 Dorsolateral Approach for Bunion Surgery
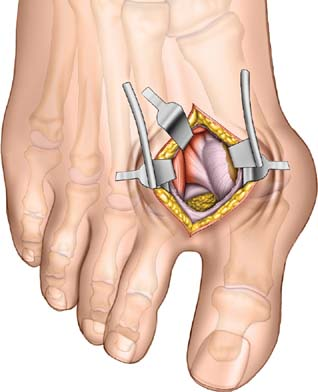
Dorsolateral Approach for Bunion SurgeryThe dorsolateral approach for bunion surgery allows access to those structures present on the lateral aspect of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the hallux. It is used almost exclusively for soft-tissue corrective procedures in cases of hallux valgus. Its uses include the following:
Tenotomy of the adductor hallucis tendon
Release of the lateral (fibular) sesamoid bone and, rarely, excision of that bone
Division of the transverse metatarsal ligament
Soft-tissue procedures in hallux valgus are often accompanied by other surgical procedures: classically, first metatarsal osteotomies. This surgical approach, therefore, is often combined with dorsomedial approaches to the metatarsophalangeal joint of the hallux.
Soft-tissue procedures, in isolation, are contraindicated in advanced arthrosis of the metatarsophalangeal joint, spasticity of any type, and when the distal metatarsal proximal phalangeal angle is greater than 15 degrees. As with all procedures on the distal part of the foot, a preoperative assessment of the vascularity of the foot is mandatory.
Position of the Patient
Place the patient supine on the operating table. After exsanguination, use a tourniquet placed on the middle of the thigh. Alternatively, use a soft rubber bandage to exsanguinate the foot, then wrap the leg tightly just around the ankle (see Fig. 1-1).
Landmarks and Incision
Palpate the head of the first metatarsal bone and the metatarsophalangeal joint on the ball of the foot and along its medial border. Palpate the extensor hallucis longus tendon on the dorsum of the foot. If you flex the toe passively in the plantar direction, the tendon stands out, making identification easier.
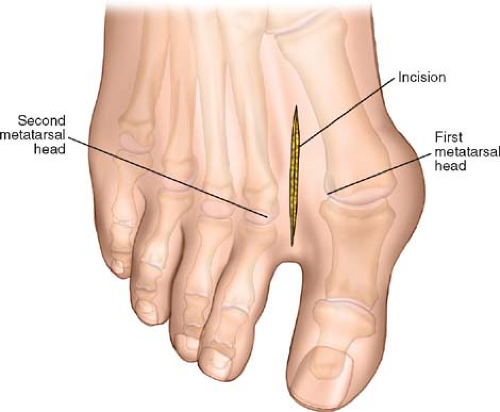 Figure 37-1 Make a 4- to 5-cm longitudinal incision on the dorsal aspect of the foot in the first web space. Center the incision between the first and second metatarsal heads. |
Make a 4- to 5-cm longitudinal incision on the dorsal aspect of the foot in the first web space. Center the incision between the first and second metatarsal heads. The incision should extend some 2 cm beyond the metatarsophalangeal joints of the hallux and second (index) toe (Fig. 37-1).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


