Flexor Tendon Repair
Patient Selection
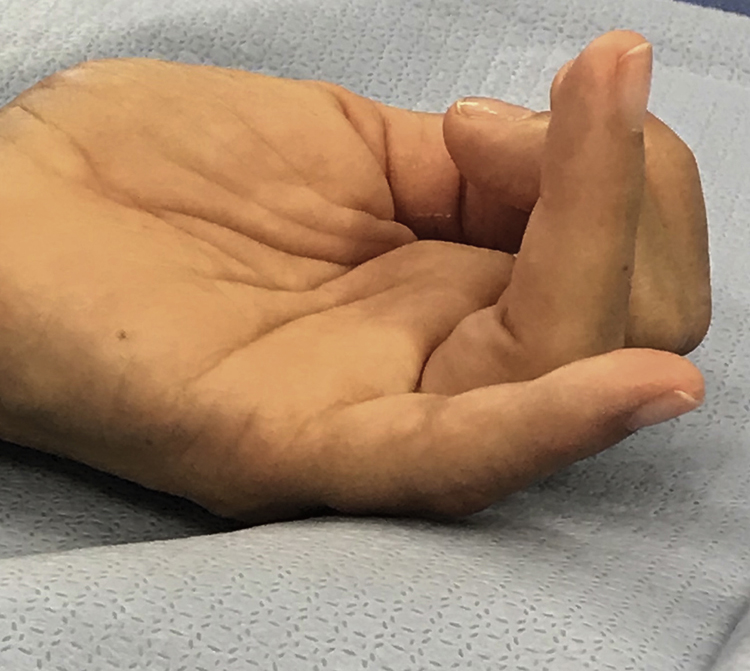
Figure 1Photograph shows demonstration of flexor tendon cascade with ring finger FDP disruption and little finger FDP and FDS disruption.
Suture techniques have become more sophisticated and rehab protocols have kept pace with surgical advances
Flexion cascade of the hand will be altered if there is flexor tendon injury (Figure 1)
Test FDS by holding uninvolved digits at the MCP Joints in hyperextension and IP joints in extension and ask patient to flex PIP joints at the level of the middle phalanx
Test FDP by holding involved digit at the middle phalanx level and ask patient to flex the DIP joint
Use wrist flexion/extension tenodesis effect to indirectly enhance examination
Assess FPL laceration by compression of the muscle belly proximal to the wrist by looking for IP joint flexion of the thumb; beware of “pseudotendon” which can mimic an intact tendon when the injured tendon retracts
Level of volar skin laceration may not represent true level of tendon injury, especially if digits were flexed
Palpate palm to reveal level of retracted stump
Observe for presence/absence of palmaris tendon; may need for graft during repair of staged reconstructive procedure
Alternative grafts include plantaris tendon, extensor digitorum longus (toe extensors)
Discuss with patient preoperatively regarding possibility of requiring graft
Special Populations/Situations
Complex Injuries
Challenging to balance immobilization requirements and rehabilitation in cases of complex open injuries with tendon lacerations and fractures
Must modify therapy protocols to balance combination of soft-tissue, nerve, artery, tendon, and osseous injury
Precedence given to neurovascular status and skeletal stabilization to the detriment of early tendon mobilization protocols
Patients With Delayed Presentation
Some cases when patients present in delayed fashion
MCP, PIP, and DIP joints must be passively supple to have surgery
Level of retraction and compliance of tendon is critical to determine if it can be repaired
Debatable whether it is necessary to fuse or tenodese DIP joint after FDP excision
Primary grafting of tendon is rarely indicated; rare exceptions where sheath remains open and both FDP and FDS tendons are rupture
Patients With Carpal Fractures
