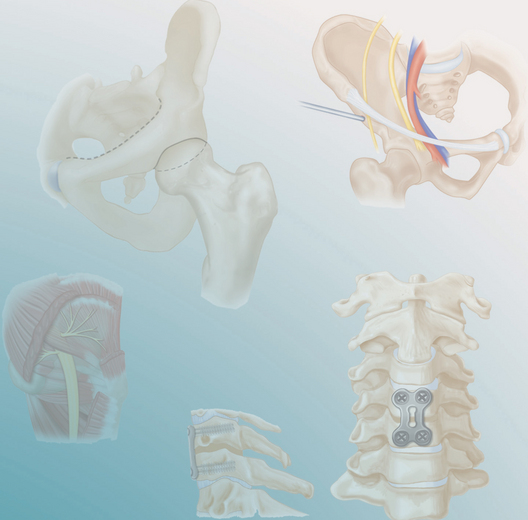
PROCEDURE 52 Optimizing Perioperative Fracture Care
 This chapter describes several perioperative principles and techniques that are of importance in the care of injured patients. The goal of this chapter is to synthesize relevant information, enabling the orthopedic surgeon to provide the best global care for his or her patient based on actual literature.
This chapter describes several perioperative principles and techniques that are of importance in the care of injured patients. The goal of this chapter is to synthesize relevant information, enabling the orthopedic surgeon to provide the best global care for his or her patient based on actual literature. The subjects selected are Advanced Trauma Life Support, initial care of the injured limb, thromboprophylaxis, antibiotic prophylaxis, psychological reaction to injury, and secondary prevention.
The subjects selected are Advanced Trauma Life Support, initial care of the injured limb, thromboprophylaxis, antibiotic prophylaxis, psychological reaction to injury, and secondary prevention.Indications
 Any patient who sustains a moderate- to high-energy injury must be evaluated with the Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) protocol.
Any patient who sustains a moderate- to high-energy injury must be evaluated with the Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) protocol.• An intoxicated patient can be misleading secondary to absence of pain sensation and a poor injury history.
Examination/Imaging
 The principle of the “golden hour” is now part of standard care in every health center from the small rural health center to the Level One Trauma Center.
The principle of the “golden hour” is now part of standard care in every health center from the small rural health center to the Level One Trauma Center.Procedure
STEP 1: AIRWAY
 Airways are evaluated first in the “primary survey.”
Airways are evaluated first in the “primary survey.”• In the primary survey, physicians must evaluate and treat the patient following the ABCDE sequence (see Examination/Imaging above).
 A patient who can speak and has a Glasgow score over 8 (see Step 4) is not likely to have airway obstruction.
A patient who can speak and has a Glasgow score over 8 (see Step 4) is not likely to have airway obstruction.STEP 2: BREATHING
 Oxygenation (normal: > 95% saturation) and breathing rhythm (normal: 15–20 breaths/min) out of normal range are red flags for deficient air entry.
Oxygenation (normal: > 95% saturation) and breathing rhythm (normal: 15–20 breaths/min) out of normal range are red flags for deficient air entry.• Posterior sternoclavicular dislocation can be involved in airway obstruction. This rare condition can be identified by palpation of the sternoclavicular joint during tracheal and neck examination. Closed reduction with traction using a towel clamp can be undertaken in extreme situations with the collaboration of a thoracic surgeon. Posterior dislocations have associated intrathoracic injuries in 30% of the cases. The mortality in this subset of patients is reported to be 12.5%, and such associated conditions must be ruled out before attempting reduction.
STEP 3: CIRCULATION
 Increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, pale skin color, and a decrease of the level of consciousness are all signs of impaired circulation.
Increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, pale skin color, and a decrease of the level of consciousness are all signs of impaired circulation. Immediate volume repletion must be initiated with 2 L of crystalloid. Units of blood and colloid and coagulation products (platelets and plasma) must be ready for use in patients with unresponsive severe shock.
Immediate volume repletion must be initiated with 2 L of crystalloid. Units of blood and colloid and coagulation products (platelets and plasma) must be ready for use in patients with unresponsive severe shock. A systematic review of possible bleeding causes includes external blood loss, thoracic bleeding, abdominal bleeding, pelvic bleeding, and internal hemorrhagic bleeding around a long-bone fracture.
A systematic review of possible bleeding causes includes external blood loss, thoracic bleeding, abdominal bleeding, pelvic bleeding, and internal hemorrhagic bleeding around a long-bone fracture.• Immediate immobilization of a fracture decreases bleeding, decreases pain, and slows the inflammatory reaction.
• Direct manual pressure is the safest way to stop external bleeding. Hemostatic clamps can damage neurologic structures when used in a suboptimal setting in the emergency room.
STEP 4: DISABILITY (NEUROLOGIC STATUS)
 Evaluation for neurologic disability must be done at the end of the primary survey using pupillary size and reaction, lateralizing signs, and level of spinal cord injury.
Evaluation for neurologic disability must be done at the end of the primary survey using pupillary size and reaction, lateralizing signs, and level of spinal cord injury.STEP 6: SECONDARY SURVEY AND TRANSFER DECISION
 Before undertaking the secondary survey, results of blood tests and arterial blood gases must be verified.
Before undertaking the secondary survey, results of blood tests and arterial blood gases must be verified. Judicious radiologic and abdominal tests must be requested.
Judicious radiologic and abdominal tests must be requested.• In the situation of an unstable patient, anteroposterior radiographs of the chest and pelvis can provide important information. Lateral cervical spine radiographs can also be obtained at this time.
 After the primary survey, the physician in charge often has enough information to determine if transfer to a trauma center is needed. Criteria for transfer are:
After the primary survey, the physician in charge often has enough information to determine if transfer to a trauma center is needed. Criteria for transfer are:• Initial treatment of life-threatening injuries or limb salvage can be undertaken before transfer in agreement with the consultant trauma center.
• A normal or inadequate radiograph does not exclude spinal injury. When in doubt, the entire spine must be protected at all times.
• The orthopedic team must ensure that the patient does not evidence any limb-threatening injuries. These injuries are easy to miss in a polytrauma patient or unconscious patient.
 After completion of the primary survey and the resuscitation phase, a second survey can begin. This is done only when the patient is stable and has normal vital signs.
After completion of the primary survey and the resuscitation phase, a second survey can begin. This is done only when the patient is stable and has normal vital signs. The role of the orthopedic surgeon in the secondary survey is to identify all significant musculoskeletal injuries, guided by injury mechanism and energy level.
The role of the orthopedic surgeon in the secondary survey is to identify all significant musculoskeletal injuries, guided by injury mechanism and energy level.• The first step is to look for deformity, redness, edema, wounds, or any sign of blunt trauma. Every part of the body must be examined.
• A careful mobilization must be done “en bloc” to examine the back, buttocks, and posterior aspect of the legs (see Logrolling Mobilization Technique below).
Indications
 This technique must be used during every patient mobilization until the complete spinal evaluation has showed no lesion.
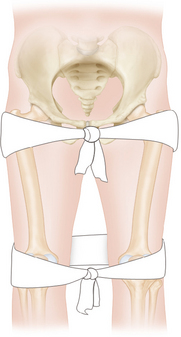
This technique must be used during every patient mobilization until the complete spinal evaluation has showed no lesion.• Logrolling a patient with an unstable pelvis fracture can increase blood loss and cause a decrease of blood pressure. An intravenous fluid bolus must be give before logrolling in these patients.
• The logrolling side must be chosen with respect to the patient’s injury. The side with more injuries must be kept up.
Positioning
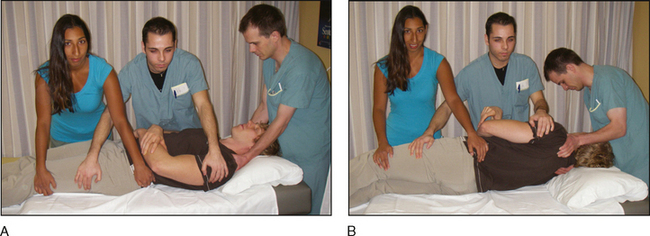
 A careful mobilization must be done “en bloc” to examine the back, buttocks, and posterior aspect of the legs. The technique of mobilization is important to minimize spinal movement.
A careful mobilization must be done “en bloc” to examine the back, buttocks, and posterior aspect of the legs. The technique of mobilization is important to minimize spinal movement. Three persons are needed.
Three persons are needed.• One person stabilizes the head and neck. This person must lead every step in patient mobilization.
Procedure
STEP 1
 The person holding the patient’s head must ensure that the team is well positioned to do the logrolling.
The person holding the patient’s head must ensure that the team is well positioned to do the logrolling.INITIAL CARE OF THE INJURED LIMB
 This topic seems very straightforward. Adequate immobilization, sufficient pain management, and providing walking aids are three easy things to do.
This topic seems very straightforward. Adequate immobilization, sufficient pain management, and providing walking aids are three easy things to do. However, a study undertaken at our center revealed alarming rates of low-level care quality by referring first-line physicians or referring orthopedic surgeons. In our study, 166 patients referred to the fracture clinic for a limb injury were evaluated during a 4-month period (Rouleau et al., 2009
However, a study undertaken at our center revealed alarming rates of low-level care quality by referring first-line physicians or referring orthopedic surgeons. In our study, 166 patients referred to the fracture clinic for a limb injury were evaluated during a 4-month period (Rouleau et al., 2009
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree