Chapter 2 The knee joint
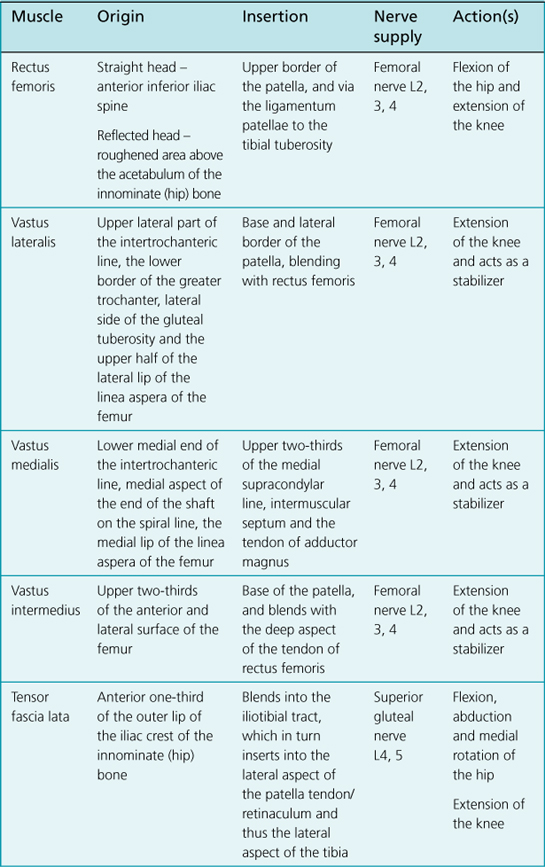
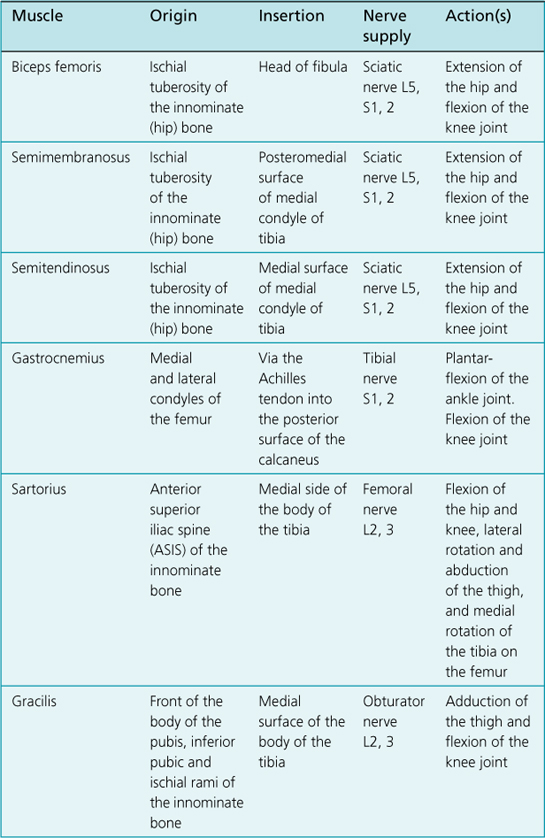
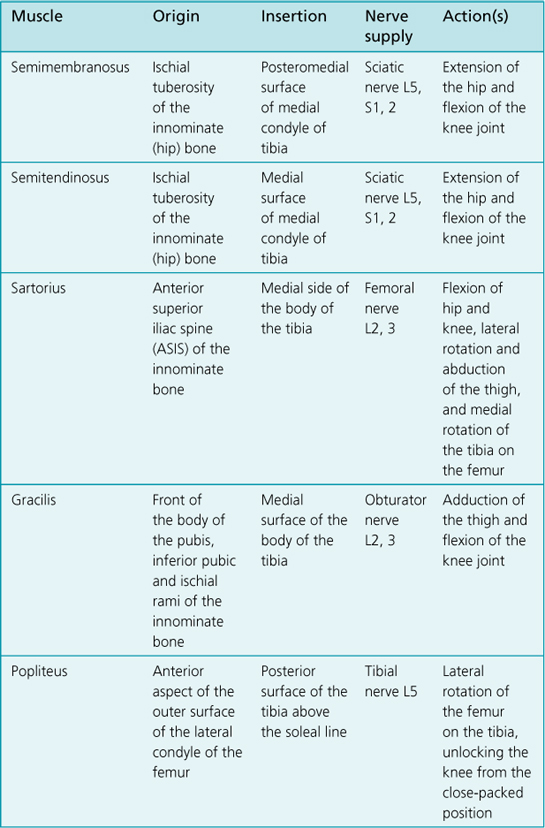
Anatomy
2. It comprises three separate articulations: two tibiofemoral joints and the patellofemoral articulation.
5. The capsular ligaments comprise oblique popliteal ligament, the arcuate popliteal ligament and the ligamentum patellae.
6. All hinge joints have collateral ligaments. The knee joint has the tibial (medial) and fibular (lateral) collateral ligaments.
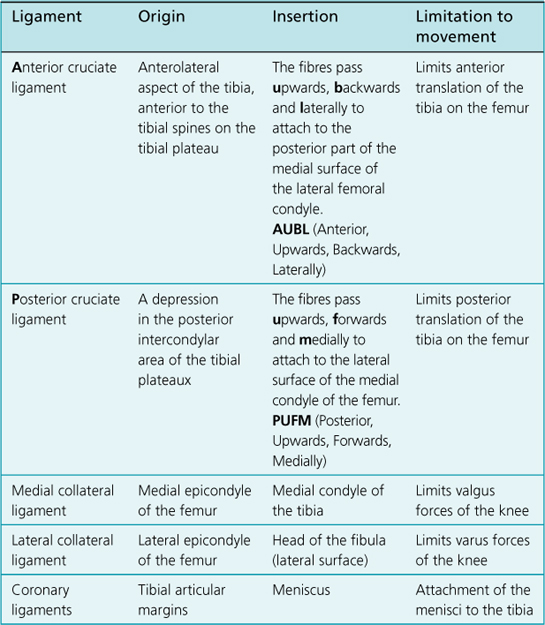
7. The intra-articular structures consist of the cruciate ligaments (anterior and posterior) and the menisci (medial and lateral).
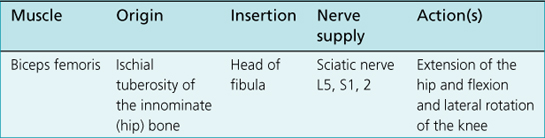
