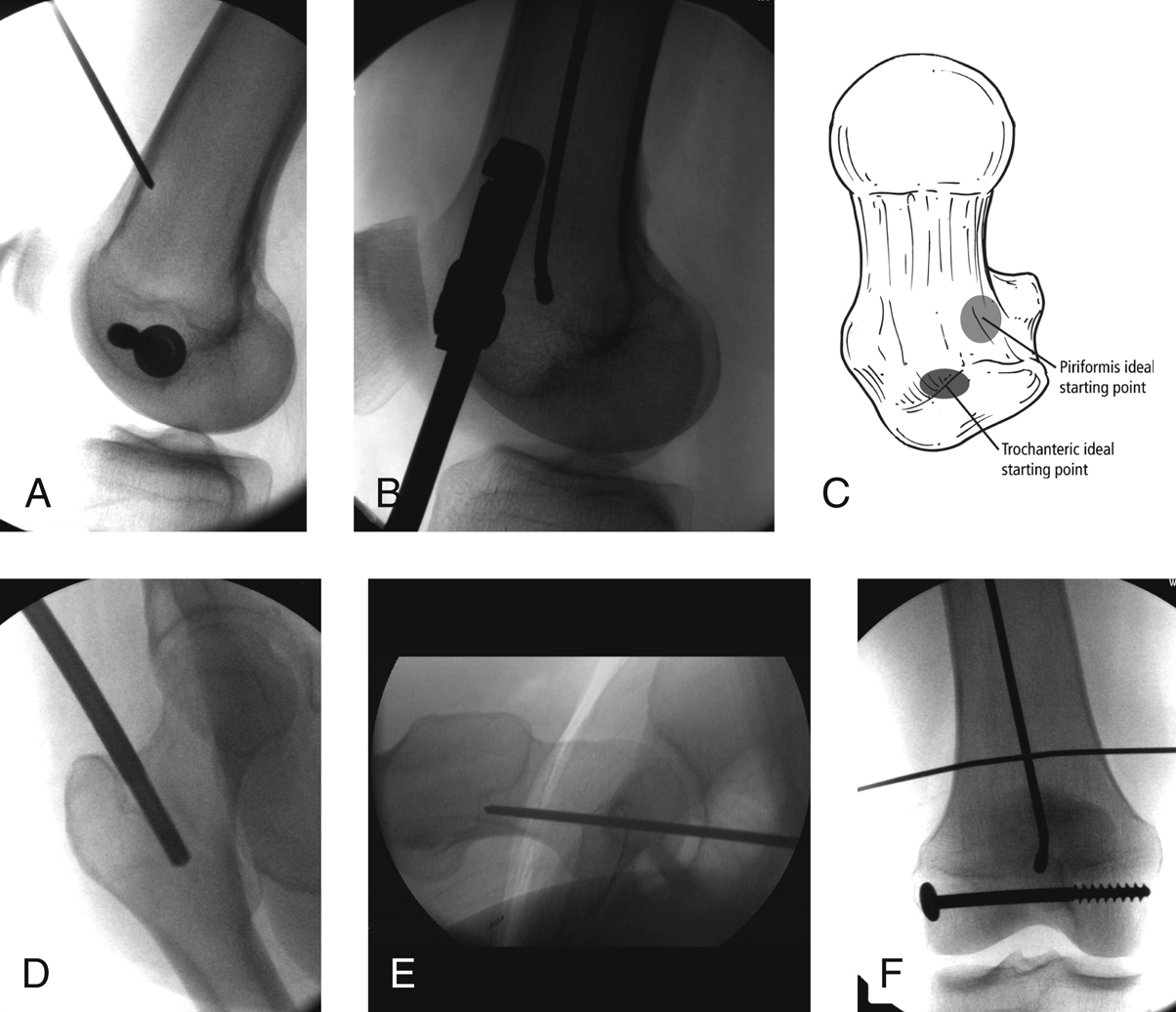
Intramedullary Nailing of Diaphyseal Femur Fractures
Patient Selection
Diaphyseal femur fractures necessitate surgical fixation
Allows earlier mobilization
Reduces risk of prolonged recumbency, including fat emboli syndrome, decubitus ulcers, muscle atrophy, and venous thromboembolic complications
Intramedullary nailing (IMN) indicated for diaphyseal femur fractures in adults able to tolerate surgery
Relative contraindications
Some pediatric femur fractures
Highly contaminated open wounds
Proximal or distal femoral involvement needing other fixation
Retrograde IMN sometimes needed in patients with obesity, for bilateral femur fractures, or for ipsilateral tibia fractures
Preoperative Imaging
AP and lateral radiographs of entire femur, including hip and knee; evaluate femoral neck for associated fracture
In severe comminution, image contralateral side to evaluate length and alignment; in bilateral fractures, fix simpler side first to assess length of comminuted side
Assess rotation by comparing lesser trochanter profile on uninjured side on AP view obtained with patella straight anterior or by obtaining a perfect lateral of the knee and rotating the C-arm 90° to obtain an AP of the hip maintaining the same position of the leg
Assess femoral anteversion by comparing angulation of proximal femur on lateral radiograph between injured and noninjured sides
Procedure
Room Setup/Patient Positioning
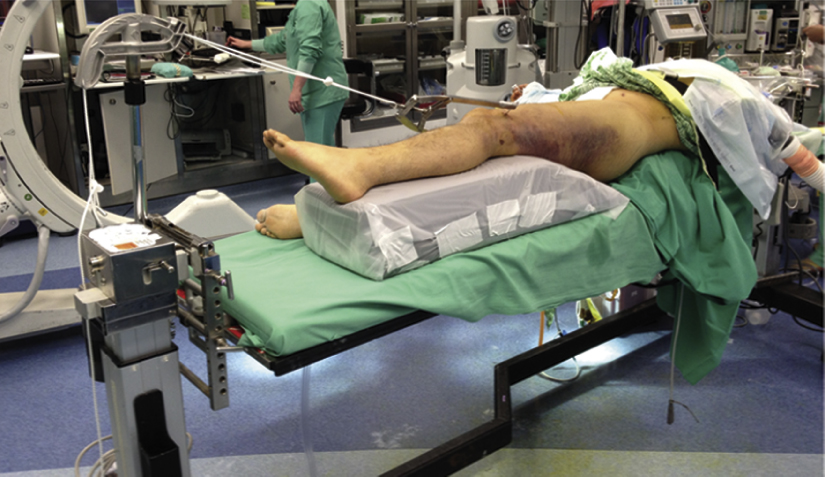
Figure 1Photograph shows patient positioning and room setup for intramedullary nailing of a femoral shaft fracture. The patient is supine on a Jackson table. The injured (left) hip has been moved laterally over the edge of the table, and the leg is elevated on a ramp (encased in plastic drapes). Traction is shown in place as an example.
Author recommends supine positioning on flat Jackson table; traction table increases risk of complications
Supine position at edge of table with bump under sacrum to provide complete access to the hip (Figure 1)
Author uses custom device to apply intraoperative traction while keeping leg free for manipulation
Elevate leg on ramp for lateral fluoroscopic imaging; position fluoroscopy unit on side opposite injured leg, rotated approximately 10° above horizontal to image lateral femur
Special Instruments/Equipment/Implants
Traction setup for Jackson table
Leg ramp and sacral bump
Traction bow, sterile rope, 5/64-in Kirschner wire (K-wire)
Femoral nail, reamers, appropriate insertion equipment
Reduction devices (eg, ball-spike pusher, shoulder hook)