1 Bone
Structure of bone
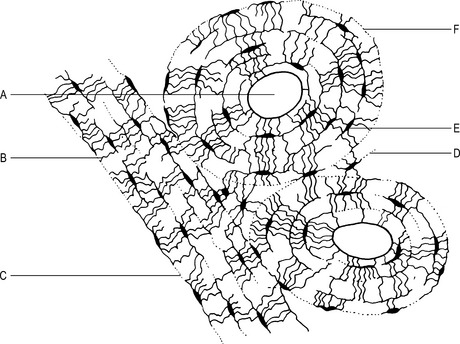
Compact bone
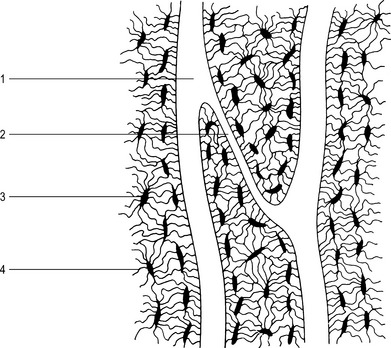
This type of bone is found mainly in the shafts of long bones where a strong, tubular structure is required. It consists of a number of cylindrical structures called haversian systems (Figs 1.1 and 1.2). Each system comprises:
Elsewhere the red bone marrow becomes inactive yellow marrow.
Ossification
Ossification is the formation of bone from connective tissue and requires:
Growth of the bone is influenced by the following hormones: