19 Foot
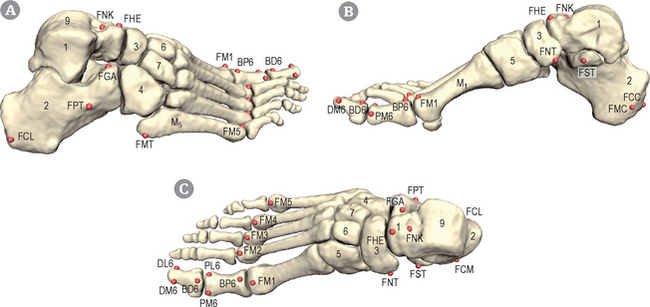
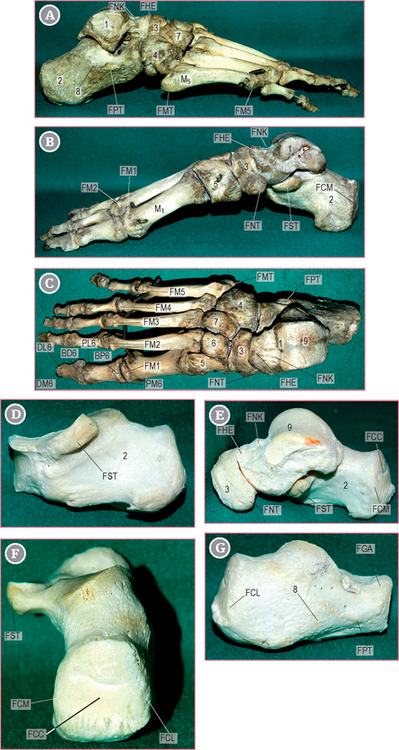
Orientation and general presentation (Figs 19.1 & 19.2)
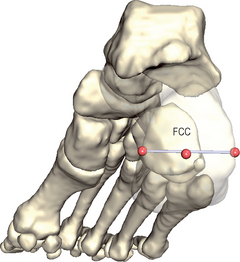
Foot/Calcaneus – posterior surface (FCC, FCM, FCL)[R,L] H|Anim 
Landmarks FCC, FCM, FCL
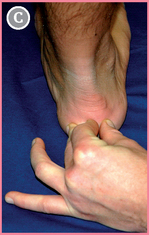
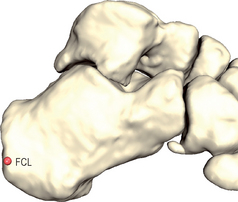
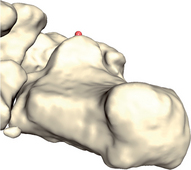
The posterior face of the calcaneus can be described as a square with four edges (see Figs 19.1 & 19.2). Both medial and lateral edges are palpated.
![]() Subject lying: The subject is lying prone, with the foot slightly extended and at rest.
Subject lying: The subject is lying prone, with the foot slightly extended and at rest.
Then follow the edges distally until you reach the the calcaneus (blue arrows).
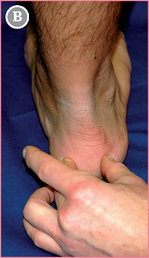
![]() FCC is located by pushing your forefinger centrally between the thumb and middle finger.
FCC is located by pushing your forefinger centrally between the thumb and middle finger.
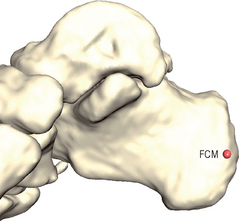 Observe the calcaneus bone from a medial view. Select the center of the medial calcaneal edge (FCM).
Observe the calcaneus bone from a medial view. Select the center of the medial calcaneal edge (FCM).
Foot/calcaneus – Sustentaculum Tali (FST)[R,L] H|Anim
Landmark FST
The sustentaculum tali is a prominent tubercle at the medial aspect of the calcaneus (see Figs 19.1 & 19.2). It also supports the medial part of the anteromedial joint surface of the talus. It is located on the border joining the superior and medial surfaces of the calcaneus.
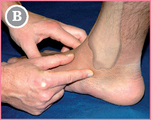
![]() Subject lying: The subject is lying supine, foot at rest.
Subject lying: The subject is lying supine, foot at rest.
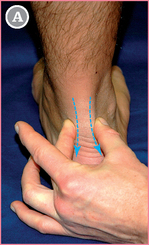
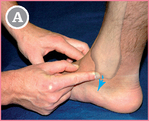
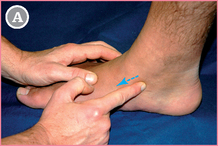
Start with the forefinger from TAM (see p. 148).
Move distally (blue arrow) in the direction of the medial border of the foot.
![]() The mid-point between the two fingers is FST.
The mid-point between the two fingers is FST.
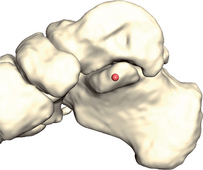
Foot/Navicular – Tuberosity (FNT)[R,L]
Landmark FNT
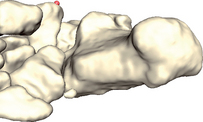
The navicular tuberosity is a prominence located on the medial aspect of the navicular bone, pointing towards the sole of the foot (see Figs 19.1 & 19.2). It receives one of the insertions of the tibialis posterior muscle.
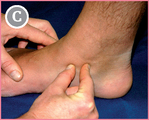
![]() Subject lying: The subject is lying supine, foot at rest.
Subject lying: The subject is lying supine, foot at rest.
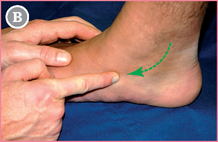
From FST (see p. 164), move anteriorly (towards the toes; blue arrow).
![]() The first bony prominence you meet is the navicular tuberosity. Select its tip.
The first bony prominence you meet is the navicular tuberosity. Select its tip.
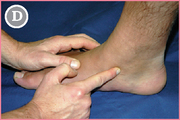
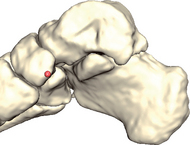 Observe the foot from a medial view (slightly posterior). Locate the center of the navicular tuberosity.
Observe the foot from a medial view (slightly posterior). Locate the center of the navicular tuberosity.