Sterile Instruments/Equipment
- Small pointed bone reduction clamps (Weber clamps)
- Shoulder hook, dental picks, and Freer elevators
- Finger traps and Mastasol for traction
- Implants
- 0.062 inch K-wires
- Mini-fragment plates and screws (2.0 and 2.4 mm)
- 0.062 inch K-wires
- K-wire driver/drill
Positioning
- Supine on radiolucent table.
- Place a small bump under ipsilateral hip so that the patella faces anteriorly.
- Use tibial nailing triangle turned long-side down to get good AP and oblique views of midfoot.
- C-arm should enter from opposite side of the table.
- Alternatively, flex knee to 90 degrees over a tibial nailing triangle. With the fluoroscopic beam perpendicular to floor, five folded towels under the forefoot gives a good view and a stable platform for reduction and pin placement (Fig. 24-1).
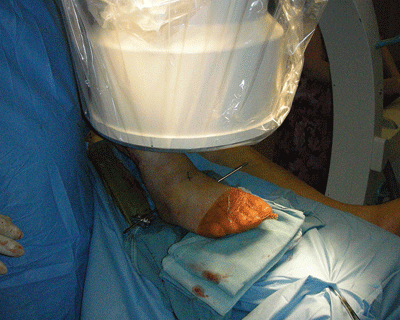
Figure 24-1. Five folded towels under the forefoot with the fluoroscopic beam perpendicular to the floor gives good visualization of the forefoot.
![]()
- The C-arm angle is often best determined on a lateral view so that the beam for AP and oblique images are oriented perpendicular to the metatarsal necks and shafts.
- Roll the foot between AP and oblique views to determine both mediolateral and dorsal-plantar K-wire vectors.
Surgical Approaches
- Percutaneous reduction and pinning
- Strategically placed small incisions for reduction instruments and K-wires.
Reduction and Implant Techniques
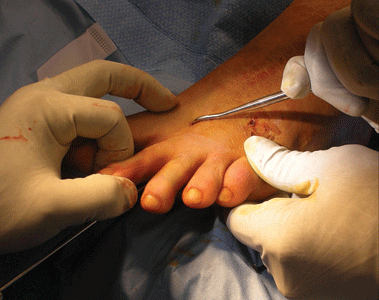
- Pull toe axially, and manipulate medially or laterally depending on the fracture obliquity and displacement (Fig. 24-2).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






