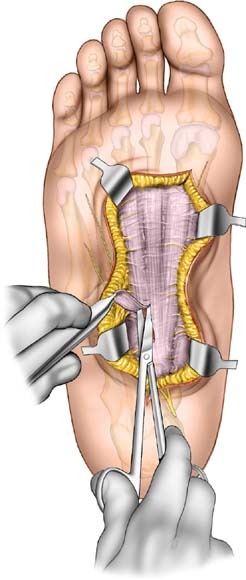
 Plantar Approach for Plantar Fibromatosis
Plantar Approach for Plantar FibromatosisThis approach is usually used to approach the plantar fascia. The fascia is much thicker in its central parts, where it is known as the plantar aponeurosis. The approach is usually used to treat plantar fibromatosis. This disease is notorious for being of varying severity. When the disease is very severe, a complete excision may need to be made over the whole of the sole of the foot, from the posterior aspect of the heel right into the forefoot. Usually smaller incisions are made directly down onto the plantar fascia, necessitating isolated smaller approaches to the sole of the foot.
The thick skin on the bottom of the sole is highly specialized, tough, and resilient. It should be respected and cut only when absolutely necessary. (Incisions should be limited where possible. See the Sole of the Foot section of Chapter 52.)
Position of the Patient
After exsanguination, apply a tourniquet to the middle of the thigh. Then place the patient prone on the operating table (see Fig. 7-1). Ensure that bony prominences are well padded around the upper extremities, chest, pelvis, and lower extremities. Be careful to ensure that ventilation is secure and that there is no pressure on the genitals.
Landmarks and Incision
Palpate the thick skin of the heel to feel the distal extension of the calcaneum. More distally palpate the first metatarsal head medially and the other metatarsal heads sequentially by moving laterally to the fifth metatarsal head.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


