Fixation of Proximal Humerus Fractures
Introduction
Increased interest in fixation of proximal humerus fractures for several reasons:
Humeral head replacement has an unpredictable outcome
Osteonecrosis is no longer seen as a clinical disaster
More accurate preoperative imaging
Improvements in fluoroscopy
Refined reduction maneuvers
Improved implants
Clinical results remain inconsistent
Patient Selection
Indications
Neer guidelines remain useful
Treat minimally displaced fractures nonsurgically; treat most displaced fractures surgically
Most two- and three-part fractures are amenable to fixation.
Contraindications
Very few absolute contraindications
Low-demand and infirm patients are likely nonsurgical candidates
Four-part fracture-dislocations and most head-split fractures
Rotator cuff tear arthropathy
Severe glenohumeral arthritis
Preoperative Imaging
Rely on intraoperative fluoroscopic imaging to assess quality of reduction
Use comparison radiograph of contralateral shoulder to assess reduction
Well-centered AP view of scapula with arm in external rotation demonstrates greater tuberosity relative to the head
Two-dimensional CT reveals extent of bone loss
Three-dimensional CT shows tuberosity attachment
Procedure
Room Setup for Fluoroscopic Imaging/Patient Positioning
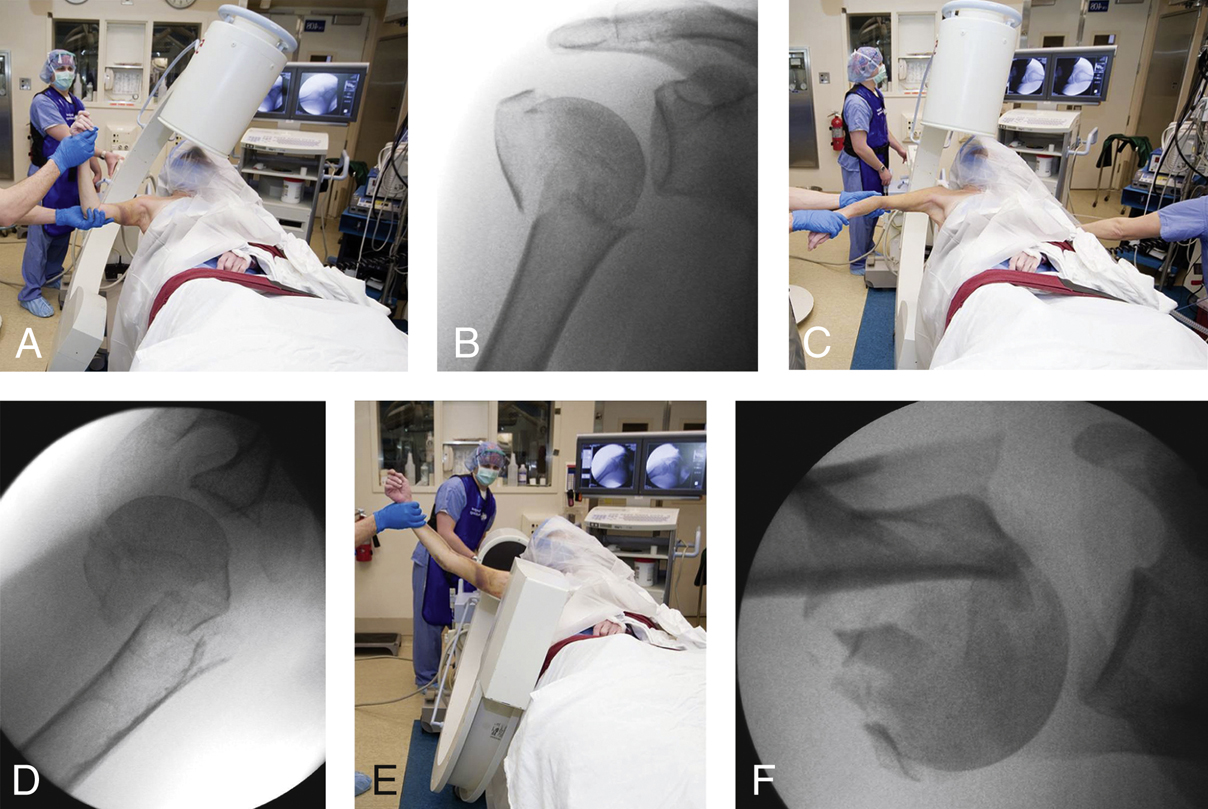
Figure 1Images show the operating room setup for fixation of a proximal humerus fracture. A, Photograph shows positioning of the fluoroscopic imaging device to direct the fluoroscopic beam perpendicular to the scapula, with the patient’s arm held in external rotation. B, Preoperative AP external rotation fluoroscopic view shows the relationship among the humeral shaft, the humeral head, and the greater tuberosity. C, Photograph shows patient positioning for the Velpeau axillary view taken with the arm held in internal rotation and slight longitudinal traction. Gentle traction lateralizes the scapula away from the operating room table and the patient’s head and allows unobstructed imaging of the proximal humerus and glenoid. D, Preoperative Velpeau axillary internal rotation fluoroscopic view depicts the typical apex anterior angulation between the shaft and head segment. E, Photograph shows patient positioning for the standard axillary view taken with the arm held in neutral rotation and longitudinal traction. F, Preoperative fluoroscopic axillary view shows the position of the lesser tuberosity and the relationship of the humeral head to the glenoid.
(Reproduced from Torchia ME : Technical tips for fixation of proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients. Instr Course Lect2010;59:553-561.)
Need unrestricted access to shoulder for fluoroscopic imaging (Figure 1)
Supine or beach-chair position
Table is rotated 90° to allow C-arm to enter
Verify access to imaging before starting the case
Special Instruments/Equipment/Implants
Intraoperative fluoroscopy
Large Weber clamp
Precontoured low-profile locking plate
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


