 Approach to the Navicular
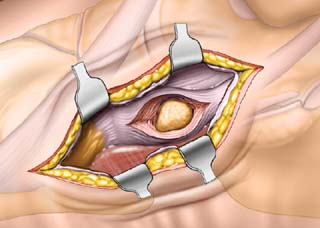
Approach to the NavicularThis approach is used mainly for the removal of an accessory navicular bone. Fractures of the navicular and other pathologies on the medial side of the foot can also be addressed with this incision. The main danger of this approach is damage to the tendon of the tibialis posterior, which attaches onto the navicular.
Position of the Patient
Place the patient supine on the operating table (see Fig. 1-1). Dorsomedial approaches and medial approaches are carried out with the leg in its natural position of slight external rotation. Exsanguinate the leg, then apply a tourniquet to the mid-thigh.
Landmarks and Incision
Palpate the first metatarsal cuneiform joint by feeling along the medial border of the foot from distal to proximal. The first metatarsal flares slightly at its base to meet the first cuneiform. Continue moving proximally along the medial border to reach the tubercle of the navicular. The medial side of the talar head is immediately proximal to the navicular. It can be located by inverting and everting the forefoot. The motion that occurs between the talus and the navicular is palpable.
Make a 5- to 6-cm longitudinal incision directly over the area to be exposed (Fig. 28-1).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


