K
keratitis inflammation of the cornea, the transparent part of the outer coat of the eyeball – the ‘window’ in front of the the iris and the pupil. Organisms do not usually infect an intact healthy cornea so this is more likely to occur when hygiene is poor, especially if contact lenses are worn. photokeratitis (also known as snowblindness) occurs as a result of excessive exposure to UV light, as when sunlight is reflected in snow and water sports. It can be very painful, may occur several hours after exposure and may last up to 2 days.
ketoacidosis decrease in pH of body fluids due to accumulation of ketone bodies (beta-hydroxybutyric acid, acetoacetic acid and acetone), products of the metabolism of fat. A complication of diabetes, because of non-availability to the tissues of glucose; also occurs in starvation and (rarely) in alcohol misuse. See also acidosis.
kidneys paired organs in the back of the abdomen. By filtration of water and small molecules from the blood flowing through the capillary complex of their glomeruli, they extract about 1/5 of the whole blood volume per minute, for passage into the tubules where, by selective reabsorption back into the blood, the quantity and content of the urine are regulated. By these means, under the influence of hormones they excrete waste substances and regulate electrolyte and acid–base balance, as well as blood volume, and the concentration of various substances in the blood. They also secrete renin and renal erythropoietic factor and are involved in vitamin D metabolism. See also appendix 5.
kinaesthesia the sense of movement of the body or body parts. Also known as kinaesthesis.
kinaesthetic imagery see imagery.
kinematic feedback see knowledge of performance.
kinematics the study (and measurement) of motion. angular kinematics the study of rotational motion. linear kinematics the study of motion which takes place in straight lines (rectilinear) or curves (curvilinear).
kinetic energy the energy possessed by a body or object due to movement. Can be translational or rotational (or both). translational kinetic energy the energy possessed by an object due to its movement along a straight or a curved line. May be calculated as ½ mv2 where m is the mass of the object and v is linear velocity. rotational kinetic energy the mechanical energy possessed by an object due to its rotation about an axis. May be calculated as ½ Iw2 where I is moment of inertia and w is angular velocity. Measured in joules (J).
kinetics the study (and measurement) of forces and moments (torques). linear kinetics the study of forces but not torques or moments. angular kinetics the study of torques or moments but not linear forces.
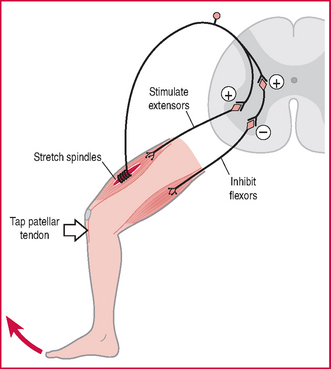
knee jerk reflex extension at the knee in response to tapping the tendon between the patella and the tibia; this stretches quadriceps muscle spindles, whence afferents to the spinal cord elicit transient reflex contraction. Tests the integrity and function of the relevant peripheral nerves and lumbar spinal segments. Syn patellar reflex. See also tendon jerk reflex.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>