 Dorsal Approach for Morton’s Neuroma
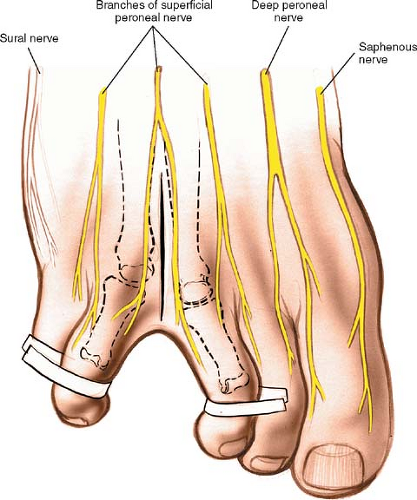
Dorsal Approach for Morton’s NeuromaThe dorsal approach to the web space allows pathology of web spaces to be explored. By far, the most common use of this approach is in the identification and excision of Morton’s neuromas. The approach is most commonly used for exploration of the cleft between the third and fourth toes, the most common site for Morton’s neuroma. Less common uses include drainage of web space infections, which are curiously much rarer in the foot than the hand.
Position of the Patient
Place the patient supine on the operating table. Apply a tourniquet either at the midpoint of the thigh or just above the ankle after the leg has been exsanguinated. Alternatively, use a soft rubber bandage to exsanguinate the foot, then use the bandage as a tourniquet at the ankle (see Fig. 45-1). Place a firm wedge or several pillows under the patient’s thigh to flex the knees, so that the foot lies flat on the operating table.
Landmarks and Incision
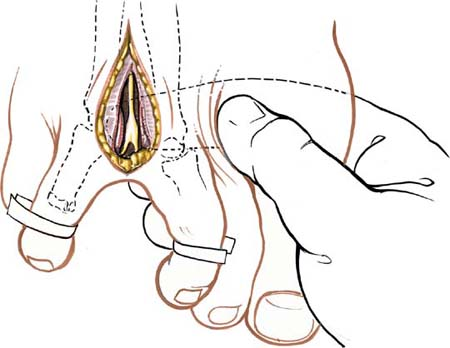
Palpate the metatarsophalangeal joint of the two adjacent toes by passively flexing and extending them. Separate the two toes of the affected web space. The easiest way to do this is to wrap a gauze swab around the adjacent toes and use it to pull the two toes apart. Make a dorsal longitudinal incision over the center of the web space starting at the distal end of the web and extending proximally some 2 to 3 cm beyond the level of the metatarsophalangeal joints (Fig. 46-1).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree