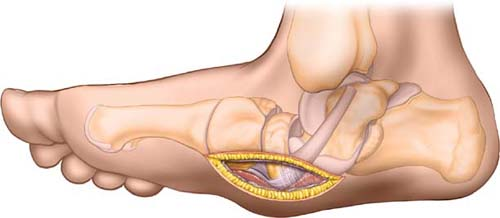
 Direct Medial Approach for Midfoot Collapse for Bony Planing and Skin Ulcer Treatment
Direct Medial Approach for Midfoot Collapse for Bony Planing and Skin Ulcer TreatmentThis approach is used to treat patients with severe foot deformity associated with diabetes or in patients with midfoot collapse due to a Charcot-type neuropathy. A bony prominence through the plantar surface in patients with neurological sensory deficits often results in severe skin ulcerations over the plantar surface. Without removing the prominence, skin ulceration will continue.
This approach is often used as part of a specialized procedure for the treatment of muscle imbalance, a mobile, pathologic flat foot, or midfoot collapse. Timing of surgery is crucial, as these patients often are diabetic or suffering from neurological deficiencies creating sensory loss. Treating local ulceration with nonoperative techniques may be necessary before surgery to optimize local soft-tissue conditions. A detailed neurological and vascular examination is mandatory. Specialist investigations such as angiography may also be indicated in specific cases.
Position of the Patient
Place the patient supine on the operating table (see Fig. 3-1). The dorsomedial approach and the longer complete medial approach are carried out with the leg in its natural position of slight external rotation. If necessary, a sandbag may be placed beneath the opposite buttock to create even more external rotation of the affected limb, making the medial aspect of the forefoot more easily accessible. After exsanguination, apply a tourniquet to the middle of the thigh. Do not use a tourniquet applied just above the ankle, as this may create vascular problems postoperatively in diabetic patients.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


