Chapter 12 Balance and Coordination
Balance exercises or training involves activities aimed at reducing instability/falls by improving patients’ ability to maintain their center of gravity within their support base. Because balance training aims to challenge stability, it is important to structure patient activities at the appropriate level and to screen patients who may be exceedingly unsafe for these activities1 (also see Screening for Falls, Chapter 4; Gait and Locomotion Training, Chapter 14).
12.2 Vestibular Exercises
Vestibular rehabilitation aims at addressing disequilibrium and dizziness symptoms related to peripheral vestibular pathology by using specific exercises to improve balance and reduce dizziness.1 Unstable conditions listed below are CIs. For CRM, correct identification of semicircular canal involvement is necessary before treatment can be appropriately administered.
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
H60-H95 DISEASES OF THE EAR AND MASTOID PROCESS
S00-T98 INJURY, POISONING, AND CERTAIN OTHER CONSEQUENCES OF EXTERNAL CAUSES
1 Shumway-Cook A. Vestibular rehabilitation: What is vestibular rehabilitation? Available at: http://www.vestibular.org/rehab.html#rehabilitation. Accessed May 16, 2005
2 Schubert MC, Herdman SJ. Vestibular rehabilitation. In O’Sullivan SB, Schmitz TJ, editors: Physical rehabilitation: assessment and treatment, ed 4, Philadelphia: FA Davis, 2001.
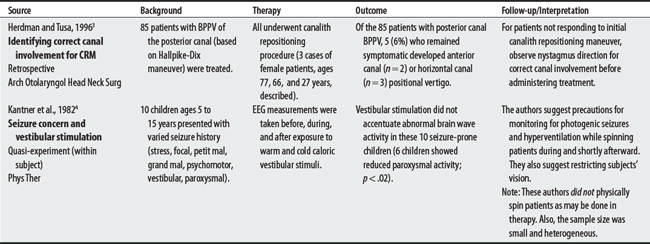
3 Herdman SJ, Tusa RJ. Complications of the canalith repositioning procedure. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996;122(3):281-286.
4 Kantner RM, Clark DL, Atkinson J, Paulson G. Effects of vestibular stimulation in seizure-prone children. An EEG study. Phys Ther. 1982;62(1):16-21.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree