CHAPTER FIVE Case studies in respiratory physiotherapy
Introduction
The area of respiratory physiotherapy reaches a number of patient groups, both in the in-patient and out-patient settings. The case studies that follow are based predominantly in the in-patient environment; however, the components of a respiratory assessment and the subsequent identification of physiotherapy problems and treatment plan could be applied to any patient with respiratory compromise in any clinical setting.
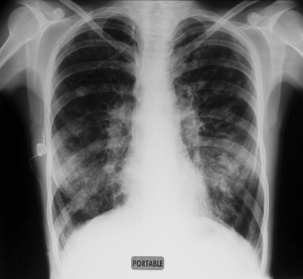
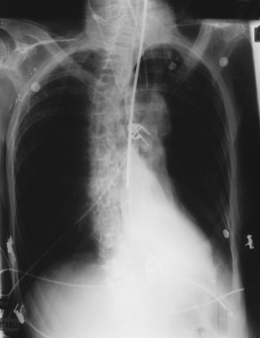
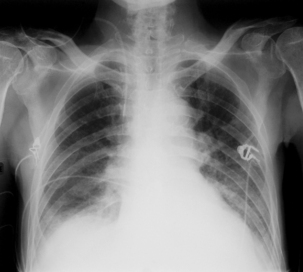
Like all other areas of physiotherapy practice, respiratory physiotherapy involves accurate patient assessment in order to identify patient problems. Respiratory assessment should include certain key elements: general observations of the patient; consideration of trends in physiological observations (e.g. HR, BP, oxygen saturations); patient position; auscultation, palpation and, where available, analysis of arterial blood gases and chest X-ray (CXR).
Another key area of work where physiotherapists are required to undertake respiratory care is in the provision of emergency duty/on-call services. Such services are available to patients who have a condition amenable to physiotherapy, which has either deteriorated or is likely to deteriorate without intervention before daytime service resumes (Scottish Intercollegiate Guideline Network 2004). This can be a very challenging area of work for the physiotherapist on-call, who needs to think clearly while being faced with an acutely unwell patient who is in need of their attention, whatever the time of day. Guidance is available to support the clinician involved in providing such care and to aid ongoing assessment of competence (Chartered Society of Physiotherapy 2002).
CASE STUDY 1 Respiratory medicine – bronchiectasis out-patient
Subjective assessment
HPC
Diagnosed 6/12 ago with bronchiectasis following an in-patient admission with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in her right lower lobe. This resulted in the development of bronchiectatic changes. Since diagnosis the patient reports daily production of mucopurulent secretions with excessive coughing and feelings of fatigue
Objective assessment
Observation
Looks well, good colour, breathing pattern normal
Patient actively trying to suppress cough and noise of secretions
Questions
CASE STUDY 2 Respiratory medicine – lung cancer patient
Subjective assessment
HPC
Diagnosed 9/12 ago following a 3/12 history of increasing shortness of breath and cough. Two episodes of frank haemoptysis also reported. Following diagnosis, patient was deemed appropriate for a course of chemotherapy, but had limited response to intervention. As an out-patient he had a CT scan, which showed brain and spinal metastases, and he has been suffering uncontrollable pain. As a result he has been bed bound for the past month and has required increasing support from Macmillan oncology nurse specialists
Objective assessment
Respiratory
CASE STUDY 3 Respiratory medicine – cystic fibrosis patient
Subjective assessment
HPC
Diagnosed at birth. Multiple hospital admissions over last 3 years due to exacerbation of CF. On admission patient reporting 1/52 history of increased breathlessness, sputum volume and cough. These symptoms have not responded to a 2/52 course of intravenous antibiotics. In respiratory distress. Dehydrated. Recent weight loss and current BMI 17. Under review for lung transplantation assessment. Patient previously agreed to perform twice daily ACBT in alternate side lying/supine for 20 minutes, but generally non-compliant with suggested airway clearance programme and prescribed medications
Questions
CASE STUDY 4 Respiratory medicine – copd patient
Subjective assessment
Objective assessment
CNS
Drowsy but able to be roused for short periods Disorientated and confused. Moving all four limbs
CASE STUDY 5 Surgical respiratory – anterior resection
Subjective assessment
SH
Lives with wife, recently retired, independent with ADL, plays golf three times a week, smoker 5 cpd
CASE STUDY 6 Surgical respiratory – division of adhesions
Subjective assessment
Objective assessment
Respiratory
CASE STUDY 7 Surgical respiratory – hemicolectomy
CASE STUDY 8 Surgical respiratory – bowel resection
CASE STUDY 9 Intensive care – patient for extubation
Subjective assessment
PC
Day 7 post-laparotomy for subtotoal colectomy and extensive bowel resection, formation of ileostomy
HPC
Emergency admission from A&E in shock with reduced BP, abdominal pain
Unwell for 3–4 days, intermittent diarrhoea and vomiting
Theatre findings – patchy infarction of small and large bowel
Questions
CASE STUDY 10 Intensive care – surgical patient
Subjective assessment
Objective assessment
Respiratory
Ventilation
SIMV ETT size 7.0 FiO2 0.35 PEEP 5 PS 10 Tv 0.419 L RR 14 SpO2 92% HMEF brown secretions