lips.

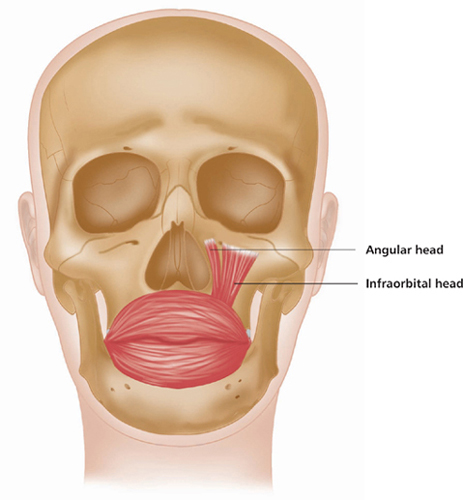
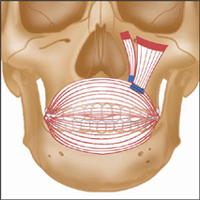
Latin, levare, to raise; labium, lip; superioris, above.
Origin
Angular head: Zygomatic bone and frontal process of maxilla. Infraorbital head: Lower border of orbit.
Insertion
Angular head: Greater alar cartilage, upper lip and skin of nose. Infraorbital head: Muscles of upper lip.
Action
Raises upper lip. Dilates nares. Forms nasolabial furrow.
Nerve
Facial V11 nerve (buccal branches).
Basic functional movement
Facilitates facial expression and kissing.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








