 Lateral Approach for Osteotomy of the Calcaneus (Vertical Portion of the Calcaneal Incision)
Lateral Approach for Osteotomy of the Calcaneus (Vertical Portion of the Calcaneal Incision)This approach is used for calcaneal osteotomies in cases in which the calcaneal fracture has healed and is malpositioned. It also may be used for excision of bony lumps on the calcaneus that are producing pressure symptoms. An accurate assessment of the vascular status of the patient is critical before undertaking surgery. Diabetes, especially with associated neuropathy and smoking, are relative contraindications to this surgical approach.
Position of the Patient
Place the patient in the lateral position on the operating table (Fig. 19-1). Ensure that the bony prominences are well padded. Position the image intensification unit in front of the patient or at the foot of the table. Place the leg that is to be operated on posteriorly with the under leg anterior.
Landmarks and Incision
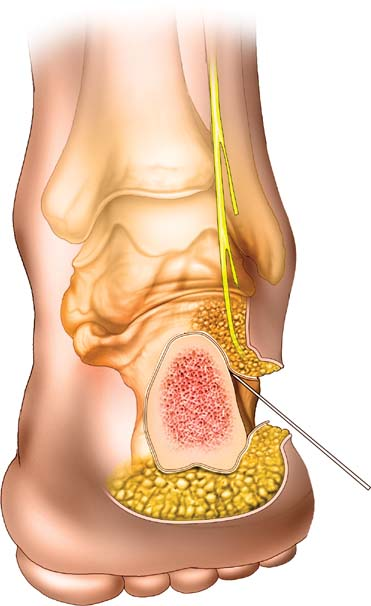
Palpate the posterior border of the distal fibula and the lateral border of the Achilles tendon. Make an 8- to 10-cm longitudinal incision beginning halfway between the posterior aspect of the fibula and the lateral aspect of the Achilles tendon at the level of the top of the calcaneus. Extend this incision distally to the point where the smooth skin of the dorsum of the foot and the wrinkled skin of the sole of the foot meet (Fig. 19-2).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree