The Leg
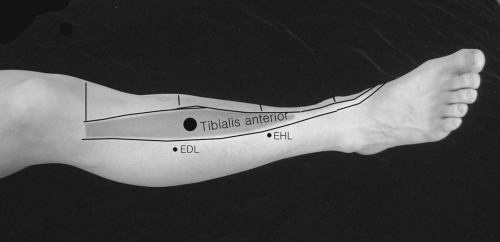
Tibialis Anterior
Patient Position:
Supine.
Needle Insertion:
Insert the needle approximately 1.5 centimeters lateral to the tibial crest and at the junction of the upper and middle third of the leg.
Activation:
Dorsiflex the ankle and invert the foot.
Clinical Notes:
Tibialis anterior tendon is the most prominent and most medial of the dorsal three tendons.
Innervation:
L4, L5, (S1)-peroneal portion of sciatic nerve-common peroneal nerve-deep peroneal nerve.
Origin:
Lateral condyle of tibia, upper two-thirds of the lateral tibial surface and anterior interosseous membrane.
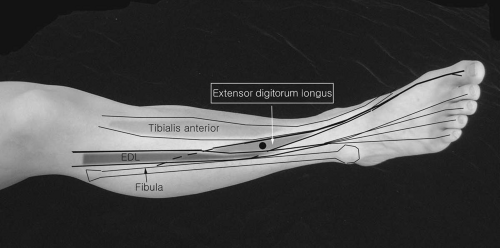
Extensor Digitorum Longus
Patient Position:
Supine or side lying.
Needle Insertion:
At the middle third of the leg, a needle is inserted midway between the anterior border of the tibia and the lateral border of the fibula.
Activation:
Extend the toes and dorsiflex the ankle.
Clinical Notes:
If a needle is inserted too medially, it will be in the tibialis anterior; too deeply, it will be in the extensor hallucis longus.
Innervation:
L5 and S1-deep peroneal nerve.
Origin:
Anterolateral tibial condyle, anterior proximal three-fourths of the fibula, and the adjacent anterior interosseous membrane.
Insertion:
Middle and distal phalanges of the lateral four digits, forming a membranous expansion over the dorsum of each respective metatarsal phalangeal joint where it fuses with the capsule. Near the proximal interphalangeal joint, the expansion divides into three slips. The central part of the aponeurosis continues distally to the dorsal base of the middle phalanx. Collateral slips continue to the base of the distal phalanx.
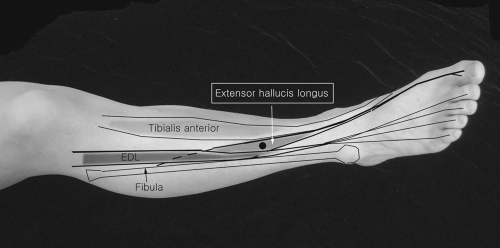
Extensor Hallucis Longus
Patient Position:
Supine or side lying.
Needle Insertion:
At the junction between the middle and lower third of the tibia and at the space between the tendons of tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus. The extensor digitorum longus tendon may be pushed laterally and the needle advanced toward the anterior surface of the fibula, with extension of the big toe and ankle dorsiflexion.
Clinical Notes:
This muscle is commonly tested to assess L5 radiculopathy and foot drop. The muscle lies deep partly to the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus.
Innervation:
L5, S1-peroneal part of sciatic nerve-common peroneal nerve-deep peroneal nerve.
Origin:
Middle third of anterior surface of fibula and the adjacent anterior interosseous membrane.
Peroneus Longus
Patient Position:
Side lying or supine.
Needle Insertion:
At 5 to 10 centimeters inferior from the fibula neck, place two fingers (thumb and index) over the anterior and lateral surfaces of the fibula, insert the needle into the space between the two fingers, and advance it toward the fibula.
Activation:
Plantar flexion of the ankle and eversion of the foot.