Attritional rupture of flexor tendons can be secondary to prior carpal fracture
A hook of the hamate fracture or nonunion can cause abrasive surface leading to flexor rupture of the ring and/or little finger
Treatment consists of hook of hamate excision and tendon reconstruction or adjacent tendon transfers
Flexor Injuries in Children
Same techniques for direct repair and tendon graft in children as it is in adults
Repair will require smaller caliber sutures
Avoid the physis with suture passage if using transosseous sutures
Casting in young children who are unable to participate therapy program yields satisfactory outcomes
Use absorbable skin sutures
Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
FPL is most commonly ruptured flexor tendon in the RA population (Mannerfelt lesion)
Also consider AIN dysfunction as a cause for lost ability to actively flex the thumb IP joint
FPL ruptures can be secondary to volar osteophyte on the scaphoid or other volar radial location; management includes osteophyte removal and tendon transfer, interposition graft, or IP joint fusion
Indications
Medically fit patient who can demonstrate compliance with rehab protocol
Emergent repairs indicated in compromised perfusion requiring microvascular repair
Contraindications
Medically unstable patient
Active infection
Noncompliant patient
Preoperative Imaging
Radiography
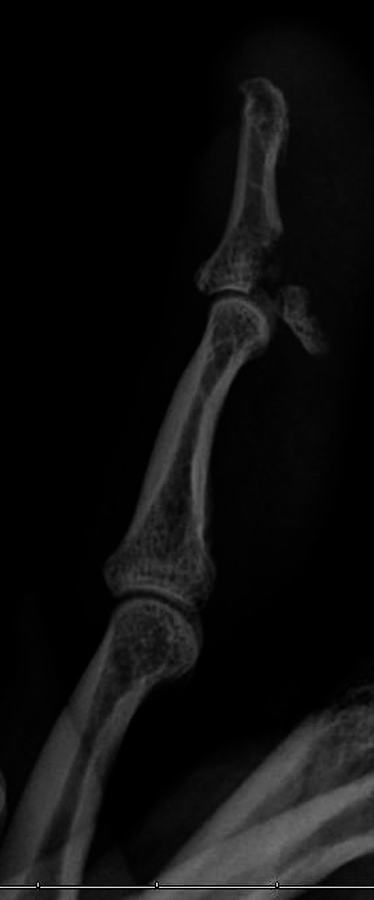
Figure 2Appearance of an FDP avulsion, which in this case includes an intra-articular distal phalanx fracture as noted on radiograph. There was a fracture combined with an FDP avulsion that was retracted to the A-2 pulley that is not visible on plain radiographs (making this a type IV injury).
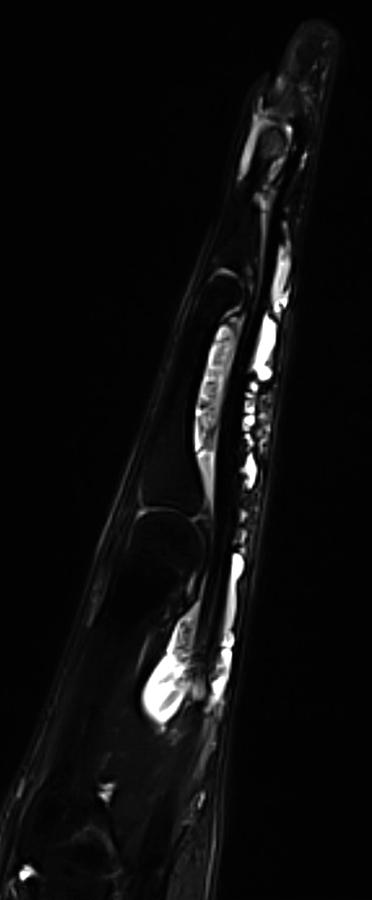
Figure 3Magnetic resonance image demonstrating an intact FDP and FDS but surrounding flexor tenosynovitis throughout the flexor sheath.
Plain radiographs of the affected digit and hand to evaluate for avulsion injury or presence of foreign body (Figure 2)
MRI or ultrasonography to evaluate continuity of tendon and assess gap distance (Figure 3)
Procedure
Room Setup/Patient Positioning
Supine with arm on radiolucent hand table
Regional or local anesthesia in unsedated patient to allow intraoperative assessment of quality of repair
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


