 Posteromedial Approach to the Posterior Process of the Talus
Posteromedial Approach to the Posterior Process of the TalusThe posteromedial approach to the ankle joint is used for exploration of the soft tissues that run around the back of the medial malleolus. It is used for soft-tissue correction of deformity, especially in children. It can also be used to access the talus and the posteromedial aspect of the ankle joint.
Position of the Patient
Three positions are available for this approach. First, place the patient supine on the operating table. Flex the hip and knee, placing the lateral side of the affected ankle on the operating table. This position will achieve full external rotation of the hip, permitting better exposure of the medial structures of the ankle (Fig. 16-1). Alternatively, place the patient in the lateral position with the affected leg nearest the table. Flex the knee of the opposite limb to get the leg out of the way. Last place the patient prone on bolsters on the operating table. The position allows for movement of the foot and ankle and ease of visualization of posteromedial structures.
Landmarks and Incision
Palpate the medial malleolus. It is the bulbous, distal subcutaneous end of the tibia. Palpate the medial border of the Achilles tendon just above the calcaneus. Make a 4-cm longitudinal incision roughly midway between the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon (Fig. 16-2A).
Superficial Surgical Dissection
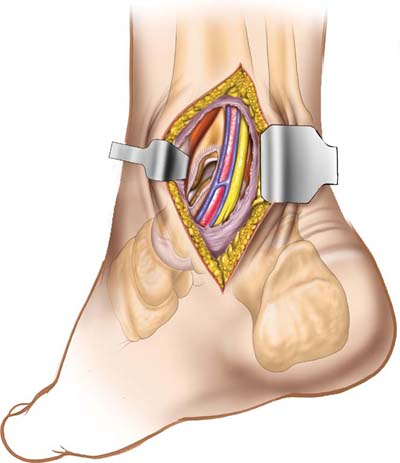
Deepen the incision in line with the skin incision to enter the fat that lies between the Achilles tendon and those structures that pass around the back of the medial malleolus (Fig. 16-2B). Identify a fascial plane in the anterior flap that covers the flexor tendons. Incise the fascia longitudinally, well away from the back of the medial malleolus.
Deep Surgical Dissection
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


