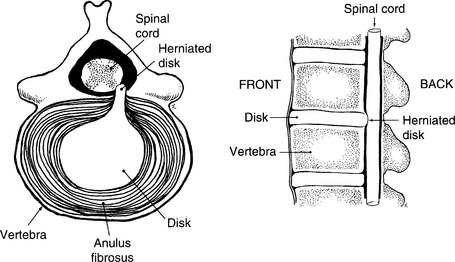
Herniated Disk (Ruptured Disk)
Common signs and symptoms
• Pain in the back that usually affects one side, is worse with movement, and may be worse with sneezing, coughing, or straining
• Pain, numbness, or weakness affecting one arm or leg (depending on whether injury is in the neck or low back, respectively)
Factors that increase risk
• Any sport in which movement causes downward or twisting pressure on the neck or spine, most commonly football, weightlifting, horseback riding or equestrian competition, bowling, tennis, jogging, track, racquetball, and gymnastics
Preventive measures
• Maintain appropriate conditioning that includes cardiovascular fitness, back and hamstring flexibility, and muscle strength and endurance training.
Medication
• Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen (do not take for 7 days before surgery), or other minor pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, are often recommended. Take these as directed by your physician, and contact your doctor immediately if any bleeding, stomach upset, or signs of an allergic reaction occur.
• Pain relievers and muscle relaxers may be prescribed. Use these only as directed, and do not use any heavy machinery or drive a car while taking these medications.
• Injections of corticosteroids into the epidural space may be given to reduce inflammation, although they are not usually given for acute injuries.
Heat and cold
• Cold is used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It should be applied for 10 to 15 minutes every 2 to 3 hours as needed and immediately after any activity that aggravates your symptoms. Use ice packs or an ice massage.
When to call your doctor
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree