Cranial Nerves
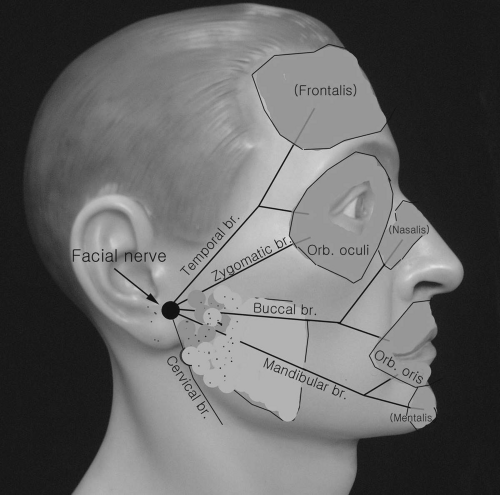
Facial Nerve
(Fig. 2-1)
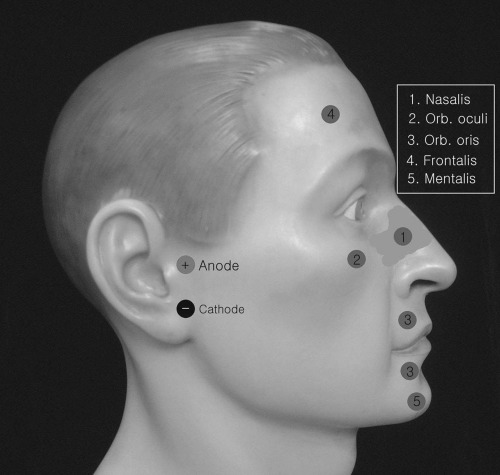 Figure 2-2. Placements of recording electrodes and stimulator for facial nerve motor conduction. |
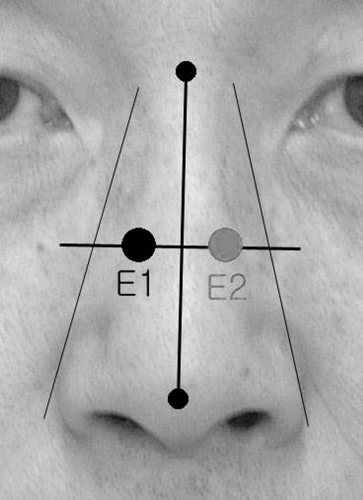 Figure 2-3. Recording electrode placements in the nasalis muscle: E1 is active electrode and E2 is reference electrode. |
E1 The surface recording electrode (E1) [10 millimeters (mm) in diameter] can be placed over the orbicularis oculi, nasalis, orbicularis oris, and frontalis muscles. When recording the motor response from any of the facial muscles, an initial positive deflection of compound muscle action potential (CMAP) is very common, but recording from the nasalis may yield the best result.
E2 The same type of E1 electrode is placed on the same muscle on the contralateral side of the face (E2).
Ground Place ground over the forehead or shoulder area.
Stimulation of Facial Nerve (Fig. 2-5)
Preauricular stimulation: The stimulating cathode is placed over the anterior tragus in front of the ear. A volume-conducted response may occur with direct stimulation of the masseter muscle, but it can be minimized with the anode placed proximally to the cathode. We prefer stimulation at this site.
(Fig. 2-4) To supramaximally activate the normal facial nerve on pre- and postauricular stimulation, a moderate degree of current intensity is required. The stimulation is painful. We start the stimulation with 40 to 50 milliamperes (mA) with current pulse width 0.2 ms and monitor the CMAP amplitude




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree