10 Lateral Retractor Systems
10.1 Introduction
Of the various minimally invasive surgery (MIS) approaches, the lateral transpsoas approach has been extensively studied in regard to complications related to surgical exposure. During this approach, retraction systems traverse the psoas muscle, placing the psoas muscle and lumbar plexus at considerable risk of injury. Symptoms are typically transient and include thigh pain, groin pain, paresthesias, numbness, hip flexor weakness, and psoas spasm.1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 Avoidance of complications can be mediated by proper placement of tubular dilators and retraction systems. Additionally, the use of real-time neuromonitoring has reduced the incidence of neurologic injury via detection of nearby neural structures and subsequent adjustment of the approach by the surgeon.10,11
10.2 Lateral Retractor Systems
Table 10.1 DePuy Synthes INSIGHT® Lateral Access System
Retractor design | ||
Retractor system Expandable | Retractor apparatus Dual tubular blades | Design feature Bifurcated direct light source |
| ||
Specifications | ||
Blade winglets Length extension up to 10 mm Width extension up to 7 mm | Tubular blades Lengths: 80–180 mm (10-mm increments) Toeing: up to 20° angulation | Posterior disk anchor blade Lengths: 80–160 mm (10-mm increments) |
Procedure | ||
MIS LLIF, MIS decompression | ||
Radiographs unavailable | ||
Compatible device | ||
DePuy Synthes COUGAR® LS Lateral Cage System | ||
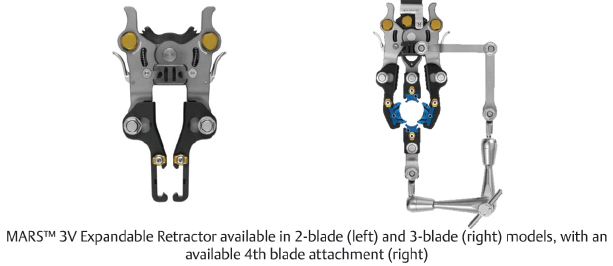
Table 10.2 Globus Medical MARS™ 3V Minimal Access Retractor System
Design | ||
Design feature 4th blade attachment, widening and lengthening shims to reduce muscle creep | Retractor system Expandable | Retractor apparatus Tubular blade |
| ||
Specifications | ||
Posterior and cephalad–caudal blade lengths 40–170 mm (10-mm increments) | Port composition Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | Angulation Up to 20° independent blade angulation |
Procedures | ||
MIS LLIF, MIS decompression | ||
Radiographs unavailable | ||