47 Excision Distal Pole of the Scaphoid
Indications
- Symptomatic, long-standing scaphoid (S) nonunion with radioscaphoid arthritis
- Margins of scaphoid nonunion sclerotic, with cystic changes in the proximal and distal poles; appearance suggests pseudarthrosis
- Patient who is poor candidate for open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF): heavy smoker, anticipated poor compliance
- No arthritis in the midcarpal joint
Pitfall
Patients with a marked dorsal intercalated segmental instability (DISI) deformity and pain emanating from the midcarpal joint are poor candidates for this procedure.
Figure 47-1
Technique
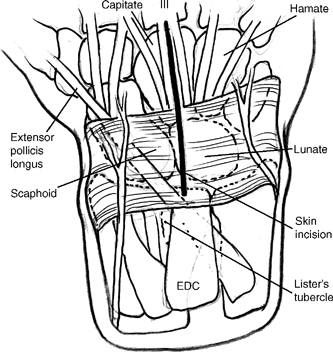
- A dorsal, longitudinal 6 to 8 cm skin incision centered over the capitate (C) (Fig. 47-1)
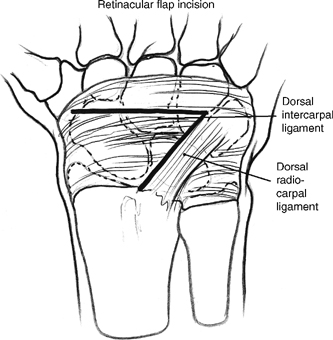
- Dissect to the wrist capsule using incisions along the dorsal radiocarpal and dorsal intercarpal ligaments creating a radial-based flap between the second and fourth compartments distal to the extensor pollicis longus (EPL) tendon.
Pearl
Incise the distal edge of the extensor retinaculum between the third and fourth compartments to the level of Lister’s tubercle to facilitate exposure (Fig. 47-2).