Chapter 13 Fractures of the tibia
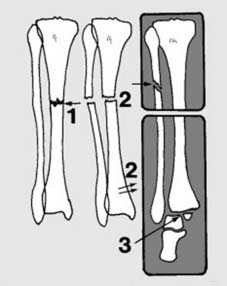
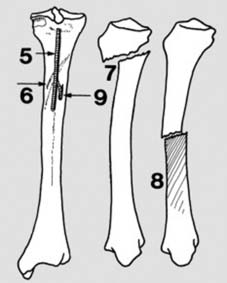
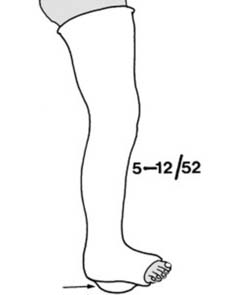
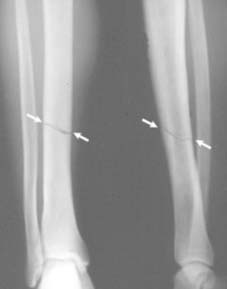
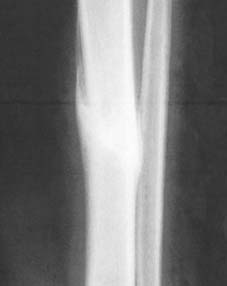
7 Undisplaced fractures (a): In children, owing to the thickness of the subcutaneous fat and periosteum, and the elasticity of the bones, fractures are often of greenstick pattern and closed. In many cases, too, the fractures are minimally displaced. (Illus.: Greenstick fracture distal tibia and fibula, betrayed by fibular kinking and tibial cortical buckling.)
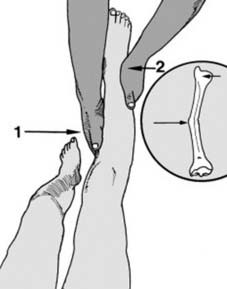
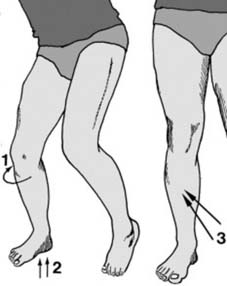
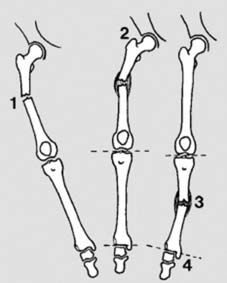
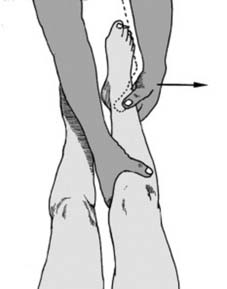
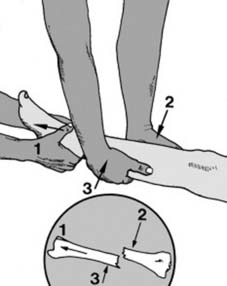
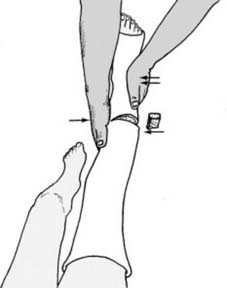
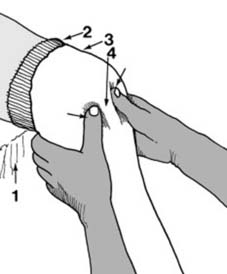
13 Angled fractures in children (a): These are reduced under general anaesthesia. One hand is placed over the fracture site (1) while the other, at the ankle (2), is used to correct the angulation. Although the AP plane only is illustrated, obviously any deformity in the lateral plane should be similarly corrected.
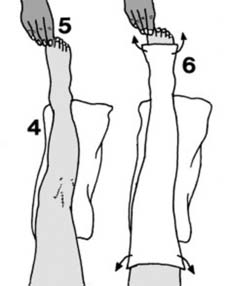
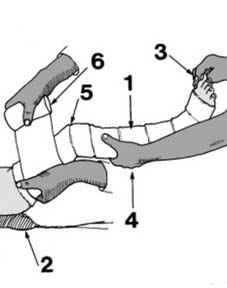
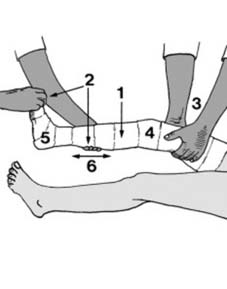
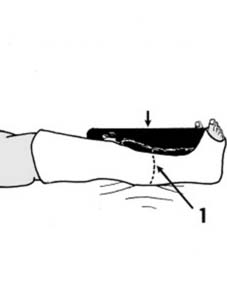
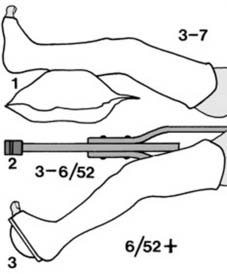
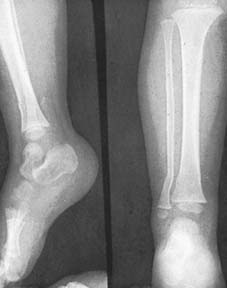
19 Displaced fractures of the tibia (c): If the reduction obtained by manipulation is somewhat precarious and it is feared that the fracture might slip during the application of plaster, place the limb on a firm pillow (4), steady the leg by holding the toes (5) and apply a thick, anterior, plaster slab (6) tucking the edges well round the limb. When it has set, the leg can then be carefully bandaged into the slab.
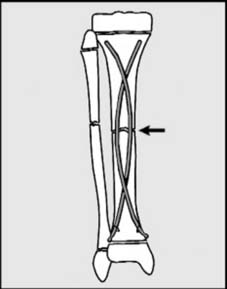
24 Flexible intramedullary nails (Nancy nails): As an alternative to conservative treatment some surgeons prefer to internally fix severely displaced or unstable fractures of the tibia in children using flexible intramedullary nails. The triangular cross-section of the tibia makes it difficult to place the nails in the configuration required to satisfy the principles of this technique, and the proximal metaphyseal flare and the presence of the proximal tibio-fibular joint make antegrade insertion difficult. The rigidity of the fixation is often far from perfect, and additional support with a cast is usually required (so that some critics might say that the benefits of this treatment are often at best somewhat marginal).
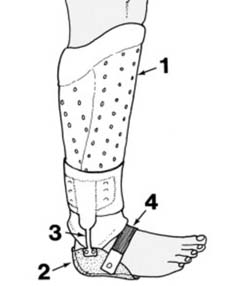
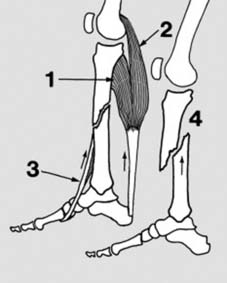
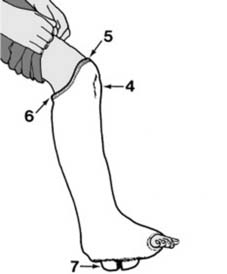
29 Functional bracing with a gaiter: In the later stages of fixation, or even as early as 4 weeks when instability is not a problem, a supporting gaiter may be used instead of plaster. The type illustrated may be fashioned from perforated Orthoplast™ (Johnson & Johnson) thermoplastic sheet (1). For additional support a plastic heel seat (2) may be secured to the brace with polyethylene hinges (3) and a garter strap (4).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree