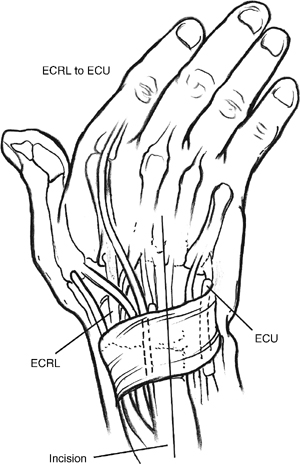
51 Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus to Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Tendon Transfer
Indications
- Radial deviation of the wrist with reduced capacity for active ulnar deviation due to an inflammatory arthropathy.
- Post-traumatic extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) disruption with radial deviation of the wrist.
Pitfall
Inability to passively correct the wrist deformity and diminished extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) or extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) function are contraindications.
Technique
- A dorsal, midline, longitudinal 6–8 cm incision is made, centered over the rim of the radius.
- Full-thickness skin flaps are raised, including the veins, nerves, and subcutaneous fat.
- The sixth extensor compartment is opened, the ECU is extracted, and a tenosynovectomy is performed.
Pearl
The entire retinaculum is raised as a radially based flap to the septum between the first and second compartments if a more complete dorsal tenosynovectomy is necessary.
- The ECRL is sharply released from its insertion on the base of the second metacarpal.
- If the second compartment has been opened for a tenosynovectomy, the ECRL is dissected free from surrounding tissue.
- When the second compartment is intact, the tendon is identified proximal to the retinaculum and carefully dissected from within the compartment while applying traction until it is free.
- Repair the retinaculum leaving the ECU and ECRL tendons superficial to it (Fig. 51-1).