8. The movements that take place at the knee joint are: extension and flexion. When the knee is flexed, axial rotation of the leg can be performed. These movements consist of lateral (external) rotation of the tibia on the femur and medial (internal) rotation of the tibia on the femur.
Bony Landmarks to be Palpated
The femur – medial condyle, lateral condyle, lateral epicondyle, medial epicondyle and adductor tubercle.
Measurement
Range of Movement
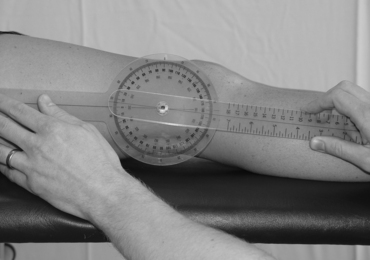
Extension
Stationary arm:
This is parallel to the longitudinal axis of the femur, pointing towards the greater trochanter of the femur.
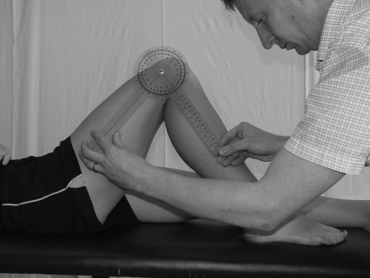
Flexion
Command to patient:
‘Bend your knee up towards you so that your heel moves towards your buttock as much as possible.’