The ICF Assessment Sheet helps rehabilitation professionals to understand the client’s functioning and to identify the needs to be addressed in rehabilitation. It provides an overview of the client’s functioning state with input from both the client and the rehabilitation professional [31]. Considering the client’s own perspective of his/her functioning problems enriches the information provided by the rehabilitation professional and can later guide intervention planning [32]. See Table 22.1.
Table 22.1
ICF assessment sheet
Body functions/structure | Activities and participation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Client | I have some pain when moving my legs | I can’t sit without using my arms to prop up | I used to go motorcycling, play golf |
I have spasticity, in particular when moving myself | Moving with the wheelchair is improving, but I still have problems overcoming obstacles | I want to do some kind of sports | |
I still get fungal skin infection | I am now able to dress my lower extremities | I like meeting my friends (at least once a week) | |
I am able to manage my bladder and control defection well | I take care of my medication and treatment schedule | I want to go home for the weekend | |
I have problems with my body balance | I want to work again but I can’t imagine working at the computer all day | ||
I am willing to learn a new profession | |||
Body functions/structures | Activities and participation | ||
Health professionals | Power of isolated muscles (arms) | Changing basic body positions | Remunerative employment |
Power of muscles in the lower half of the body | Maintaining a sitting position | ||
Power of muscles of the trunk | Moving around in different locations | ||
Supportive functions of the arms | Moving around using equipment | ||
Structure of areas of the skin – at risk | Driving motorized vehicles | ||
Caring for the skin | |||
Regulating urination | |||
Regulating defection | |||
Environmental factors | Personal factors | ||
Health professionals and client | Wheelchair does not fit ideally | 26 years old, male | Is able to cope with health situation |
Car is not wheelchair adapted | Sharing a flat with a friend | Has a strong will to be able to walk again | |
Accident insurance is paying for health services | Trained as a salesperson for home electronics, but worked as a mover before accident | Willing to learn a new profession | |
Parents support him | Very motivated to clarify vocational future | ||
Friends support him | |||
Health professionals | |||
To facilitate the identification of intervention targets that are related to common goals identified by the client and the rehabilitation professional, an ICF Categorical Profile is generated. The ICF Categorical Profile serves as the central source of information for the rehabilitation team for intervention planning. It is generally set up using a suitable ICF Core Set in combination with a rating of the respective ICF categories using ICF qualifiers. ICF qualifiers are used to rate the extent of a problem for each ICF category by estimating the level of difficulties (“0” = no problem; “1” = mild problem; “2” = moderate problem; “3” = severe problem; “4” = complete problem). Environmental factors can be rated either as a barrier or as a facilitator, and in some cases an environmental factor can be rated as both a barrier and a facilitator [17], e.g., a spouse can be a facilitator by providing essential care but can also be a barrier if this care becomes too sheltering and prevents the person from becoming more independent. Although personal factors are not yet classified in the ICF, they have an influence on the client’s functioning in terms of the rehabilitation process [33, 34], including vocational rehabilitation [35]. Thus, personal factors are rated as having a positive, neutral, or negative influence on the client’s functioning. See Table 22.2.
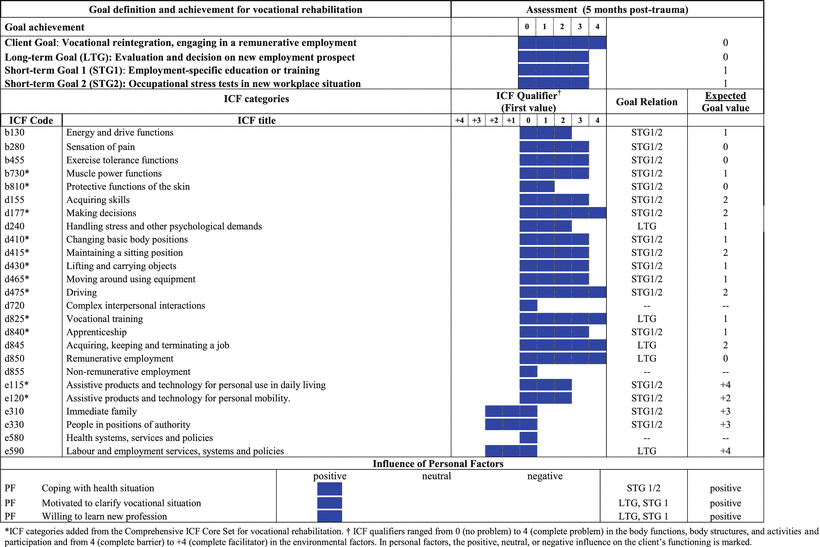
Table 22.2
ICF categorical profile

To facilitate the coordination of interventions, roles, and resources within an inter-professional team in vocational rehabilitation, the ICF Intervention Table provides a comprehensive overview of all the intervention targets (represented by ICF categories), the interventions, and the corresponding rehabilitation professional who is assigned to address each intervention target. More than one rehabilitation professional may be assigned to one intervention target. The ICF Intervention Table also displays the expected goals (goal value) for each target. See Table 22.3.
