Injections
1.1 General Principles
Medications:
Dexamethasone acetate (Decadron LA) 8 mg/cc
Triamcinolone diacetate (Aristocort) 40 mg/cc
Local anesthetics: lidocaine 1%, bupivacaine 0.25%
Mode of Action/Effects:
Inhibits release of prostaglandin synthesis, cytokines, and chemical mediators.
Inhibit activation and function of neutrophils, macrophages, fibroblasts, and basophils.
General Side Effects/Complications:
Local effects and complications: infection (very low risk with proper technique), nerve injury, pneumothorax, subcutaneous fat atrophy, skin color changes.
Allergic reactions: anesthetic or corticosteroid preparation.
Tendon and joint complications: tendon rupture, articular cartilage damage, osteoporosis.
Other reactions: steroid flare (2% of injections), vasovagal response (most common with upper extremity injections).
Diabetes mellitus: hyperglycemia.
Glaucoma: Reported potential complication. Rare in practice.
Contraindications:
Acute systemic infection, joint infection, or cellulitis at injection site.
Poorly controlled diabetes.
History of reaction to any components of injection solution.
Injection into a prosthetic joint or fracture site.
1.2 de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Indication:
Reduce pain in extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis to allow adequate rehabilitation and tissue healing.
Anatomy:
EPB and abductor pollicis tendons contained in 1st dorsal wrist compartment.
Tendons form the dorsal and volar boundaries of the anatomic snuffbox.
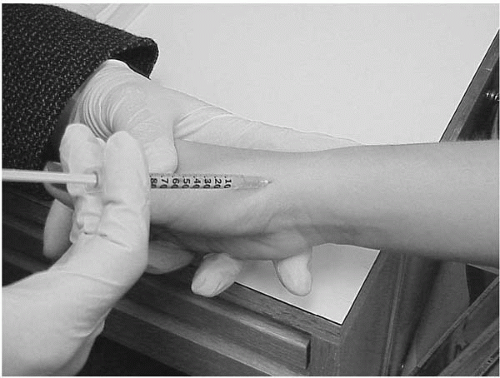
Procedure:
25-gauge, 1½-inch needle is inserted at the anatomic snuffbox into the 1st dorsal wrist compartment directed proximally (Figure 1.1).
Medication:
1-2 cc dexamethasone acetate (Decadron LA) 8 mg/cc in 3 cc of lidocaine (1%).
1-2 cc triamcinolone (40 mg/cc) in 3 cc of lidocaine (1%).
Precautions:
Avoid injection into subcutaneous fat (may cause fat atrophy).
Superficial injection may cause skin discoloration.
1.3 Trigger Finger
Indication:
Painful catching or locking of finger with active flexion.
Anatomy:
Flexor tendon nodule typically just proximal to MCP joint.
Will translate with active flexion/extension of the affected digit.
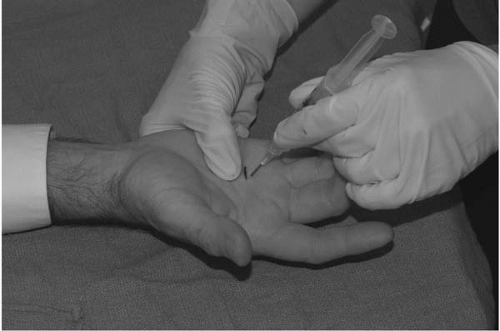
Procedure:
Using a 5/8-inch, 25-gauge instill solution into flexor tendon sheath at the palpable nodule (Figure 1.2).
Medication:
¾ cc dexamethasone acetate (Decadron LA) 8 mg/cc in 3 cc of lidocaine (1%).
¾ cc triamcinolone (40 mg/cc) in ¼ cc of lidocaine (1%).
Precautions:
Ensure that pain is not the result of infectious flexor tenosynovitis.
Avoid injection into subcutaneous fat (may cause fat atrophy).
1.4 Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Indication:
Ulnar wrist pain related to inflammation of the ECU tendon.
Anatomy:
ECU tendon palpable at distal ulna with swelling in the sheath often appreciated several cm proximal from this point.
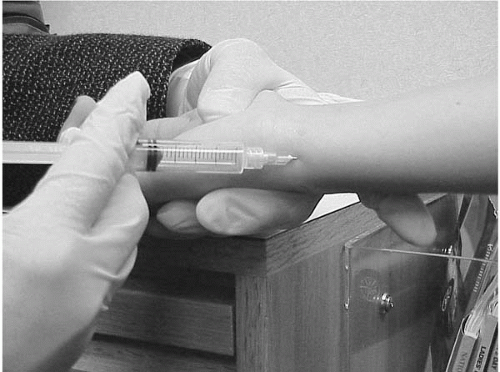
Procedure:
Medial wrist at the distal ulna is sterilely prepared and a 1½-inch, 25-gauge needle is inserted at the distal ulna directed proximally. Solution should be palpable as it fills the ECU sheath (Figure 1.3).
Medication:
1-2 cc dexamethasone acetate (Decadron LA) 8 mg/cc in 3 cc of lidocaine (1%).
1-2 cc triamcinolone (40 mg/cc) in 3 cc of lidocaine (1%).
Precautions:
Avoid injection into subcutaneous fat (may cause fat atrophy).
Superficial injection may cause skin discoloration.
1.5 Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex
Indication:
Chronic ulnar-sided wrist pain due to tear or degeneration of the TFCC.
Anatomy:
TFCC fills the space between the distal ulna (ulnar styloid) and proximal medial carpus.
Procedure:
After sterile prep, solution is injected through a 1½-inch, 25-gauge needle via a medial approach. The needle is inserted just distal to the ulnar styloid (Figure 1.4).
Medication:
1-2 cc triamcinolone (40 mg/cc) in 3 cc of lidocaine (1%).
1-2 cc dexamethasone acetate (Decadron LA) 8 mg/cc in 3 cc of lidocaine (1%).
Precautions:
Avoid injection into subcutaneous fat (may cause fat atrophy).
Superficial injection may cause skin discoloration.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree