The Hand
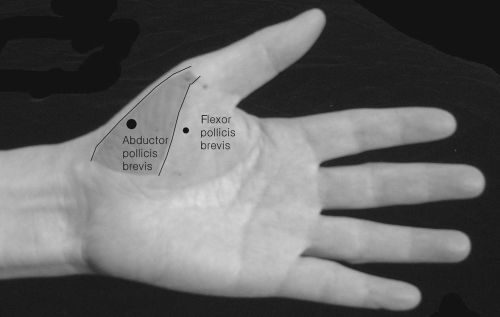
Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Patient Position:
Forearm supinated with the palm up.
Needle Insertion:
Insert the needle obliquely from the radial side of the thenar eminence at about the proximal half of the first metacarpal bone.
Activation:
Abduct the thumb with some medial rotation.
Clinical Notes:
If inserted too medially in the thenar eminence, the needle will penetrate the flexor pollicis brevis (superficial or deep head); if too deep, opponence pollicis will be penetrated. It is thin and is the most superficial muscle of the thenar muscles. In severe median neuropathy, a needle recording from this muscle may not eliminate the volume-conducted response from adjacent ulnar nerve innervated muscles. This muscle is very painful to needle!
Innervation:
C8, T1-lower trunk-medial cord-median nerve (recurrent branch).
Origin:
Flexor retinaculum, scaphoid, trapezium.
Insertion:
Radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of thumb, and lateral sesamoid bone of the thumb.
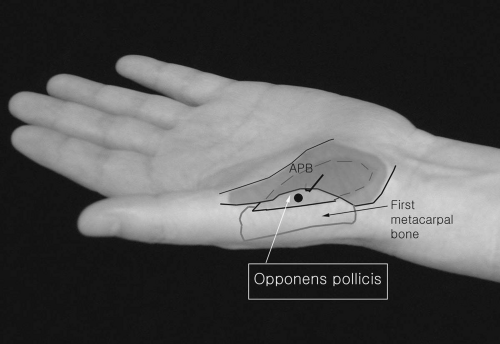
Opponens Pollicis
Patient Position:
Palm up (supination of hand).
Needle Insertion:
This muscle is deep to the abductor pollicis brevis in the thenar eminence. Insert the needle close to the anterior surface of the first metacarpal bone.
Activation:
Opposition of the thumb or flexion of the metacarpal bone of the thumb.
Clinical Notes:
It is found deep to the abductor pollicis brevis. It occasionally may be innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve.
Innervation:
C8, T1-lower trunk-medial cord-median nerve (recurrent branch).
Origin:
Flexor retinaculum and trapezium.
Insertion:
Lateral border of the metacarpal bone.
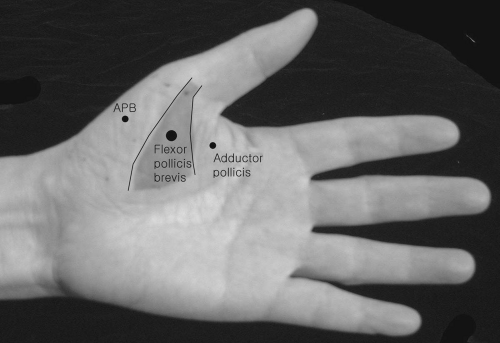
Flexor Pollicis Brevis—Superficial and Deep Head
Patient Position:
Supine with the forearm supinated and palm up.
Needle Insertion:
The thenar eminence can be divided into a lateral half and a medial half by a longitudinal section. Insert the needle into the medial-half area of the thenar eminence.
Activation:
Flex the thumb (proximal phalanx); it also aids opposition and adduction.
Clinical Notes:
This muscle is found medial to the abductor pollicis brevis and is somewhat overlapped by it. It is particularly active in a firm grip between the thumb, index, and middle fingers.
Innervation:
C8, T1-superficial head, median nerve (recurrent branch); deep head, ulnar nerve.
Origin:
Superficial head; flexor retinaculum, trapezium, and trapezoid.
Deep head; trapezoid and capitate.
Insertion:
Radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb (medial to the insertion of the abductor pollicis brevis).
Lumbricals/First Lumbrical
Patient Position:
Palm up (supinated).