Table 22.3
ICF intervention table
Intervention targets | Intervention | Psych | OT | SW | Voc trainer | Phys | PT | Nurse | First value | Goal value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Body function | b130 | Energy and drive functions | Psychological therapy | x | 2 | 1 | ||||||
b280a | Sensation of pain | Medication | x | 3 | 0 | |||||||
Manual therapy | x | |||||||||||
b455 | Exercise tolerance functions | Movement training | x | 3 | 0 | |||||||
b730a | Muscle power functions | Training with equipment | x | 3 | 1 | |||||||
b810a | Protective functions of the skin | Instruction for skin control | x | 1 | 0 | |||||||
Activities and participation | d155 | Acquiring skills | Skill training | x | x | 3 | 2 | |||||
d177a | Making decisions | Counseling | x | x | 4 | 2 | ||||||
d240 | Handling stress and other psychological demands | Counseling | x | 3 | 1 | |||||||
d410a | Changing basic body positions | Training of changing body positions | x | x | x | 3 | 1 | |||||
d415a | Maintaining a sitting position | Reaction training | x | 3 | 2 | |||||||
d430a | Lifting and carrying objects | Training with equipment | x | 3 | 1 | |||||||
d465a | Moving around using equipment | Wheelchair training | x | 3 | 1 | |||||||
Instruction of “Swiss trac®” | x | |||||||||||
d475a | Driving | Counseling for adapted devices | x | 4 | 2 | |||||||
Driving lessons | x | |||||||||||
d825a | Vocational training | Vocational training | x | x | 2 | 1 | ||||||
d840a | Apprenticeship | Counseling/instruction | x | 3 | 1 | |||||||
d845 | Acquiring, keeping and terminating a job | Counseling/instruction | x | 4 | 2 | |||||||
d850 | Remunerative employment | Vocational testing and training, coaching/liaison with former employer | x | x | x | 4 | 0 | |||||
Environmental factors | e115a | Assistive products and technology for personal use in daily living | Choice of assistive devices | x | x | 2 | +4 | |||||
e120a | Assistive products and technology for personal mobility … | Choice of wheelchair | x | 2 | +2 | |||||||
e310 | Immediate family | Counseling/ instruction | x | x | x | +2 | +3 | |||||
e330 | People in positions of authority | Coaching/Liaison with former employer | x | x | +2 | +3 | ||||||
e590 | Labour and employment services, systems and policies | Counseling | x | x | +2 | +4 | ||||||
Influence of personal factors | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Intervention targets | Intervention | Responsible Professional | First Value | Goal Value | ||||||
Pos. | Neutral | Neg. | Pos | Neutral | Neg. | |||||
Personal factors | PF | Coping with health situation | Psychological therapy | Psych | x | x | ||||
PF | Motivated to clarify vocational situation | Counseling/instruction | Voc trainer, Psych | x | x | |||||
PF | Willing to learn new profession | Counseling/instruction Skill training | Voc trainer, OT | x | x | |||||
The ICF Evaluation Display based on ICF Core Set categories illustrates the results of the assessment and reexamination of the client’s functioning. It displays long-term and short-term goals and reflects the extent of a problem the client is experiencing in a particular ICF category as rated with ICF qualifiers before (first value) and after intervention (final value). A goal value is defined, in order to determine whether a goal has been achieved following an intervention (see Tables 22.2, 22.3, and 22.4).
Table 22.4




ICF evaluation display comprises initial assessment
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







